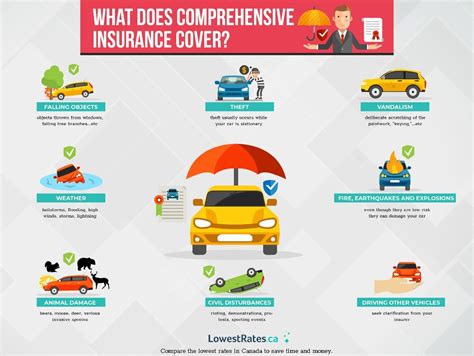
What Is Co Insurance
Co-insurance, a fundamental concept in the insurance industry, plays a crucial role in determining the financial responsibilities of policyholders and insurance companies. Understanding co-insurance is essential for individuals and businesses seeking insurance coverage, as it directly impacts their out-of-pocket expenses and overall insurance experience.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of co-insurance, exploring its definition, how it works, and its implications for various types of insurance policies. By the end of this article, you'll have a thorough understanding of co-insurance and its significance in the insurance landscape.
Unraveling the Concept of Co-Insurance

Co-insurance, often referred to as coinsurance, is a contractual agreement between an insured party (the policyholder) and an insurer that dictates how certain losses or expenses will be shared between the two parties.
In simpler terms, co-insurance involves splitting the financial burden of a claim according to predetermined ratios or percentages outlined in the insurance policy.
Key Elements of Co-Insurance
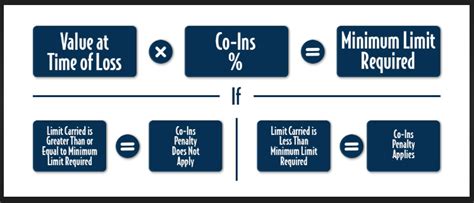
- Policyholder’s Responsibility: Co-insurance typically requires the policyholder to pay a certain percentage of the claim amount, known as the co-insurance percentage or coinsurance rate. This percentage is often specified in the insurance policy and can vary based on the type of insurance and the insurer’s policies.
- Insurer’s Contribution: The remaining portion of the claim, after the policyholder’s contribution, is covered by the insurer. This is calculated by subtracting the policyholder’s co-insurance percentage from 100%.
- Example: For instance, if an insurance policy has a co-insurance rate of 80%, the policyholder is responsible for 20% of the claim amount, while the insurer covers the remaining 80%.
How Co-Insurance Works
The operation of co-insurance can be understood through the following steps:
- Claim Occurrence: When a covered loss or expense occurs, the policyholder submits a claim to the insurer.
- Determining Co-Insurance Percentage: The insurer calculates the applicable co-insurance rate based on the policy terms.
- Policyholder’s Payment: The policyholder is responsible for paying their portion of the claim amount as specified by the co-insurance rate.
- Insurer’s Payment: After receiving the policyholder’s payment, the insurer covers the remaining portion of the claim.
Types of Co-Insurance Arrangements

Co-insurance can take various forms depending on the type of insurance and the insurer’s policies. Here are some common types of co-insurance arrangements:
Fixed Co-Insurance Percentage
In this arrangement, the co-insurance rate remains constant throughout the policy term. For example, if the policy has an 80⁄20 co-insurance rate, the policyholder’s responsibility remains 20% for all claims during that policy period.
Sliding Scale Co-Insurance
Some insurance policies feature a sliding scale co-insurance arrangement. In this scenario, the co-insurance rate can change based on certain conditions or factors, such as the policyholder’s claims history or the severity of the claim.
Aggregate Deductible Co-Insurance
Aggregate deductible co-insurance involves a combination of a fixed deductible and a co-insurance rate. The policyholder pays a specified deductible for each claim, and any amount exceeding the deductible is subject to the co-insurance rate.
Implications of Co-Insurance
Co-insurance has several implications for policyholders and insurers, including:
- Cost Sharing: Co-insurance encourages policyholders to share a portion of the financial risk, which can lead to more careful decision-making and reduced claims frequency.
- Incentivizing Preventive Measures: By requiring policyholders to contribute to claims, co-insurance motivates individuals and businesses to take preventive actions to avoid or minimize losses.
- Claim Processing: Co-insurance can impact the claim processing timeline, as policyholders must first pay their portion of the claim before receiving the insurer’s contribution.
