How Insurance Works
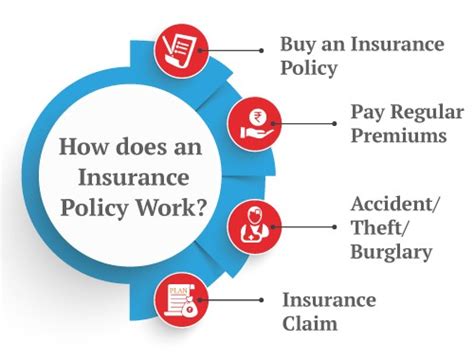
Insurance is a fundamental aspect of modern life, providing individuals and businesses with financial protection against unforeseen events and risks. It plays a crucial role in managing uncertainties and ensuring peace of mind. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of insurance, exploring its history, principles, and various types, while also highlighting real-world examples and the impact it has on our daily lives.
The Evolution of Insurance: A Historical Perspective

The concept of insurance can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where early forms of risk-sharing agreements were established. In medieval Europe, the development of maritime insurance policies protected merchants from losses incurred during sea voyages. Over time, insurance evolved to cover a wide range of risks, and by the 17th century, the first life insurance policies were introduced in England.
The 18th and 19th centuries witnessed significant advancements in the insurance industry. The establishment of Lloyd's of London, a prominent insurance marketplace, in the 1680s, played a pivotal role in shaping the industry's future. Lloyd's innovative approach to underwriting and risk assessment set a precedent for modern insurance practices.
Understanding the Principles of Insurance
At its core, insurance operates on a few key principles that ensure fairness and effectiveness.
Risk Pooling and Spread
Insurance companies bring together a large number of individuals or entities, creating a risk pool. By pooling resources, the financial burden of losses is spread across the group, making it more manageable for each participant. This principle is fundamental to the concept of insurance, as it allows for the sharing of risks and reduces the impact of unforeseen events on any single individual.
Law of Large Numbers
The law of large numbers is a statistical principle that underpins insurance. It states that as the number of observations (in this case, policyholders) increases, the actual results (losses) will tend to stabilize and align with the expected results. Insurance companies use this law to calculate premiums and ensure the long-term sustainability of their business.
Indemnity and Subrogation
Insurance policies typically follow the principle of indemnity, which means that the insured party is compensated for their actual loss, but not more. This prevents individuals from profiting from insurance claims. The process of subrogation allows the insurance company to step into the shoes of the insured to recover losses from a third party responsible for the damage.
Types of Insurance: A Comprehensive Overview
Insurance covers a vast array of risks, and understanding the different types is essential for making informed decisions.
Life Insurance
Life insurance provides financial protection to the policyholder’s beneficiaries in the event of their death. There are two main types: term life insurance, which offers coverage for a specific period, and permanent life insurance, which provides lifelong coverage and often includes a cash value component. For instance, a 35-year-old individual with a family might opt for a 20-year term life insurance policy to ensure their family’s financial security until their children become independent.
Health Insurance
Health insurance covers the cost of medical expenses, ensuring individuals have access to necessary healthcare services. It can include various plans, such as HMO (Health Maintenance Organization), PPO (Preferred Provider Organization), and POS (Point of Service). In the United States, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has expanded access to health insurance, with millions now benefiting from its provisions. A recent study showed that ACA-compliant plans provided coverage for an average of 10 essential health benefits, including hospitalization, prescription drugs, and mental health services.
Property and Casualty Insurance
This category encompasses a wide range of insurance policies, including homeowners, renters, auto, and business insurance. These policies protect against losses resulting from damage to property or liability claims. For instance, a homeowner’s insurance policy might cover damage caused by a fire, while auto insurance provides financial protection in the event of an accident.
Specialty Insurance
Specialty insurance covers unique risks that are not typically included in standard policies. This can include travel insurance, which protects against trip cancellations and medical emergencies while abroad, pet insurance for veterinary costs, and cyber insurance to safeguard businesses from cyber-attacks and data breaches.
The Impact of Insurance on Society
Insurance has a profound impact on individuals, businesses, and the economy as a whole.
Personal and Financial Security
Insurance provides individuals with a safety net, ensuring they can recover financially from unexpected events. For example, in the event of a severe illness or accident, health insurance can cover costly medical treatments, preventing individuals from incurring crippling debt. Life insurance policies offer peace of mind, knowing that loved ones will be financially secure in the event of a premature death.
Business Stability and Growth
Businesses rely on insurance to protect their assets and operations. Property and casualty insurance shields companies from financial ruin in the event of natural disasters or liability claims. Additionally, business interruption insurance provides coverage for lost income during periods of business interruption, ensuring companies can recover and continue operations.
Economic Stability and Development
Insurance plays a crucial role in promoting economic stability and growth. By spreading risk and providing financial security, insurance encourages investment and entrepreneurship. It also facilitates international trade by offering protection against various risks, such as political instability and currency fluctuations.
Performance Analysis and Industry Insights

The insurance industry is a dynamic sector, constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of its customers. Here’s a closer look at some key performance indicators and industry trends.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
| KPI | Description |
|---|---|
| Loss Ratio | Measures the proportion of premiums used to pay claims, indicating the efficiency of an insurance company’s underwriting. |
| Combined Ratio | Represents the sum of the loss ratio and expense ratio, providing an overview of an insurer’s overall profitability. |
| Premium Growth | Tracks the increase in insurance premiums over time, reflecting market demand and industry growth. |
| Claim Settlement Ratio | Indicates the percentage of claims that are settled by an insurance company, showcasing their efficiency in processing claims. |
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The insurance industry is undergoing significant transformations, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer preferences.
- Digitalization and InsurTech: The rise of digital technologies has led to the emergence of InsurTech companies, which leverage data analytics and artificial intelligence to streamline insurance processes and offer innovative products. This trend is expected to continue, with insurance companies investing heavily in technology to enhance customer experiences and operational efficiency.
- Personalized Insurance: With the availability of vast data, insurance companies are moving towards personalized insurance products. By analyzing individual risk profiles, insurers can offer tailored coverage options, providing customers with more accurate and affordable policies.
- Sustainability and Environmental Risks: As climate change and environmental concerns take center stage, the insurance industry is adapting to address these emerging risks. Insurers are developing products to protect against natural disasters and extreme weather events, while also investing in sustainable practices to reduce their environmental impact.
Conclusion: Navigating the World of Insurance
Insurance is an indispensable tool for managing risks and securing our financial future. By understanding the principles, types, and impact of insurance, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions to protect themselves and their assets. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing technology and adapting to new challenges, insurance will remain a crucial component of modern life, providing stability and peace of mind in an uncertain world.
What is the difference between term life insurance and permanent life insurance?
+Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. It is often more affordable but offers no cash value. Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, provides lifelong coverage and includes a cash value component that can be accessed through loans or withdrawals. The choice between the two depends on individual needs and financial goals.
How does health insurance help with medical expenses?
+Health insurance covers a wide range of medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription drugs, and specialized treatments. By paying a premium, policyholders gain access to a network of healthcare providers, and their insurance plan covers a portion or all of the costs associated with medical care. This helps individuals manage their healthcare expenses and ensures they can receive necessary treatment without facing financial hardship.
What are some common exclusions in insurance policies?
+Insurance policies often exclude certain risks or events from coverage. Common exclusions may include acts of war, nuclear incidents, intentional self-injury, and pre-existing conditions. It’s important to carefully review the policy documents to understand the specific exclusions applicable to your policy, as these can vary depending on the type of insurance and the insurer.



