Irs Rules For Health Insurance Reimbursement
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) plays a crucial role in regulating and providing guidelines for health insurance reimbursement in the United States. Understanding the IRS rules surrounding this topic is essential for individuals, employers, and healthcare providers to ensure compliance and maximize tax benefits. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of health insurance reimbursement, shedding light on the IRS regulations and offering practical insights for various stakeholders.
IRS Guidelines for Health Insurance Reimbursement

The IRS has established a set of rules and regulations to govern the reimbursement of health insurance premiums and medical expenses. These guidelines are designed to provide clarity and ensure fairness in the healthcare system while also offering tax advantages to individuals and employers.
Reimbursement of Health Insurance Premiums
One of the key aspects of IRS regulations is the treatment of health insurance premium reimbursements. The IRS allows employers to provide tax-free reimbursements for employee health insurance premiums under specific conditions. Here's an overview:
- Employer-Provided Coverage: Employers can offer health insurance coverage to their employees as a taxable benefit. However, to make it tax-free for the employee, the employer must meet certain criteria. The coverage must be provided through a qualified health plan as defined by the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and must be offered to all eligible employees.
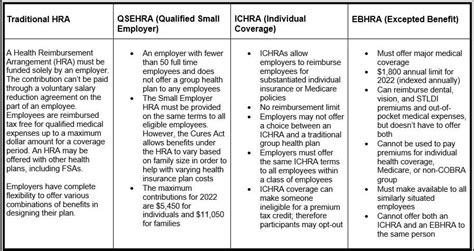
- Reimbursement Method: The IRS permits two primary methods for reimbursing health insurance premiums: Premium Reimbursement Arrangement (PRA) and Health Reimbursement Arrangement (HRA). These arrangements allow employers to reimburse employees for their insurance premiums on a tax-free basis.
- PRA vs. HRA: Premium Reimbursement Arrangements are typically simpler and involve direct reimbursements to employees for their insurance premiums. Health Reimbursement Arrangements, on the other hand, offer more flexibility and can reimburse not only premiums but also other qualified medical expenses. HRAs are subject to specific contribution limits and must comply with IRS regulations.
- Eligibility: To qualify for tax-free reimbursement, employees must generally be enrolled in a qualified health plan and meet specific eligibility criteria. The IRS provides guidelines on determining eligibility based on factors such as hours worked, length of service, and other defined requirements.
Medical Expense Reimbursements
In addition to premium reimbursements, the IRS also allows for the tax-free reimbursement of certain medical expenses. Here's what you need to know:
- Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs): Employers can set up FSAs to allow employees to contribute pre-tax dollars to cover eligible medical expenses. FSAs offer a tax advantage as the contributions are not subject to federal income tax, Social Security tax, or Medicare tax. Employees can use these funds to reimburse themselves for qualified medical expenses.
- Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): HSAs are another tax-advantaged savings option for individuals with high-deductible health plans. Contributions to HSAs are tax-deductible, and funds can be used tax-free for qualified medical expenses. HSAs offer a way to save for future healthcare needs while enjoying tax benefits.
- Qualified Medical Expenses: Both FSAs and HSAs have specific guidelines for what constitutes a qualified medical expense. These expenses include a wide range of healthcare-related costs such as doctor visits, prescription medications, dental care, vision care, and more. It's important to refer to IRS publications for a comprehensive list of qualified expenses.
IRS Reporting Requirements
Compliance with IRS regulations extends beyond just providing tax-free reimbursements. Employers and individuals must also meet certain reporting requirements to ensure accuracy and transparency. Here are some key considerations:
- Form W-2 Reporting: Employers must report the value of employer-provided coverage on employees' Form W-2. This includes the cost of the employer's share of the health insurance premiums. Reporting this information accurately is essential to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
- Form 1099 Reporting: When reimbursing employees for medical expenses through a PRA or HRA, employers must issue a Form 1099-MISC to the employee. This form reports the amount reimbursed to the IRS and helps track tax-free reimbursements.
