Telemedicine Coverage In Health Insurance

The world of healthcare is undergoing a significant transformation with the rapid integration of technology, and one of the most prominent developments is the rise of telemedicine. As the healthcare industry embraces digital solutions, the question of telemedicine coverage in health insurance plans has become a critical concern for patients, providers, and insurers alike. This comprehensive article aims to delve into the intricacies of telemedicine coverage, exploring its benefits, challenges, and the evolving landscape of healthcare insurance.
Understanding Telemedicine and Its Impact
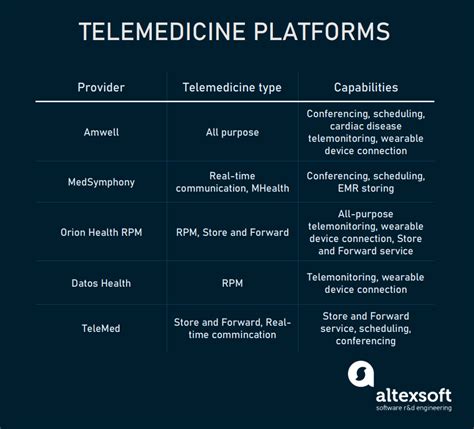
Telemedicine, or the use of digital information and communication technologies to provide healthcare services remotely, has revolutionized the way patients access medical care. With the click of a button, individuals can now consult with doctors, receive diagnoses, and obtain prescriptions without the need for physical visits to medical facilities. This technology-driven approach has proven particularly beneficial in rural and underserved areas, where access to healthcare professionals is often limited.
The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, as social distancing measures and lockdown protocols made traditional in-person consultations challenging. Telemedicine offered a safe and efficient alternative, allowing patients to continue receiving medical care without risking exposure to the virus. This period highlighted the importance of digital healthcare solutions and prompted many insurance providers to reconsider their coverage policies.
The Current Landscape of Telemedicine Coverage

The coverage of telemedicine services in health insurance plans varies significantly across different regions and insurance providers. While some insurers have embraced the potential of telemedicine and incorporated it into their standard coverage, others remain hesitant, citing concerns about cost, quality, and the potential for abuse.
Insurers Embracing Telemedicine
Several leading insurance companies have recognized the benefits of telemedicine and have taken proactive steps to integrate it into their plans. These insurers understand that telemedicine can improve access to care, enhance patient satisfaction, and even reduce overall healthcare costs by preventing unnecessary emergency room visits and hospitalizations.
For instance, UnitedHealthcare, one of the largest healthcare insurance providers in the United States, offers comprehensive telemedicine coverage. Their plans cover a wide range of virtual healthcare services, including primary care consultations, mental health counseling, and even some specialty care. UnitedHealthcare's approach ensures that their policyholders have access to convenient and affordable healthcare options, regardless of their physical location.
Similarly, Aetna has expanded its telemedicine services to include not only primary care but also certain specialty care services. This move has been particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions, who can now receive regular check-ins and consultations without having to travel long distances.
Challenges and Hesitations
Despite the growing recognition of telemedicine’s benefits, there are still insurers who approach telemedicine coverage with caution. These insurers often cite concerns about the accuracy of virtual diagnoses, the potential for fraud, and the overall cost of implementing telemedicine services.
One of the primary challenges is ensuring that telemedicine services meet the same quality standards as traditional in-person care. Insurers worry that without proper oversight, telemedicine could lead to misdiagnoses or inappropriate treatment plans. To address this concern, some insurers require that telemedicine services be provided by approved, licensed healthcare professionals and that certain types of care, such as complex procedures, still be conducted in-person.
Additionally, the cost of implementing and maintaining telemedicine infrastructure can be a barrier for smaller insurers or those with more limited budgets. The initial investment in technology, training, and administrative support can be significant, and insurers must carefully consider the return on investment before committing to widespread telemedicine coverage.
The Benefits of Telemedicine Coverage
The advantages of telemedicine coverage are vast and have the potential to transform the healthcare industry in numerous ways.
Improved Access to Healthcare
One of the most significant benefits of telemedicine coverage is the improved access it provides to healthcare services. Individuals living in rural or remote areas often face challenges in accessing medical care due to geographical barriers or a lack of nearby healthcare facilities. Telemedicine bridges this gap, allowing patients to consult with healthcare professionals from the comfort of their homes.
For example, a patient living in a remote village can now schedule a virtual consultation with a specialist in a major city, eliminating the need for a lengthy and potentially expensive journey. This increased access to healthcare ensures that patients receive the care they need, when they need it, regardless of their location.
Enhanced Patient Convenience and Satisfaction
Telemedicine offers patients a level of convenience that traditional healthcare models cannot match. Patients can schedule appointments at their convenience, without having to take time off work or arrange for childcare. They can receive medical advice and prescriptions without the hassle of waiting rooms or long travel times.
Furthermore, telemedicine can improve patient satisfaction by providing a more personalized and efficient healthcare experience. Patients can easily communicate their concerns and symptoms to healthcare providers, who can then offer tailored advice and treatment plans. This level of personalization and efficiency often leads to higher patient satisfaction and improved health outcomes.
Cost Savings for Patients and Insurers
Telemedicine has the potential to significantly reduce healthcare costs for both patients and insurers. By avoiding unnecessary in-person visits, patients can save on transportation costs, childcare expenses, and lost wages from missed work. For insurers, telemedicine can reduce the overall cost of providing healthcare by preventing unnecessary emergency room visits and hospitalizations.
Studies have shown that telemedicine can lead to cost savings of up to $100 per patient encounter compared to traditional in-person visits. This reduction in costs can be particularly beneficial for patients with limited financial means or those who are managing chronic conditions that require frequent medical attention.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of telemedicine coverage are compelling, there are several challenges and considerations that must be addressed to ensure the sustainable and effective integration of telemedicine into healthcare insurance plans.
Quality Assurance and Regulation
As telemedicine becomes more widespread, ensuring the quality and accuracy of virtual healthcare services becomes increasingly important. Regulatory bodies and insurance providers must work together to establish standards and guidelines for telemedicine practices to maintain patient safety and trust.
This includes setting criteria for the qualification and training of telemedicine providers, defining the scope of services that can be delivered virtually, and establishing protocols for patient follow-ups and referrals. By implementing robust quality assurance measures, insurers can mitigate the risks associated with telemedicine and ensure that patients receive the same high-quality care they would expect from traditional healthcare settings.
Privacy and Security Concerns
With the increased use of digital technologies in healthcare, protecting patient privacy and ensuring the security of sensitive medical information becomes a top priority. Insurers must invest in secure telemedicine platforms and infrastructure to safeguard patient data and prevent unauthorized access or breaches.
This involves implementing robust encryption protocols, secure data storage systems, and robust authentication mechanisms to verify the identities of patients and healthcare providers. Additionally, insurers should provide clear guidelines and education to patients on how to protect their own privacy when using telemedicine services, such as ensuring a private and secure environment for virtual consultations.
Technological Infrastructure and Accessibility
To make telemedicine coverage truly accessible to all, insurers must address the technological barriers that some patients may face. This includes ensuring that telemedicine platforms are user-friendly, compatible with a range of devices and internet connections, and accessible to individuals with disabilities or limited digital literacy.
Insurers should also consider providing support and resources to help patients navigate the technology, such as offering technical assistance hotlines or providing devices and internet access to those who may not have the necessary equipment. By removing technological barriers, insurers can ensure that telemedicine coverage reaches a wider population and truly improves access to healthcare.
The Future of Telemedicine Coverage

