Medicare Insurances

Medicare, a cornerstone of the American healthcare system, provides essential health insurance coverage to millions of individuals aged 65 and older, as well as younger people with specific disabilities and conditions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Medicare insurance, offering an in-depth analysis of its various components, benefits, and implications.
Understanding the Medicare Insurance Program

Medicare is a federal health insurance program administered by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), a branch of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Established in 1965 under the Social Security Act, Medicare has undergone significant expansions and improvements over the years to better serve its beneficiaries.
The program is divided into several parts, each covering different aspects of healthcare. The four main parts of Medicare are:
- Part A (Hospital Insurance): This covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and some home health care.
- Part B (Medical Insurance): Part B helps cover doctor's services, outpatient care, durable medical equipment, and some preventative services.
- Part C (Medicare Advantage Plans): Also known as MA Plans, these are offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare. They provide all the benefits of Part A and Part B, and often additional benefits as well.
- Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage): Part D plans, also run by private insurance companies approved by Medicare, provide coverage for prescription medications.
Additionally, there's the Medicare Supplemental Insurance (Medigap), which can help fill in some of the gaps in Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) coverage, such as copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles.
Eligibility and Enrollment
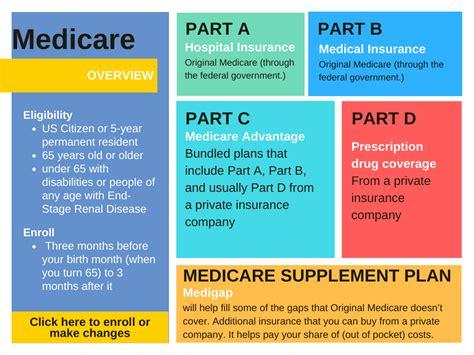
Understanding eligibility and enrollment is crucial for anyone approaching Medicare. Individuals become eligible for Medicare based on specific criteria, primarily age and certain disabilities.
Age-Based Eligibility
Most people become eligible for Medicare when they turn 65. However, it’s important to note that eligibility is not automatically triggered by age. Individuals need to actively enroll during specific enrollment periods to ensure coverage begins on time.
Disability-Based Eligibility
For individuals under the age of 65, Medicare eligibility can be established if they meet certain disability criteria. This includes being disabled for at least 24 months, having End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD), or having Lou Gehrig’s disease (ALS). In these cases, individuals may be eligible for Medicare benefits without having to wait until they are 65.
Enrollment Periods
Medicare has different enrollment periods, each with its own rules and implications. The Initial Enrollment Period (IEP) is the time when individuals can first enroll in Medicare. It begins three months before the month of their 65th birthday, includes the birthday month, and ends three months after the birthday month.
There are also Special Enrollment Periods (SEPs) for those who miss their Initial Enrollment Period due to specific circumstances. Additionally, General Enrollment Periods are available for individuals who did not qualify for Medicare at age 65 but later become eligible.
Medicare Coverage and Benefits
Medicare offers a wide range of benefits, designed to meet the diverse healthcare needs of its beneficiaries. These benefits can be broadly categorized into preventive care, hospital stays, outpatient services, and prescription drug coverage.
Preventive Care
Medicare covers a range of preventive services to help beneficiaries stay healthy and catch potential health issues early. This includes annual wellness visits, cancer screenings, vaccinations, and more. These services are often covered at no cost to the beneficiary, emphasizing the program’s focus on preventative health.
Hospital Stays
Medicare Part A covers inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility care, and some home health care services. This coverage ensures that beneficiaries have access to necessary medical treatments and rehabilitation services when hospitalized or recovering from serious illnesses or injuries.
Outpatient Services
Medicare Part B covers a wide array of outpatient services, including doctor visits, diagnostic tests, durable medical equipment, and certain outpatient procedures. These services are crucial for ongoing healthcare management and monitoring.
Prescription Drug Coverage
Medicare Part D, offered through private insurance companies, provides coverage for prescription drugs. This is a vital component of Medicare, given the importance of medication management in maintaining health and managing chronic conditions.
| Medicare Part | Coverage |
|---|---|
| Part A | Inpatient hospital care, skilled nursing facility care, home health care |
| Part B | Doctor visits, outpatient care, durable medical equipment |
| Part C | All Part A and Part B benefits, often additional benefits as well |
| Part D | Prescription drug coverage |