- Financial Planning: Policyholders need to consider their co-insurance obligations when budgeting for potential claims, ensuring they have adequate funds to cover their share of expenses.
Examples of Co-Insurance in Practice
Let’s explore how co-insurance works in different types of insurance policies:
Health Insurance
In health insurance, co-insurance is often applied to medical services. For instance, if a policy has an 80⁄20 co-insurance rate, the policyholder pays 20% of the approved cost for covered services, while the insurer covers the remaining 80%.
| Medical Service | Approved Cost | Policyholder's Co-Insurance Payment | Insurer's Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Doctor's Visit | $100 | $20 | $80 |
| Lab Tests | $250 | $50 | $200 |
Property Insurance
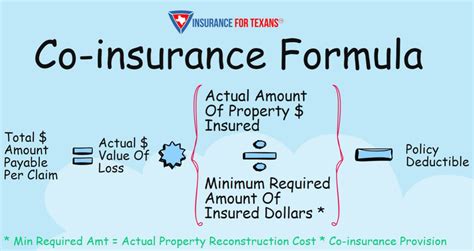
Co-insurance is commonly used in property insurance, particularly for commercial properties. If a business suffers a loss, the policyholder’s co-insurance percentage determines their financial responsibility.
For example, if a business with a 90/10 co-insurance rate suffers a loss of $10,000, the policyholder is responsible for $1,000 (10% of the loss), while the insurer covers the remaining $9,000.
Auto Insurance
Auto insurance policies may include co-insurance provisions for certain coverage types, such as collision or comprehensive coverage. The co-insurance rate applies to the actual cash value of the vehicle, influencing the policyholder’s out-of-pocket expenses in the event of a claim.
Benefits of Co-Insurance for Policyholders
Co-insurance offers several advantages to policyholders:
- Lower Premiums: Co-insurance arrangements often result in lower insurance premiums compared to policies without co-insurance. This is because policyholders share a portion of the risk, reducing the insurer’s potential liability.
- Incentive for Careful Decision-Making: By requiring policyholders to contribute to claims, co-insurance encourages them to make thoughtful choices to avoid unnecessary expenses.
- Increased Awareness of Costs: Co-insurance makes policyholders more conscious of the costs associated with claims, promoting financial responsibility and budget planning.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
While co-insurance offers benefits, there are also considerations to keep in mind:
- Financial Impact of Co-Insurance: Policyholders need to be prepared to cover their portion of claims, which can be a significant expense if they have multiple or large claims in a short period.
- Understanding Policy Terms: It’s essential for policyholders to thoroughly understand the co-insurance terms and conditions outlined in their insurance policies to avoid any surprises or misunderstandings when filing claims.
- Claim Processing Time: The claim processing timeline may be affected by the co-insurance arrangement, as policyholders must pay their share before receiving the insurer’s contribution.
The Future of Co-Insurance
As the insurance industry continues to evolve, co-insurance arrangements are likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping the landscape. Insurers may explore innovative ways to customize co-insurance rates based on individual risk profiles and claims history.
Additionally, advancements in technology and data analytics may enable insurers to offer more tailored co-insurance options, further incentivizing policyholders to adopt preventive measures and make informed decisions.
In conclusion, co-insurance is a vital component of insurance policies, impacting the financial responsibilities of both policyholders and insurers. By understanding the concept and implications of co-insurance, individuals and businesses can make informed choices when selecting insurance coverage and managing their financial risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What happens if I fail to pay my co-insurance percentage for a claim?
+
If you do not pay your co-insurance percentage for a claim, the insurer may deny payment for the claim until you fulfill your financial obligation. It’s important to understand your policy terms and promptly pay your share to ensure timely claim processing.
Can co-insurance rates change during the policy term?
+
In most cases, co-insurance rates remain fixed throughout the policy term. However, some insurance policies may have sliding scale co-insurance, where the rate can change based on factors like claims history. It’s essential to review your policy terms to understand any potential changes.
How does co-insurance impact my insurance premiums?
+
Co-insurance arrangements often lead to lower insurance premiums compared to policies without co-insurance. By sharing a portion of the risk, policyholders can benefit from reduced premiums, making insurance coverage more affordable.