Mortgage Insurance Definition

Mortgage insurance, often referred to as MI, is a critical component of the home-buying process for many individuals and families. It plays a vital role in the real estate and financial industries, providing protection and facilitating access to homeownership. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of mortgage insurance, exploring its definition, purpose, and its significance in the modern market.
Understanding Mortgage Insurance

Mortgage insurance is a safeguard designed to protect lenders and, by extension, borrowers in the event of a homeowner defaulting on their mortgage payments. It serves as a financial safety net, mitigating the risks associated with providing home loans to buyers who may have a lower credit score or a higher loan-to-value ratio.
When an individual purchases a home using a mortgage, the lender assumes a certain level of risk. Mortgage insurance acts as a risk-sharing mechanism, ensuring that if the borrower encounters financial difficulties and is unable to meet their mortgage obligations, the lender will not suffer a significant loss.
Key Characteristics of Mortgage Insurance
- Protection for Lenders: Mortgage insurance primarily benefits the lender by covering a portion of the loan amount in case of default. This protection allows lenders to offer loans to a wider range of borrowers, including those who might not traditionally qualify for conventional mortgages.
- Lower Down Payment Options: One of the most notable advantages for borrowers is the ability to purchase a home with a lower down payment. Mortgage insurance makes it possible for individuals to enter the housing market sooner, as they are not required to save a substantial amount for the initial investment.
- Risk Mitigation: By requiring mortgage insurance, lenders can mitigate the risks associated with high-ratio mortgages (those with a loan-to-value ratio exceeding 80%). This ensures that even if the borrower defaults, the lender can recover a significant portion of the loan amount.
- Flexibility in Lending: Mortgage insurance enables lenders to offer more flexible lending criteria, allowing individuals with varying financial backgrounds and credit histories to access homeownership.
How Mortgage Insurance Works

The process of mortgage insurance involves several key players and steps. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it operates:
- Homebuyer's Application: An individual interested in purchasing a home submits an application to a lender, providing financial information and details about the property they wish to buy.
- Lender's Assessment: The lender evaluates the borrower's creditworthiness, income stability, and other relevant factors. If the borrower meets the basic requirements, the lender approves the mortgage.
- Mortgage Insurance Requirement: In cases where the borrower's down payment is less than 20% of the home's value (resulting in a loan-to-value ratio above 80%), the lender typically requires mortgage insurance.
- Insurance Premium Payment: The borrower pays a mortgage insurance premium, which can be paid in a lump sum or added to the monthly mortgage payments. This premium is used to purchase insurance coverage from a mortgage insurer.
- Coverage and Protection: The mortgage insurer, often an independent entity, provides coverage to the lender. In the event of a borrower default, the insurer compensates the lender for a portion of the outstanding loan amount.
- Termination of Mortgage Insurance: Mortgage insurance is not a permanent feature. Once the borrower's equity in the property reaches a certain threshold (usually 20% or more), the insurance requirement can be waived, and the borrower can stop paying the insurance premium.
Types of Mortgage Insurance
Mortgage insurance comes in various forms, each designed to cater to specific borrower profiles and mortgage types. Here are some common types of mortgage insurance:
- Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI): PMI is the most common type of mortgage insurance, typically required for conventional loans with a loan-to-value ratio exceeding 80%. It is often provided by private insurance companies and can be canceled once the borrower reaches a certain equity level.
- FHA Mortgage Insurance: The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) offers mortgage insurance for FHA-insured loans. These loans are popular among first-time homebuyers and those with lower credit scores. FHA mortgage insurance is known for its competitive rates and flexible terms.
- VA Mortgage Insurance: The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provides mortgage insurance for eligible military veterans and service members. VA mortgage insurance is a benefit that allows veterans to purchase homes with no down payment and competitive interest rates.
- USDA Mortgage Insurance: The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) offers mortgage insurance for homes located in rural areas. This program aims to promote homeownership in underserved communities.
| Mortgage Insurance Type | Provider | Eligibility |
|---|---|---|
| Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) | Private Insurance Companies | Conventional Loans with LTV > 80% |
| FHA Mortgage Insurance | Federal Housing Administration | FHA-Insured Loans |
| VA Mortgage Insurance | Department of Veterans Affairs | Military Veterans and Service Members |
| USDA Mortgage Insurance | United States Department of Agriculture | Homes in Rural Areas |

