Price For Health Insurance Individual
In today's world, health insurance is an essential financial safeguard for individuals and families, providing peace of mind and access to necessary medical care. However, the cost of individual health insurance policies can vary significantly based on a multitude of factors. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the factors influencing individual health insurance prices, offering valuable insights for those seeking to navigate the complexities of the healthcare system.
Understanding the Landscape of Individual Health Insurance
The market for individual health insurance is diverse, catering to a wide range of needs and preferences. From comprehensive plans offering extensive coverage to more basic options with limited benefits, the choices are vast. Factors influencing the price of these plans include the provider, coverage type, location, age, and the individual’s medical history.
The Role of Providers and Coverage Types
Different health insurance providers offer a variety of plans, each with its own unique set of features and costs. Major providers like Aetna, Blue Cross Blue Shield, and UnitedHealthcare typically provide a wide range of options, including PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations), HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations), and POS plans (Point of Service). Each plan type has its advantages and disadvantages, impacting the overall cost of the insurance.
PPO plans, for instance, offer flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, often at a higher cost. HMOs, on the other hand, may be more affordable but restrict the choice of providers to those within the network. POS plans provide a balance, allowing individuals to choose between in-network and out-of-network providers, with varying cost implications.
The scope of coverage also significantly affects the price. Plans offering more comprehensive coverage, including prescription drugs, mental health services, and specialized care, tend to be more expensive. Conversely, basic plans that cover only essential benefits, such as hospitalization and emergency care, are generally more affordable.
| Plan Type | Key Features | Cost Implications |
|---|---|---|
| PPO | Flexible provider choice | Higher premium costs |
| HMO | Restricted provider network | Generally more affordable |
| POS | Balanced between PPO and HMO | Varies based on provider choice |

Geographic and Demographic Factors
The location of the insured individual plays a significant role in determining health insurance prices. Insurance costs can vary greatly between different states and even within the same state, influenced by local healthcare costs, the availability of healthcare providers, and the general health of the population in that area.
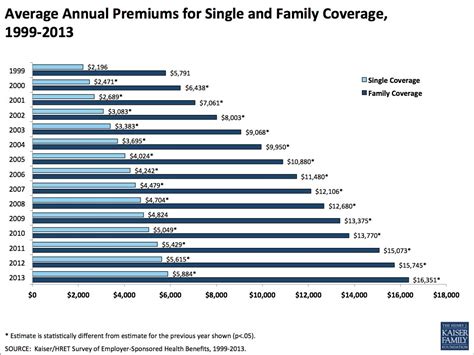
Demographic factors such as age are also crucial. Generally, younger individuals pay lower premiums as they are less likely to require extensive medical care. As people age, their insurance costs typically increase due to the higher likelihood of developing health issues. For example, a 25-year-old might pay an average of $250 per month for individual health insurance, while a 60-year-old might pay closer to $500 per month, depending on other factors.
Medical History and Lifestyle Considerations
An individual’s medical history and current health status are significant determinants of health insurance prices. Pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, can lead to higher premiums or even denial of coverage. Insurance companies carefully evaluate medical records and may charge more for individuals with a history of costly or chronic illnesses.
Lifestyle factors also come into play. For instance, individuals who smoke may face higher premiums due to the increased health risks associated with smoking. Similarly, individuals with hazardous hobbies or occupations might be considered higher-risk, resulting in higher insurance costs.
Analyzing Real-World Examples

To illustrate the variability in individual health insurance prices, let’s examine some real-world scenarios. These examples provide a tangible understanding of how different factors influence the cost of health insurance.
Case Study 1: Young, Healthy Individual
Consider a 28-year-old individual, Sarah, who leads an active lifestyle and has no significant medical history. She opts for a PPO plan with Blue Cross Blue Shield in a metropolitan area. The plan offers comprehensive coverage, including dental and vision benefits. Sarah’s premium for this plan comes to approximately $350 per month. While this may seem high, it is significantly lower than what older individuals or those with health issues might pay.
