Re Insurance

Reinsurance, often referred to as the "insurance for insurers," is a crucial aspect of the global insurance industry, playing a pivotal role in managing risks, enhancing financial stability, and ensuring the long-term viability of insurance companies. This complex yet essential practice involves the transfer of a portion or all of an insurance company's risks and liabilities to another insurance company or a dedicated reinsurance entity. In essence, reinsurance acts as a safety net, providing insurers with the necessary tools to navigate unforeseen events and maintain their operational and financial integrity.
In today's dynamic and increasingly complex risk landscape, the role of reinsurance has become even more critical. From natural disasters and catastrophic events to emerging risks like cyber attacks and pandemics, the need for effective risk management and financial protection is greater than ever. Reinsurance not only helps insurers manage these risks but also allows them to offer a wider range of products and services, benefiting both businesses and individuals worldwide.
The Fundamentals of Reinsurance

Reinsurance operates on the principle of risk transfer, a mechanism that allows primary insurers to offload a portion of their risk exposure to specialized reinsurers. This transfer of risk can take various forms, including proportional and non-proportional reinsurance. Proportional reinsurance, also known as treaty reinsurance, involves a pre-agreed percentage of risks being transferred to the reinsurer, typically on a policy-by-policy basis. In contrast, non-proportional reinsurance, or excess-of-loss reinsurance, provides coverage above a specified loss amount, offering protection against large, unexpected losses.
The primary benefit of reinsurance is its ability to strengthen the financial resilience of insurance companies. By ceding risks to reinsurers, primary insurers can effectively manage their exposure, especially in the face of large-scale or unpredictable events. This risk transfer mechanism not only helps insurers maintain adequate capital reserves but also ensures they can honor their policy commitments, even in the wake of major disasters.
Key Players in the Reinsurance Landscape
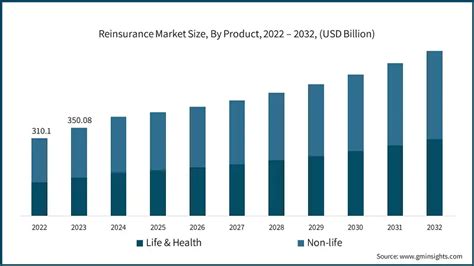
The reinsurance market is characterized by a diverse range of players, each with its own unique role and specialization. At the forefront are the reinsurance companies, also known as reinsurers, who provide the risk-transfer services to primary insurers. These entities can be further categorized into traditional reinsurers, which operate as independent entities, and captive reinsurers, which are owned by insurance groups and often focus on providing reinsurance coverage to their parent companies.
In addition to reinsurance companies, there are also reinsurance intermediaries, who play a vital role in facilitating the reinsurance process. These intermediaries, often called brokers, act as intermediaries between primary insurers and reinsurers, helping to structure and negotiate reinsurance contracts. They provide valuable expertise and insights into the reinsurance market, ensuring that insurers can access the best possible coverage at competitive rates.
Understanding the Role of Reinsurance Brokers
Reinsurance brokers are an indispensable part of the reinsurance ecosystem. They serve as trusted advisors to insurance companies, offering guidance on risk management strategies, reinsurance program design, and market access. Brokers also play a critical role in managing relationships between insurers and reinsurers, ensuring that the reinsurance process is efficient, transparent, and aligned with the insurer’s strategic goals.
One of the key responsibilities of reinsurance brokers is to match insurers with the most suitable reinsurers. This involves a comprehensive understanding of the insurer's risk profile, business objectives, and specific needs. By leveraging their market knowledge and relationships, brokers can negotiate favorable terms and conditions, ensuring that insurers can access the coverage they need at the most competitive rates.
| Reinsurance Player | Role and Impact |
|---|---|
| Reinsurance Companies | Provide risk transfer services, offering financial protection to primary insurers. |
| Reinsurance Brokers | Facilitate the reinsurance process, providing expertise and market access to insurers. |
| Captive Reinsurers | Owned by insurance groups, offering reinsurance coverage specifically to their parent companies. |