Medicare Costs and Out-of-Pocket Expenses
While Medicare provides extensive coverage, it’s important to understand the associated costs and potential out-of-pocket expenses. These costs can vary based on the specific Medicare plan and the services received.
Premiums
Most people don’t pay a monthly premium for Medicare Part A because they or their spouse paid Medicare taxes while working. However, there is a monthly premium for Medicare Part B, which can vary based on income.
Deductibles and Coinsurance
Medicare typically has an annual deductible for Part A and Part B, which must be met before Medicare starts to pay its share. Additionally, there may be coinsurance, which is the beneficiary’s share of the cost for a covered health care service.
Medicare Advantage and Medigap Plans
Medicare Advantage and Medigap plans can help cover some of the costs not covered by Original Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans often have additional benefits, while Medigap plans can help cover deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments.
Choosing the Right Medicare Plan
With a multitude of Medicare plans available, selecting the right one can be a complex decision. Factors to consider include personal health needs, prescription drug requirements, and preferred healthcare providers.
Assessing Personal Health Needs
Understanding your current and potential future health needs is essential. Consider factors like chronic conditions, required medications, and the frequency of doctor visits. This self-assessment can guide your choice between Original Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans, as well as the specific Part D prescription drug plan that best suits your needs.
Comparing Plan Options
Research and compare different Medicare plans to find the best fit. This includes reviewing the plan’s covered services, out-of-pocket costs, and provider networks. Tools like the Medicare Plan Finder on the official Medicare website can be invaluable in this process.
Considering Prescription Drug Coverage
For individuals with ongoing medication needs, selecting the right Part D prescription drug plan is crucial. This involves checking which drugs are covered by the plan (the formulary) and understanding any potential restrictions or costs associated with obtaining these medications.
Enrolling in Medicare
The enrollment process for Medicare involves several steps, each with its own considerations. Whether you’re enrolling during the Initial Enrollment Period, a Special Enrollment Period, or the General Enrollment Period, it’s important to understand the process and the implications of your choices.
Initial Enrollment Period
During the Initial Enrollment Period, individuals can enroll in Medicare Part A and Part B, or just Part A if they already have health insurance coverage through their employer or a spouse’s employer. This period is time-sensitive, and missing it may result in late enrollment penalties.
Special Enrollment Periods
Special Enrollment Periods allow individuals to enroll in Medicare outside of the Initial Enrollment Period due to specific circumstances. This might include losing employer-sponsored health insurance, moving to a new state, or other qualifying life events.
General Enrollment Period
The General Enrollment Period is a seven-month period from January 1 to March 31, with coverage starting on July 1. This period is for individuals who did not enroll in Medicare when they were first eligible but have since become eligible.
Medicare’s Impact and Future Prospects
Medicare’s impact on the healthcare landscape is profound, providing crucial health insurance coverage to a significant portion of the population. As the program continues to evolve, its future prospects are closely tied to ongoing policy discussions and healthcare reforms.
Policy and Reform Discussions
Medicare is a key topic in healthcare policy debates, with proposals for expansion, cost control, and improved efficiency. These discussions often center around how to best serve the growing population of Medicare beneficiaries while ensuring the program’s financial sustainability.
Future Innovations
Looking ahead, Medicare is likely to incorporate more innovative technologies and approaches. This could include increased use of telemedicine, improved data analytics for more personalized care, and further integration of preventive health measures into the program.
Ensuring Access and Affordability
A critical aspect of Medicare’s future is ensuring continued access and affordability for all eligible individuals. This involves ongoing efforts to control costs, streamline administrative processes, and enhance the program’s overall efficiency and effectiveness.
What is the difference between Original Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans?
+Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) is the traditional fee-for-service Medicare program administered by the federal government. It covers a wide range of health services but may have higher out-of-pocket costs. Medicare Advantage plans (Part C) are offered by private insurance companies approved by Medicare. These plans often have additional benefits and lower out-of-pocket costs, but may have more limited provider networks.
How do I choose the right Medicare Part D plan for my prescription drug needs?
+When selecting a Part D plan, consider the medications you take regularly and whether they are covered by the plan's formulary. Also, look at the plan's cost-sharing structure, including deductibles, copays, and coinsurance, to ensure it aligns with your budget. You can use the Medicare Plan Finder tool to compare different Part D plans based on your specific drug needs.
What happens if I miss my Initial Enrollment Period for Medicare?
+If you miss your Initial Enrollment Period, you may be able to enroll during a Special Enrollment Period if you meet certain criteria, such as losing other health coverage or moving to a new state. However, if you don't qualify for a Special Enrollment Period, you may need to wait for the General Enrollment Period, which has higher premiums and may result in late enrollment penalties.
In conclusion, Medicare insurance is a vital component of the American healthcare system, offering comprehensive coverage to millions of individuals. By understanding the program’s structure, eligibility criteria, and the range of benefits it provides, individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage. As Medicare continues to adapt and evolve, it remains a critical safety net for those in need.