As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the future of telemedicine coverage looks increasingly promising. With the ongoing advancements in technology and the growing recognition of telemedicine’s benefits, we can expect to see further integration of telemedicine into health insurance plans.
Wider Adoption and Improved Coverage
As more insurers recognize the value of telemedicine, we can anticipate a wider adoption of telemedicine coverage across the industry. This will lead to improved access to telemedicine services for a larger portion of the population, especially in underserved areas. Insurers will likely expand the scope of covered services, incorporating a broader range of specialties and conditions into their telemedicine offerings.
Additionally, insurers may explore innovative ways to integrate telemedicine into their plans, such as offering incentives for patients who utilize telemedicine services or providing rewards for achieving certain health goals through virtual care.
Enhanced Collaboration and Integration
The future of telemedicine coverage will likely involve enhanced collaboration between insurers, healthcare providers, and technology companies. Insurers will work closely with healthcare professionals to ensure that telemedicine services are integrated seamlessly into existing healthcare models, providing a holistic and patient-centric approach to care.
Furthermore, the development of advanced telemedicine platforms and technologies will enable insurers to offer more interactive and personalized virtual care experiences. This could include the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze patient data and provide tailored healthcare recommendations, or the integration of wearable devices and sensors to monitor patient health remotely.
Addressing Disparities and Improving Health Outcomes
Telemedicine coverage has the potential to address healthcare disparities and improve health outcomes for vulnerable populations. By making healthcare more accessible and affordable, telemedicine can help reduce health disparities among rural, low-income, and minority communities. Insurers can play a crucial role in this by offering tailored telemedicine plans that address the specific healthcare needs of these populations.
Additionally, telemedicine can facilitate better management of chronic conditions, allowing patients to receive regular check-ins and monitoring without the burden of frequent in-person visits. This can lead to improved disease control, reduced complications, and better overall health outcomes.
Conclusion
The integration of telemedicine into health insurance plans represents a significant step forward in the evolution of healthcare. As we have explored in this article, telemedicine coverage offers improved access to care, enhanced patient convenience, and potential cost savings. However, to fully realize these benefits, insurers must carefully navigate the challenges and considerations associated with telemedicine, such as quality assurance, privacy, and technological accessibility.
The future of telemedicine coverage looks bright, with the potential for wider adoption, improved coverage, and enhanced collaboration between insurers and healthcare providers. As technology continues to advance and our understanding of telemedicine deepens, we can expect to see even more innovative and effective ways of delivering healthcare through digital means. Ultimately, the goal is to provide patients with the highest quality care, regardless of their location or circumstances, and telemedicine coverage is a crucial step towards achieving this vision.
Is telemedicine coverage available for all types of medical conditions?
+The scope of telemedicine coverage can vary depending on the insurance provider and the specific plan. While some insurers offer comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medical conditions, others may have more limited coverage, focusing on primary care or certain specialty areas. It’s important to review the details of your insurance plan or consult with your insurer to understand the specific coverage available for telemedicine services.
How do I access telemedicine services with my insurance coverage?
+To access telemedicine services, you can typically contact your insurance provider or healthcare provider to understand the process. Many insurers have dedicated telemedicine platforms or partner with specific telemedicine service providers. Your healthcare provider may also have their own telemedicine system in place. It’s important to follow the guidelines provided by your insurer or healthcare team to ensure smooth access to telemedicine services.
Are there any limitations or restrictions on the use of telemedicine services under insurance coverage?
+Yes, there may be certain limitations or restrictions on the use of telemedicine services under insurance coverage. These limitations can vary depending on the insurer and the specific plan. Some common restrictions include the types of conditions that can be treated via telemedicine, the number of telemedicine visits allowed per year, or the requirement for a prior in-person consultation before initiating telemedicine services. It’s crucial to review your insurance policy or consult with your insurer to understand any limitations or restrictions that may apply to your coverage.



