How Much Does Longterm Care Insurance Cost For A 65Yearold

As individuals approach their golden years, the question of long-term care insurance becomes increasingly pertinent. With rising healthcare costs and the potential need for extended care, understanding the financial implications of such coverage is crucial. This article aims to delve into the specific costs associated with long-term care insurance for a 65-year-old, providing an in-depth analysis of the factors that influence premiums and offering valuable insights to make informed decisions.
The Financial Landscape of Long-Term Care Insurance

Long-term care insurance is designed to provide financial protection against the high costs of extended medical care, be it at home, in an assisted living facility, or a nursing home. For a 65-year-old individual, this insurance can be a vital component of their retirement planning, ensuring they have the necessary resources to maintain their quality of life and independence.
The cost of long-term care insurance is a complex calculation, influenced by a multitude of factors. These factors include the individual's age, health status, the chosen coverage limits, and the type of policy selected. Let's explore these variables in detail to understand their impact on the premium.
Age and Health: The Primary Determinants
Age is a significant factor in determining long-term care insurance costs. As individuals age, their likelihood of requiring long-term care increases, leading to higher premiums. For a 65-year-old, premiums are generally higher compared to someone in their 50s, as the insurance provider anticipates a greater likelihood of claims being made within a shorter timeframe.
Health status is another critical factor. Insurance companies assess an individual's health through medical underwriting, which involves reviewing their medical history and current health condition. Those with pre-existing conditions or a history of chronic illnesses may face higher premiums or even be declined coverage altogether. Maintaining good health and managing any existing conditions can help mitigate these costs.
| Health Factor | Impact on Premium |
|---|---|
| Chronic Conditions | Increased premiums or policy exclusions |
| Pre-existing Illnesses | Potential for higher rates or coverage denial |
| Age-related Health Changes | Gradual increase in premiums over time |
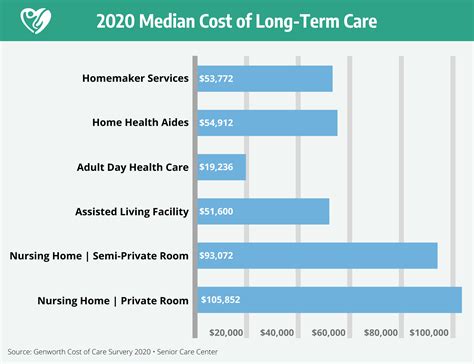
Coverage Limits and Policy Types
The level of coverage an individual chooses significantly impacts the cost of their long-term care insurance. Policies typically offer daily benefit amounts, which represent the maximum amount the insurer will pay toward the insured’s care each day. Higher daily benefit amounts mean increased costs, as the insurer assumes greater financial responsibility.
Additionally, the duration of coverage plays a role. Some policies offer lifetime benefits, while others have a set number of years or a specific dollar amount limit. Longer durations or unlimited coverage will generally result in higher premiums.
Policy types also vary, with traditional long-term care insurance, hybrid policies (combining life insurance and long-term care benefits), and short-term care insurance being the primary options. Each type has its own cost structure and considerations. For instance, hybrid policies may offer tax advantages or the potential for a death benefit if long-term care is not needed.
Other Factors Influencing Premiums
Beyond age, health, and coverage choices, several other factors can influence long-term care insurance premiums:
- Inflation Protection: Policies with inflation protection can increase benefits over time to keep pace with rising healthcare costs. This feature typically adds to the premium.
- Elimination Period: The length of time an individual must wait before benefits are payable (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days) can affect the premium. Longer elimination periods often result in lower premiums.
- Location: The cost of care varies by region, with urban areas and states with higher costs of living often resulting in higher premiums.
- Policy Riders: Optional riders, such as those for home health care or care coordination services, can increase the policy's cost.
Analyzing Real-World Premiums: A Case Study

To provide a tangible understanding of long-term care insurance costs, let’s consider a case study for a 65-year-old individual, Jane, who is interested in purchasing a policy.
Jane, in good health, opts for a traditional long-term care insurance policy with the following specifications:
- Daily Benefit: $200
- Elimination Period: 90 days
- Duration: Lifetime benefits
- Inflation Protection: 3% compound growth
Based on these choices, Jane's annual premium could range from $2,500 to $4,000, depending on the insurance company and her specific health assessment. This range reflects the variability in pricing across different providers and the impact of Jane's health status on her premium.
If Jane were to opt for a hybrid policy with a death benefit, her premium might increase by approximately 10-15%, offering both long-term care coverage and a potential financial legacy.
Strategies for Managing Costs
While long-term care insurance premiums can be substantial, there are strategies to help manage these costs:
- Purchase Early: Buying long-term care insurance earlier in life, such as in one's 50s, can result in significantly lower premiums. This is due to the lower likelihood of needing care and the better health status typically associated with younger ages.
- Choose a Longer Elimination Period: Opting for a longer period before benefits become payable can reduce premiums. However, this strategy requires careful consideration, as it means paying out-of-pocket for care during that initial period.
- Consider Limited-Duration Policies: Policies with a set number of years of coverage, rather than lifetime benefits, can be more affordable. These policies may be suitable for individuals who anticipate a shorter need for care or have other financial resources to fall back on.
- Explore State Partnership Programs: Many states offer partnership programs that combine private long-term care insurance with Medicaid benefits. These programs can provide additional protection and potentially lower costs.
The Future of Long-Term Care Insurance Costs
Looking ahead, the cost of long-term care insurance is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Rising healthcare costs, an aging population, and evolving policy designs all contribute to this trend. However, the exact rate of increase is difficult to predict and can vary significantly based on individual circumstances and policy choices.
Despite the rising costs, long-term care insurance remains a critical component of retirement planning. It provides peace of mind and financial security, ensuring that individuals can access the care they need without depleting their retirement savings or relying solely on Medicaid.
As with any financial decision, it is essential to thoroughly research and understand the options available. Consulting with a financial advisor or insurance professional can provide valuable guidance tailored to an individual's specific needs and circumstances.
Can I get long-term care insurance after retirement?
+While it is possible to purchase long-term care insurance after retirement, premiums tend to be higher due to age and potential health changes. However, some insurance providers offer policies specifically designed for retirees.
Are there any tax benefits associated with long-term care insurance premiums?
+Yes, in many countries, including the United States, long-term care insurance premiums may be tax-deductible, especially if they are part of a business expense or a qualified retirement plan. It’s advisable to consult a tax professional for specific guidance.
What if I can’t afford long-term care insurance premiums?
+If premiums are a concern, exploring alternative options like limited-duration policies, state partnership programs, or even long-term care annuities can provide more affordable coverage. It’s important to carefully assess one’s financial situation and seek professional advice.