Case Study 2: Middle-Aged Individual with Pre-Existing Conditions
Now, let’s look at John, a 45-year-old with a history of high blood pressure and diabetes. John, who lives in a suburban area, opts for an HMO plan with UnitedHealthcare due to its more affordable rates. However, given his health conditions, John’s premium is higher than average, at around $600 per month. This example highlights how pre-existing conditions can significantly impact insurance costs.
Case Study 3: Senior Citizen with Limited Income
Emily, a 65-year-old retiree, lives on a fixed income and needs affordable health insurance. She chooses a basic HMO plan with Aetna, which covers essential medical services. Despite her age, the plan is reasonably priced at $300 per month due to its limited coverage. This scenario demonstrates the importance of finding a balance between cost and coverage to suit individual needs.
Navigating the Cost of Individual Health Insurance
Understanding the factors that influence health insurance prices is the first step in making informed decisions. Here are some tips for navigating the cost of individual health insurance:
- Shop Around: Compare plans and providers to find the best fit for your needs and budget. Online tools and health insurance brokers can be valuable resources.
- Evaluate Coverage: Assess your health needs and consider the coverage you require. Overpaying for extensive coverage you may not need can be avoided by understanding your health risks and priorities.
- Consider High-Deductible Plans: If you're generally healthy and have a limited budget, high-deductible plans can be a cost-effective option. These plans often have lower premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs, so they're best suited for those who rarely need medical care.
- Look for Subsidies: Depending on your income, you may be eligible for subsidies to reduce your health insurance costs. The Affordable Care Act provides financial assistance for those who qualify.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Leading a healthy lifestyle can not only improve your well-being but also reduce your insurance costs. Insurance companies often offer incentives or lower premiums for individuals who maintain healthy habits.
Future Implications and Market Trends
The landscape of individual health insurance is continually evolving, influenced by regulatory changes, technological advancements, and shifts in consumer preferences. As the healthcare industry adapts to these changes, the cost of individual health insurance is likely to be affected in the following ways:
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory bodies, such as the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, play a significant role in shaping the health insurance market. Future policies and regulations could impact the cost and availability of individual health insurance. For instance, changes to the Affordable Care Act could affect subsidies and mandate requirements, directly influencing insurance prices.
Technological Advancements
The integration of technology in the healthcare industry, such as telemedicine and digital health records, has the potential to reduce administrative costs and improve efficiency. This could lead to lower insurance premiums over time as providers and insurers save on operational costs.
Consumer Preferences and Market Competition
As consumers become more health-conscious and informed, they are likely to demand more affordable and transparent health insurance options. Increased market competition among insurers could drive down prices and lead to more innovative plans tailored to specific consumer needs.
Summary of Key Insights
Understanding the factors that influence individual health insurance prices is crucial for making informed decisions. From provider and plan type to geographic location, age, and medical history, each factor contributes to the overall cost of insurance. By staying informed about these factors and keeping abreast of market trends, individuals can navigate the complex world of health insurance with greater ease and confidence.
What is the average cost of individual health insurance in the United States?
+The average monthly premium for individual health insurance in the U.S. varies based on several factors, including age, location, and the type of plan. As of 2021, the average premium for an individual was around 450 per month, although this can range from 200 to over $1,000 depending on the aforementioned factors.
How do pre-existing conditions affect health insurance costs?
+Pre-existing conditions can significantly increase health insurance costs. Insurance companies may charge higher premiums or even deny coverage to individuals with certain health issues. However, under the Affordable Care Act, insurers cannot deny coverage or charge more based on health status for plans purchased through the Health Insurance Marketplace.
Are there any ways to reduce the cost of individual health insurance?
+Yes, there are several strategies to reduce the cost of individual health insurance. These include shopping around for different plans and providers, considering high-deductible plans if you’re generally healthy, taking advantage of subsidies if you qualify, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which can often lead to lower premiums.



