State Unemployment Insurance

State Unemployment Insurance (SUI) is a vital system in the United States that provides temporary financial assistance to individuals who have lost their jobs through no fault of their own. This safety net, established as part of the Social Security Act of 1935, serves as a critical component of the nation's social safety network, offering crucial support during periods of unemployment.
Understanding State Unemployment Insurance
State Unemployment Insurance is a state-administered program funded primarily through payroll taxes levied on employers. While the federal government sets the broad guidelines for unemployment insurance, each state has its own specific laws, regulations, and benefits packages. This decentralization ensures that the program can adapt to the unique economic and labor market conditions of each state.
The primary objective of SUI is to provide income support to eligible workers who are involuntarily unemployed, helping them meet basic needs while they seek new employment opportunities. This assistance not only aids individuals and families but also contributes to the overall economic stability of communities and the nation.
Eligibility Criteria
To qualify for State Unemployment Insurance benefits, individuals must meet several criteria. These typically include having earned a minimum amount of wages from an employer during a specified period, known as the base period. This base period varies by state but generally covers the most recent 12 to 18 months.
Additionally, claimants must demonstrate that they are able, available, and actively seeking work. This means they must be physically capable of working, willing to accept suitable employment, and taking concrete steps to find a new job. Failure to meet these requirements can result in the denial or discontinuation of benefits.
The Application Process
The process of applying for SUI benefits begins with the filing of a claim. This can be done online, by phone, or in person at a local unemployment office. During the application process, claimants provide information about their employment history, including the dates of employment, earnings, and the reason for separation from their job.
Once the application is submitted, it undergoes a review process to determine eligibility. This involves verifying the information provided, assessing the circumstances of the separation from employment, and calculating the potential benefit amount. If approved, claimants will receive a monetary benefit, typically paid on a weekly or biweekly basis.
Benefit Calculations and Disbursements
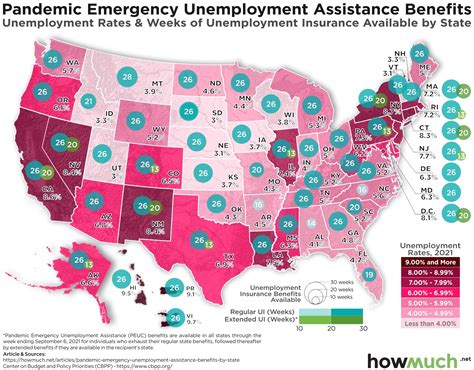
The amount of unemployment benefits an individual receives is calculated based on their previous earnings. Each state has its own method for computing benefits, but the general formula takes into account the highest-paid quarters of the base period. This ensures that benefits are proportional to the individual’s prior earnings, providing a measure of financial stability during unemployment.
| State | Maximum Weekly Benefit Amount |
|---|---|
| California | $450 |
| New York | $504 |
| Texas | $535 |
| Florida | $275 |
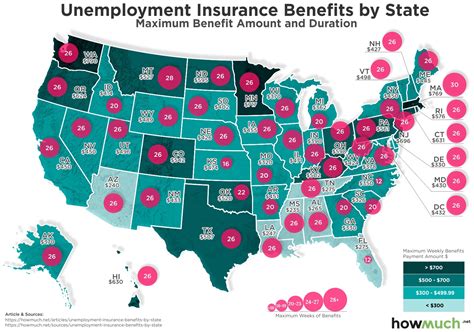
While the maximum weekly benefit amount varies by state, the average weekly benefit across the nation is around $380. These benefits are generally taxable and may impact an individual's future tax obligations.
Benefits are typically disbursed via direct deposit, debit card, or check. Claimants are responsible for providing accurate banking information to ensure timely and secure payment of benefits.
Impact and Significance of State Unemployment Insurance
State Unemployment Insurance plays a pivotal role in supporting the economic well-being of individuals and communities during periods of economic downturn or personal job loss. By providing a temporary income, SUI enables individuals to meet essential needs, such as housing, food, and healthcare, while they search for new employment opportunities.
The program also has broader economic implications. During recessions, unemployment benefits serve as a form of economic stimulus, boosting consumer spending and supporting local businesses. This multiplier effect can help stabilize the economy and promote a faster recovery.
Program Challenges and Reforms
Despite its importance, State Unemployment Insurance faces several challenges. One of the primary concerns is the program’s sustainability, particularly during periods of high unemployment when more individuals qualify for benefits. To address this, states often make adjustments to their unemployment insurance laws, including increasing payroll taxes, reducing benefit amounts or durations, or implementing more stringent eligibility requirements.
Another challenge is the timely processing of claims, especially during economic downturns when the volume of applications increases dramatically. States have been investing in technology and streamlining processes to improve the efficiency of benefit disbursement.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the future of State Unemployment Insurance is likely to be shaped by ongoing economic trends, technological advancements, and changing workforce dynamics. As the gig economy continues to grow, policymakers will need to consider how best to extend unemployment benefits to this increasingly large segment of the workforce.
Additionally, efforts to enhance the program's efficiency and effectiveness will likely continue, with a focus on utilizing technology to streamline processes, improve data collection and analysis, and provide better services to claimants.
Conclusion
State Unemployment Insurance is a critical component of the social safety net in the United States, offering vital support to individuals facing unemployment. By providing temporary financial assistance, the program not only aids individuals and families but also contributes to the overall economic stability of communities and the nation. As the labor market and economy continue to evolve, the importance of this program and the need for its continuous improvement remain evident.
How do I know if I’m eligible for State Unemployment Insurance benefits?
+Eligibility for State Unemployment Insurance benefits depends on several factors, including your earnings during a specified base period, the reason for your job loss, and your availability and efforts to find new work. Each state has its own specific criteria, so it’s important to check with your state’s unemployment office for detailed information.
How long does it typically take to receive unemployment benefits after applying?
+The time it takes to receive unemployment benefits can vary depending on several factors, including the volume of applications, the efficiency of your state’s unemployment office, and the complexity of your individual case. Generally, it can take anywhere from a few weeks to a month or more to start receiving benefits after your application is approved.
Are unemployment benefits taxable?
+Yes, unemployment benefits are generally taxable. You will need to report these benefits as income on your federal and state tax returns. It’s important to consult with a tax professional or refer to IRS guidelines for specific details on how unemployment benefits affect your tax obligations.



