Private Healthcare Insurance

Private healthcare insurance is a vital component of the healthcare system, offering individuals and families access to personalized medical care and a range of benefits. With the rising costs of healthcare and the complexities of modern medical treatments, having private insurance has become increasingly important. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of private healthcare insurance, exploring its benefits, how it works, and its impact on individuals and society.
Understanding Private Healthcare Insurance
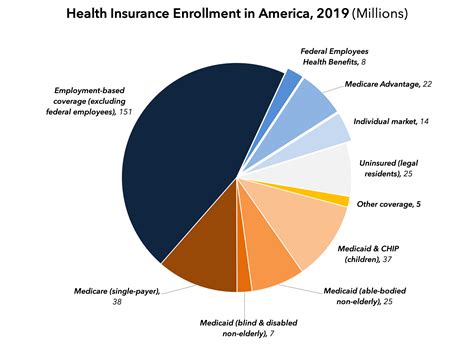
Private healthcare insurance, often referred to as private medical insurance (PMI) or simply medical insurance, is a voluntary health insurance scheme that provides coverage for medical expenses and treatments. Unlike public healthcare systems, which are typically funded by governments, private insurance is offered by insurance companies and is purchased by individuals or provided as a benefit by employers.
The primary goal of private healthcare insurance is to offer policyholders faster access to medical treatment, often with shorter waiting times and a more personalized experience. It covers a wide range of medical services, including specialist consultations, diagnostic tests, surgeries, hospital stays, and sometimes even alternative therapies. Additionally, private insurance often includes additional benefits such as dental care, optical coverage, and mental health support.
Key Features of Private Healthcare Insurance
- Coverage Options: Private insurance plans come in various forms, offering different levels of coverage. Some plans focus on basic healthcare needs, while others provide comprehensive coverage for a wide range of treatments and conditions. Policyholders can choose plans that suit their individual needs and budget.
- Premiums and Deductibles: Like any insurance, private healthcare plans require policyholders to pay premiums, which are typically paid monthly or annually. These premiums can vary based on factors such as age, medical history, and the level of coverage chosen. Additionally, deductibles, or excess payments, may be applicable, where the policyholder pays a certain amount before the insurance coverage kicks in.
- Provider Networks: Many private healthcare insurance plans operate with a network of preferred providers, which includes hospitals, clinics, and individual healthcare professionals. Policyholders often have the flexibility to choose their preferred providers within this network, ensuring they receive care from trusted medical experts.
- Claim Processes: When a policyholder requires medical treatment, they must follow the insurance company’s claim process. This typically involves submitting relevant documentation, such as medical records and invoices, to the insurer for reimbursement. Some plans offer direct billing, where the insurance company pays the provider directly, reducing the financial burden on the policyholder.
The Benefits of Private Healthcare Insurance

Private healthcare insurance offers a multitude of advantages, both to individuals and to the healthcare system as a whole. Here are some key benefits:
Faster Access to Treatment
One of the most significant advantages of private healthcare insurance is the reduced waiting times for medical treatment. In public healthcare systems, long waitlists for surgeries, specialist consultations, and diagnostic tests are common. Private insurance policyholders often have priority access to these services, ensuring they receive timely and efficient care.
For example, a patient with private insurance who requires knee surgery may be able to schedule the procedure within a few weeks, compared to the months-long wait times often experienced in public healthcare settings.
Personalized Care and Choice
Private healthcare insurance provides policyholders with the freedom to choose their preferred healthcare providers and facilities. This allows individuals to seek care from specialists they trust and build long-term relationships with their healthcare teams. It also ensures that policyholders have access to the latest medical technologies and treatments, as private healthcare often invests in state-of-the-art equipment and facilities.
Comprehensive Coverage
Private insurance plans offer a wide range of coverage options, allowing policyholders to tailor their plans to their specific needs. This includes coverage for chronic conditions, mental health support, and even experimental treatments that may not be available in public healthcare settings. Additionally, many plans include coverage for routine check-ups, preventative care, and wellness programs, promoting a proactive approach to health.
Financial Protection
The financial burden of unexpected medical expenses can be significant, and private healthcare insurance provides a safety net. With private insurance, policyholders have peace of mind knowing that their medical costs are covered, reducing the risk of financial hardship due to illness or injury. This is especially beneficial for those with pre-existing conditions or those who require ongoing medical care.
| Fact | Impact |
|---|---|
| Private insurance often covers a broader range of treatments. | Policyholders have access to a wider array of medical options. |
| Premiums vary based on age and health status. | Younger, healthier individuals may find more affordable plans. |
| Some plans offer worldwide coverage. | Travelers can receive medical care while abroad. |