The Benefits and Considerations of Mortgage Insurance
Mortgage insurance presents both advantages and considerations for homebuyers and lenders alike. Let’s explore some of the key benefits and factors to keep in mind:
Benefits of Mortgage Insurance
- Increased Accessibility: Mortgage insurance opens up opportunities for individuals who may not have the means to make a substantial down payment. It allows buyers to enter the housing market sooner, fostering greater homeownership rates.
- Risk Mitigation for Lenders: Lenders benefit from mortgage insurance by having a safety net in place. This risk mitigation strategy enables them to offer loans to a broader range of borrowers, contributing to a more inclusive lending environment.
- Competitive Interest Rates: With the added security of mortgage insurance, lenders can offer competitive interest rates to borrowers. This makes homeownership more affordable and accessible for many prospective homeowners.
- Protection for Borrowers: Mortgage insurance provides a layer of protection for borrowers as well. In the event of financial hardship, borrowers can rely on the insurance coverage to help prevent foreclosure and maintain their homeownership status.
Considerations and Potential Drawbacks
- Additional Costs: Mortgage insurance premiums can add to the overall cost of homeownership. Borrowers should carefully consider their financial situation and budget to ensure they can afford both the monthly mortgage payments and the insurance premiums.
- Length of Coverage: Mortgage insurance typically remains in effect until the borrower reaches a certain equity level in their home. This means that borrowers may be paying insurance premiums for an extended period, even after they have built significant equity.
- Termination Requirements: The process of terminating mortgage insurance can vary depending on the type of insurance and the lender’s policies. Borrowers should familiarize themselves with the requirements and plan accordingly to cancel insurance coverage when eligible.
- Alternative Options: Depending on their financial circumstances, some borrowers may explore alternative options, such as saving for a larger down payment or seeking out loans that do not require mortgage insurance. These alternatives can help reduce long-term costs and streamline the homeownership process.
The Future of Mortgage Insurance
As the housing market continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of mortgage insurance. Here are some potential future implications and trends to consider:
Technology and Innovation
The integration of technology in the mortgage insurance industry is expected to bring about significant changes. Digital platforms and automated processes can streamline the insurance application and approval process, making it more efficient and convenient for borrowers and lenders.
Enhanced Risk Assessment
Advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms can improve risk assessment in mortgage insurance. By analyzing a broader range of borrower data points, insurers can more accurately predict default risks and tailor insurance coverage accordingly.
Flexibility in Insurance Options
Mortgage insurers may offer more flexible insurance products in the future, catering to the diverse needs of borrowers. This could include customizable coverage options, allowing borrowers to choose the level of insurance that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Collaborative Approaches
There is a growing trend towards collaboration between lenders, insurers, and borrowers. By working together, these parties can develop innovative solutions that benefit all stakeholders, such as shared-equity programs or alternative mortgage structures.
Regulatory Changes
Government regulations and policies play a crucial role in the mortgage insurance industry. Any changes in regulatory frameworks can impact the availability, cost, and eligibility criteria for mortgage insurance. Staying informed about potential policy shifts is essential for borrowers and lenders alike.
Is mortgage insurance mandatory for all home loans?
+Mortgage insurance is generally required for loans with a loan-to-value ratio above 80%. However, there are exceptions, such as VA loans for military veterans, which do not require mortgage insurance.
Can I cancel my mortgage insurance once I've paid off a certain percentage of my loan?
+Yes, mortgage insurance can often be canceled once your loan-to-value ratio reaches a certain threshold, typically 78% or 80%. However, the exact requirements may vary depending on your lender and the type of mortgage insurance you have.
How much does mortgage insurance cost?
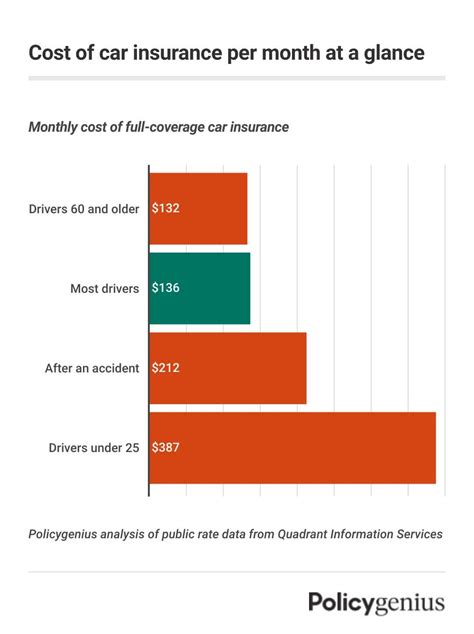
+The cost of mortgage insurance varies based on factors such as the loan amount, loan-to-value ratio, and the type of insurance. On average, PMI can range from 0.5% to 1% of the loan amount annually, while FHA mortgage insurance premiums are typically around 0.85% of the loan amount annually.
Mortgage insurance is a fundamental aspect of the home-buying journey, offering protection and opportunities to individuals seeking to own their homes. By understanding the purpose, process, and implications of mortgage insurance, borrowers and lenders can navigate the real estate market with confidence and make informed decisions that lead to successful homeownership.