The Impact of Reinsurance on the Insurance Industry
The benefits of reinsurance extend far beyond individual insurers. By providing a robust risk management framework, reinsurance plays a pivotal role in strengthening the overall stability and resilience of the insurance industry. This, in turn, has a positive impact on the wider economy, as a stable and reliable insurance sector is crucial for fostering economic growth and supporting businesses and individuals in times of need.
Reinsurance also enables insurers to expand their product offerings and enter new markets. By partnering with reinsurers, insurers can access the capacity and expertise needed to underwrite larger risks and offer a broader range of insurance products. This expansion not only enhances insurers' competitive advantage but also benefits consumers by providing them with more choices and tailored coverage options.
Reinsurance as a Catalyst for Innovation
In recent years, the reinsurance industry has been at the forefront of driving innovation in the insurance sector. With the rise of new technologies and changing risk landscapes, reinsurers have been instrumental in developing innovative solutions to address emerging risks. From parametric insurance products that provide rapid payouts in the event of a predefined trigger to the use of advanced analytics and AI for more accurate risk assessment, reinsurers are leading the way in shaping the future of insurance.
Moreover, reinsurance has played a crucial role in fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing within the insurance industry. By bringing together insurers, reinsurers, and other industry stakeholders, the reinsurance market has become a hub for exchanging ideas, best practices, and emerging trends. This collaborative environment has accelerated the adoption of new technologies and risk management strategies, ultimately benefiting the entire insurance ecosystem.
Navigating the Future: Trends and Opportunities in Reinsurance
As the insurance industry continues to evolve, the role of reinsurance is set to become even more critical. With the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters, the rise of new risks associated with climate change, and the ongoing digital transformation, reinsurers will need to adapt and innovate to meet the changing needs of the market.
Digital Transformation in Reinsurance
The digital revolution has had a profound impact on the insurance industry, and reinsurance is no exception. Reinsurers are increasingly leveraging digital technologies to enhance their operations, improve efficiency, and provide better services to their clients. From digital platforms that streamline the reinsurance placement process to the use of data analytics for more precise risk assessment, digital transformation is reshaping the reinsurance landscape.
Moreover, the adoption of insurtech solutions is gaining momentum in the reinsurance sector. These technologies, which range from AI-powered risk modeling to blockchain-based smart contracts, are revolutionizing the way reinsurance is conducted. By embracing these innovations, reinsurers can enhance their risk management capabilities, improve operational efficiency, and offer more tailored and responsive coverage to their clients.
Addressing Emerging Risks
One of the key challenges facing the reinsurance industry is the need to address emerging risks, especially those associated with climate change and the digital realm. As natural disasters become more frequent and severe, reinsurers are developing innovative solutions to manage these risks, including parametric insurance products and climate risk modeling. Similarly, with the rise of cyber threats and digital risks, reinsurers are partnering with specialist underwriters to develop tailored coverage for these emerging risks.
In conclusion, reinsurance is a critical component of the global insurance industry, providing insurers with the tools they need to manage risks, enhance financial stability, and offer a wide range of products and services. As the industry continues to evolve, the role of reinsurance will become increasingly important, driving innovation, fostering collaboration, and ensuring the long-term viability of the insurance sector. With its unique ability to transfer and manage risks, reinsurance will continue to be a cornerstone of the insurance industry, shaping its future and benefiting businesses and individuals worldwide.
How does reinsurance benefit primary insurers?
+Reinsurance provides primary insurers with several key benefits, including risk transfer, which allows them to manage their exposure more effectively, especially in the face of large-scale or unpredictable events. This, in turn, strengthens their financial resilience and ensures they can honor their policy commitments. Reinsurance also enables insurers to expand their product offerings and enter new markets, enhancing their competitive advantage and providing more choices for consumers.
What is the role of reinsurance brokers in the reinsurance process?
+Reinsurance brokers play a critical role in facilitating the reinsurance process. They act as intermediaries between primary insurers and reinsurers, providing valuable expertise and market access. Brokers help insurers structure and negotiate reinsurance contracts, matching them with the most suitable reinsurers based on their risk profile and business objectives. They also manage relationships between insurers and reinsurers, ensuring a smooth and efficient reinsurance process.
How is reinsurance driving innovation in the insurance industry?
+Reinsurance is a key driver of innovation in the insurance industry. By bringing together insurers, reinsurers, and other stakeholders, the reinsurance market has become a hub for exchanging ideas and best practices. Reinsurers are at the forefront of developing innovative solutions to address emerging risks, such as parametric insurance products for natural disasters and specialized coverage for cyber risks. They also leverage digital technologies and insurtech solutions to enhance their operations and provide more responsive coverage.