How Private Healthcare Insurance Works
The process of obtaining and utilizing private healthcare insurance involves several key steps. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Selecting a Plan
Policyholders have the option to choose from a range of insurance plans offered by different providers. Factors to consider when selecting a plan include the level of coverage, the network of providers, the cost of premiums and deductibles, and any additional benefits offered.
It's essential to carefully review the plan's policy document, which outlines the specifics of coverage, including any exclusions or limitations. Understanding these details ensures that policyholders are aware of what is and isn't covered by their plan.
Applying for Coverage
To obtain private healthcare insurance, individuals typically need to complete an application process. This may involve providing personal and medical information, such as age, health status, and any pre-existing conditions. Insurance companies use this information to assess the risk associated with insuring the individual and determine the premium rates.
In some cases, individuals may need to undergo a medical examination or provide additional health records to support their application.
Paying Premiums
Once the application is approved, policyholders are required to pay regular premiums to maintain their coverage. Premiums can be paid monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the insurance provider and the policyholder’s preference. It’s important to keep up with premium payments to avoid gaps in coverage.
Utilizing Coverage
When a policyholder requires medical treatment, they can contact their chosen healthcare provider or facility. The provider will then verify the policyholder’s coverage and ensure that the treatment is within the scope of the insurance plan.
In some cases, policyholders may need to obtain prior authorization from their insurance company before undergoing certain treatments or procedures. This helps ensure that the treatment is medically necessary and covered by the plan.
Claiming Reimbursement
After receiving medical treatment, policyholders must submit a claim to their insurance company to receive reimbursement for their expenses. This typically involves providing detailed documentation, such as medical records, invoices, and receipts, to support the claim.
Insurance companies will review the claim and, if approved, will reimburse the policyholder for the covered expenses. The reimbursement process may vary depending on the insurance provider and the terms of the plan.
The Impact of Private Healthcare Insurance
Private healthcare insurance has a significant impact on both individuals and the healthcare system. Here are some key ways it influences healthcare:
Reducing Healthcare Burden on Public Systems
Private healthcare insurance provides an alternative to public healthcare systems, which can often be overwhelmed by high demand and limited resources. By offering faster access to treatment and reducing wait times, private insurance alleviates some of the pressure on public healthcare facilities, allowing them to focus on those who cannot afford private coverage.
Promoting Health Equity
Private healthcare insurance plays a role in promoting health equity by providing individuals with the means to access quality healthcare services. It ensures that those with the financial means can receive timely and specialized care, which can improve health outcomes and overall quality of life.
Driving Innovation in Healthcare
Private healthcare insurance encourages innovation in the medical field. With the ability to choose their providers and access the latest treatments, policyholders benefit from advancements in medical technology and research. This drives healthcare professionals and institutions to stay at the forefront of medical developments, ultimately benefiting the entire healthcare system.
Influencing Healthcare Policy
The presence of private healthcare insurance in a country’s healthcare landscape can influence healthcare policy and regulations. Governments and healthcare policymakers may consider the role of private insurance when designing and implementing healthcare strategies, aiming to strike a balance between public and private healthcare sectors.
Frequently Asked Questions

Can anyone apply for private healthcare insurance?
+
Yes, most private healthcare insurance providers offer plans to individuals of all ages and health statuses. However, some plans may have age limits or specific requirements for certain conditions. It’s important to review the plan’s eligibility criteria before applying.
Are there any tax benefits associated with private healthcare insurance?
+
In some countries, private healthcare insurance premiums may be eligible for tax deductions or credits. These incentives vary by jurisdiction, so it’s advisable to consult with a tax professional or refer to local tax regulations for specific information.
How do I choose the right private healthcare insurance plan for me?
+
When selecting a private healthcare insurance plan, consider your individual needs and budget. Evaluate the level of coverage, the network of providers, and any additional benefits offered. It’s also beneficial to compare plans from different providers to find the best fit for your circumstances.
What happens if I need to cancel my private healthcare insurance policy?
+
Canceling a private healthcare insurance policy typically involves providing notice to the insurance company and settling any outstanding premiums. Some policies may have cancellation fees or require a minimum notice period. It’s important to review the policy terms and conditions to understand the cancellation process.
Can I use my private healthcare insurance when traveling abroad?
+
Many private healthcare insurance plans offer worldwide coverage, allowing policyholders to receive medical treatment while traveling abroad. However, the level of coverage and any additional requirements may vary depending on the plan and the country of travel. It’s essential to check the plan’s terms and conditions before traveling.
Private healthcare insurance is a valuable tool for individuals seeking faster, more personalized medical care. With its wide range of benefits and coverage options, it provides peace of mind and financial protection during times of medical need. Understanding how private healthcare insurance works and its impact on the healthcare system empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.



