Secondary Medical Insurance

In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, the concept of secondary medical insurance has emerged as a crucial aspect, offering additional financial protection and peace of mind to individuals and families. This form of insurance acts as a backup plan, complementing primary health coverage and ensuring that medical expenses are comprehensively managed. As healthcare costs continue to rise, understanding the intricacies of secondary insurance becomes essential for informed decision-making.
The Role of Secondary Medical Insurance
Secondary medical insurance serves as a vital supplement to primary health plans, filling gaps and covering expenses that primary insurance might not fully address. It is designed to mitigate the financial burden of unexpected medical emergencies, providing an added layer of security for policyholders.
Understanding Primary vs. Secondary Coverage
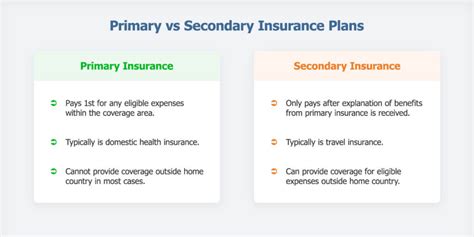
Primary medical insurance is typically the first line of defense, covering a broad range of healthcare services and expenses. It often includes essential benefits like doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription medications. However, primary plans may have limitations, such as high deductibles, copayments, or specific exclusions.
This is where secondary insurance steps in. It acts as a safety net, picking up where the primary coverage leaves off. For instance, if a primary plan has a high deductible, secondary insurance can help cover that initial out-of-pocket expense. It can also provide benefits for services not typically covered by primary plans, ensuring a more comprehensive level of financial protection.
| Primary Insurance | Secondary Insurance |
|---|---|
| Broad coverage for essential services | Fills gaps in primary coverage |
| May have high deductibles or copayments | Covers deductibles and copayments |
| Exclusions for certain services | Provides benefits for excluded services |
Types of Secondary Medical Insurance
Secondary medical insurance comes in various forms, each designed to cater to specific needs and situations. Some common types include:
- Supplemental Health Insurance: This type of insurance provides additional coverage for services not typically covered by primary plans, such as dental, vision, or alternative therapies.
- Gap Insurance: Gap insurance is specifically designed to cover the gap between what a primary plan pays and the actual cost of medical services, ensuring that policyholders aren’t left with unexpected expenses.
- Travel Medical Insurance: For those who frequently travel, this insurance provides coverage for medical emergencies that occur while abroad, ensuring access to quality healthcare regardless of location.
- Medigap Insurance: Targeted towards individuals enrolled in Medicare, Medigap insurance helps cover costs that Medicare doesn’t, including deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
Benefits and Considerations

Secondary medical insurance offers a multitude of benefits, making it an appealing option for many. Here are some key advantages and considerations to keep in mind:
Financial Protection and Peace of Mind
The primary advantage of secondary insurance is the enhanced financial protection it provides. By covering deductibles, copayments, and services not included in primary plans, it ensures that policyholders can access necessary medical care without facing overwhelming financial strain.
Customization and Flexibility
Secondary insurance plans often offer a high degree of customization, allowing individuals to tailor their coverage to their specific needs. Whether it’s adding dental coverage, enhancing prescription drug benefits, or focusing on travel-related emergencies, the flexibility of secondary insurance ensures a personalized approach.
Cost Efficiency
While secondary insurance adds an extra layer of coverage, it can also be cost-effective in the long run. By mitigating the risk of large, unexpected medical bills, it helps individuals and families avoid potential financial disasters. Additionally, some secondary plans offer discounts or bundled rates when combined with primary insurance.
Eligibility and Coverage Limits
It’s important to note that eligibility for secondary insurance may vary depending on the type of plan and the primary insurance coverage in place. Additionally, secondary plans often have their own coverage limits and restrictions, so it’s crucial to carefully review the policy details to ensure it meets individual needs.
Performance Analysis and Real-World Examples
The effectiveness of secondary medical insurance can be gauged through real-world examples and performance analysis. Consider the following scenarios:
Case Study: Ms. Johnson’s Emergency Surgery
Ms. Johnson, a 52-year-old teacher, had a primary health plan with a high deductible. When she unexpectedly required emergency surgery, her primary plan covered the procedure, but left her with a significant deductible. Fortunately, Ms. Johnson had a gap insurance policy as her secondary coverage. This policy covered the entirety of her deductible, ensuring she didn’t face financial hardship during her recovery.
Analyzing Travel Medical Insurance
Travel medical insurance is particularly valuable for individuals who frequently travel abroad. In a recent study, it was found that travelers with secondary insurance had significantly lower out-of-pocket expenses when facing medical emergencies during their trips. This highlights the effectiveness of secondary insurance in mitigating financial risks associated with international travel.
Medigap Insurance Success Stories
For seniors enrolled in Medicare, Medigap insurance has proven to be a crucial component of their healthcare coverage. A recent survey revealed that individuals with Medigap insurance were more satisfied with their healthcare experience, citing reduced financial stress and improved access to necessary medical services.
Future Implications and Industry Insights
The role of secondary medical insurance is likely to evolve and expand as healthcare systems continue to adapt. Here are some key trends and insights to consider:
Integration with Digital Health Solutions
As digital health solutions become more prevalent, the integration of secondary insurance with these technologies is expected to enhance efficiency and convenience. This could include seamless claim processing, real-time benefit verification, and personalized health management tools.
Focus on Preventive Care
The industry is increasingly recognizing the importance of preventive care in managing healthcare costs. Secondary insurance providers are likely to offer incentives and benefits for policyholders who prioritize preventive measures, such as regular check-ups, vaccinations, and lifestyle management programs.
Customized Plans for Specific Demographics
Insurance providers are expected to develop tailored secondary plans for specific demographic groups, such as young adults, seniors, or those with chronic conditions. These plans would address the unique healthcare needs and challenges of these populations, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
Frequently Asked Questions

How does secondary medical insurance differ from primary insurance?
+Secondary medical insurance serves as a backup plan, covering expenses not fully addressed by primary insurance. It helps manage deductibles, copayments, and services excluded from primary plans, providing a comprehensive level of financial protection.
What types of secondary medical insurance are available?
+Secondary insurance comes in various forms, including supplemental health insurance, gap insurance, travel medical insurance, and Medigap insurance. Each type caters to specific needs and situations.
Is secondary medical insurance cost-effective?
+Yes, secondary insurance can be cost-effective in the long run. By mitigating the risk of large, unexpected medical bills, it helps individuals avoid financial strain. Additionally, some secondary plans offer discounts or bundled rates.
How do I choose the right secondary medical insurance plan?
+When choosing a secondary plan, consider your specific healthcare needs and the gaps in your primary coverage. Evaluate the coverage limits, eligibility requirements, and customization options to find a plan that aligns with your requirements.



