Out Of Pocket Insurance Definition

In the complex world of healthcare and insurance, understanding the various terms and concepts is crucial. "Out of pocket" is a phrase often associated with healthcare expenses, but what does it truly mean, and how does it impact individuals and their insurance coverage? Let's delve into the definition and implications of "out of pocket" insurance expenses, shedding light on this essential aspect of healthcare finance.
Understanding “Out of Pocket” Insurance Costs
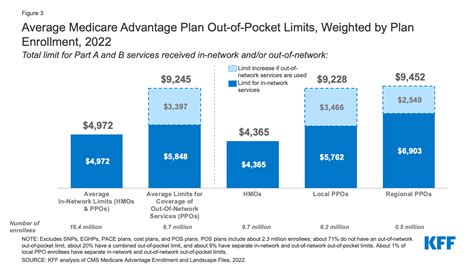
The term “out of pocket” in the context of insurance refers to the expenses or costs that an individual pays directly from their own finances, without any immediate reimbursement or compensation from their insurance provider. These are expenses that are not covered by the insurance policy or are subject to specific conditions and limits.
In simpler terms, when a medical service or treatment is considered "out of pocket," it means the individual is responsible for paying the full amount at the time of service. This can include a wide range of healthcare-related expenses, from co-pays and deductibles to certain procedures and medications not covered by the insurance plan.
Key Components of Out-of-Pocket Costs
-
Deductibles: This is the amount an insured individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance company starts to cover a claim. For instance, if your annual deductible is $1,500, you’ll need to pay that amount first before your insurance kicks in to cover a portion of the costs.
-
Co-pays: A co-payment, or co-pay, is a fixed amount an individual pays for a covered healthcare service, usually at the time of service. Co-pays can vary depending on the type of service and the insurance plan.
-
Coinsurance: After meeting the deductible, many insurance plans require individuals to pay a percentage of the costs, known as coinsurance. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, you pay 20% of the cost of the service, and your insurance provider pays the remaining 80%.
-
Non-Covered Services: Certain medical procedures, treatments, or medications may not be included in your insurance plan. When this happens, you’ll be responsible for paying the full cost, which is considered an out-of-pocket expense.
The Impact on Healthcare Consumers
Out-of-pocket expenses can significantly influence an individual’s healthcare choices and financial well-being. Here’s how they can impact consumers:
Financial Planning
Knowing the potential out-of-pocket costs associated with your insurance plan is essential for financial planning. It allows individuals to set aside funds specifically for healthcare expenses, especially for those with high deductibles or co-insurance plans.
Healthcare Decision-Making
The awareness of out-of-pocket costs can influence an individual’s decision to seek medical care or opt for specific treatments. For example, a person might choose a more affordable healthcare provider or procedure to minimize their financial burden.
Budgeting and Cost Management
Understanding out-of-pocket expenses helps individuals budget effectively. They can estimate the costs of various medical services and plan their finances accordingly, reducing the risk of unexpected financial strains.
Managing Out-of-Pocket Costs
While out-of-pocket expenses are an inherent part of many insurance plans, there are strategies to manage and reduce these costs:
Choosing the Right Insurance Plan
When selecting an insurance plan, carefully review the out-of-pocket maximums, deductibles, and co-pays. Opt for a plan that aligns with your healthcare needs and financial situation. Consider the potential costs of your regular healthcare services and any known health conditions.
Utilizing Preventive Care
Many insurance plans cover preventive care services, such as annual check-ups, screenings, and immunizations, without any out-of-pocket costs. Taking advantage of these services can help identify health issues early, potentially reducing future medical expenses.
Exploring Cost-Saving Options
Research alternative healthcare providers or facilities that offer discounted rates or sliding scale fees. Additionally, consider generic medications, which are often more affordable than brand-name drugs.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
If eligible, contribute to a Health Savings Account. HSAs allow individuals to set aside pre-tax dollars specifically for medical expenses, providing a tax-efficient way to cover out-of-pocket costs.
The Future of Out-of-Pocket Costs
The concept of out-of-pocket expenses is evolving with advancements in healthcare and insurance. Here’s a glimpse into the potential future:
Enhanced Transparency
Insurance providers and healthcare facilities are increasingly focused on providing clear and transparent pricing information. This allows consumers to make more informed choices about their healthcare and potentially negotiate better rates.
Value-Based Care Models
The shift towards value-based care models, where providers are incentivized to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care, may lead to reduced out-of-pocket expenses for consumers. These models aim to improve health outcomes while controlling costs.
Digital Health Solutions
Digital health technologies, such as telemedicine and remote monitoring, can reduce the need for in-person visits, potentially lowering out-of-pocket costs associated with travel and facility fees.
| Insurance Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Deductible | The amount an insured individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance company covers a claim. |
| Co-pay | A fixed amount paid by the insured at the time of service for a covered healthcare service. |
| Coinsurance | The percentage of costs an insured individual pays after meeting their deductible. |
| Out-of-Pocket Maximum | The maximum amount an insured individual is required to pay out of pocket for covered services in a given period, often a year. |

Are there any ways to reduce out-of-pocket costs beyond what’s mentioned above?
+Yes, exploring additional options like negotiating medical bills, seeking financial assistance programs offered by healthcare providers or pharmaceutical companies, and utilizing employee benefits or wellness programs can help reduce out-of-pocket expenses.
How do out-of-pocket expenses differ between insurance plans?
+Out-of-pocket expenses can vary significantly between insurance plans. Factors like deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance rates can be different, influencing the overall cost to the insured individual. It’s crucial to compare these aspects when choosing an insurance plan.
What happens if I exceed my out-of-pocket maximum for the year?
+Once you reach your out-of-pocket maximum, your insurance plan will cover 100% of the costs for covered services for the remainder of the year. This provides financial protection against high medical expenses.