- Form 1095-C Reporting: For applicable large employers (ALEs), the ACA requires them to report offer and coverage information to the IRS and employees using Form 1095-C. This form details the health coverage provided to full-time employees and helps enforce the employer shared responsibility provision of the ACA.
Maximizing Tax Benefits

Understanding the IRS rules for health insurance reimbursement opens up opportunities for individuals and employers to maximize their tax benefits. Here are some strategies to consider:
Employer Strategies
- Offer Comprehensive Coverage: By providing a qualified health plan to employees, employers can take advantage of tax-free premium reimbursements. This not only benefits employees but also enhances the company's reputation as an attractive employer.
- Utilize HRAs Strategically: Health Reimbursement Arrangements can be a powerful tool for employers to control healthcare costs while offering tax-free benefits to employees. Employers can design HRAs to cover specific medical expenses and provide a flexible healthcare benefit.
- Educate Employees: Ensuring that employees understand the tax advantages of health insurance reimbursement is crucial. Employers can provide educational resources and workshops to help employees make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage and expenses.
Individual Strategies
- Explore FSA and HSA Options: Individuals should consider the benefits of Flexible Spending Accounts and Health Savings Accounts. FSAs can help cover current medical expenses, while HSAs offer long-term savings and investment potential for future healthcare needs.
- Keep Track of Expenses: To maximize tax benefits, individuals should maintain accurate records of their qualified medical expenses. This includes keeping receipts, statements, and other documentation to support their reimbursements.
- Stay Informed: IRS regulations can change, so it's essential for individuals to stay updated on the latest guidelines. Subscribing to IRS newsletters or following reputable healthcare and tax resources can ensure individuals are aware of any updates that may impact their health insurance reimbursement strategies.
Conclusion
The IRS rules for health insurance reimbursement provide a framework for individuals and employers to navigate the complex world of healthcare benefits while maximizing tax advantages. By understanding these regulations and implementing strategic approaches, stakeholders can ensure compliance, control costs, and enhance the overall healthcare experience. Staying informed and leveraging the tax benefits offered by the IRS is key to making the most of health insurance reimbursement.
FAQs
Can employers reimburse employees for any type of health insurance plan?
+No, employers must ensure that the health insurance plan they reimburse employees for meets the qualifications outlined by the IRS and the Affordable Care Act (ACA). This typically includes plans offered through the healthcare marketplace or plans that meet specific minimum coverage requirements.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there limits to the amount of health insurance premiums an employer can reimburse tax-free?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, the IRS sets annual limits on the amount of health insurance premiums that can be reimbursed tax-free. These limits are adjusted each year and vary based on the type of coverage (self-only or family coverage) and the age of the employee. Employers should refer to the latest IRS guidelines for specific limits.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can employees receive tax-free reimbursements for their spouse's or dependent's health insurance premiums?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, employees can receive tax-free reimbursements for their spouse's or dependent's health insurance premiums as long as the coverage is considered qualified family coverage under the IRS guidelines. However, employers should ensure that the reimbursement amounts are consistent with the IRS limits for family coverage.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Are there any penalties for non-compliance with IRS health insurance reimbursement regulations?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, the IRS imposes penalties for non-compliance with health insurance reimbursement regulations. Employers may face penalties for not providing accurate reporting on Forms W-2 and 1095-C, as well as for failing to meet the requirements of qualified health plans. Employees may also face tax consequences if they receive tax-free reimbursements for non-qualified expenses.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can employers offer health insurance reimbursement as a standalone benefit or must it be part of a larger benefits package?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Employers can offer health insurance reimbursement as a standalone benefit, but it is often more effective when integrated into a comprehensive benefits package. By offering a range of benefits, employers can attract and retain top talent while also providing employees with the flexibility to choose the healthcare coverage that best suits their needs.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>



