Health Insurance In America

Health insurance is a crucial aspect of healthcare in the United States, impacting millions of Americans and their access to medical services. With a complex system and various options available, understanding the ins and outs of health insurance is essential for individuals and families. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the intricacies of health insurance in America, providing an expert analysis of the key components, coverage options, and the future landscape of this vital industry.
The Foundation of Health Insurance in America
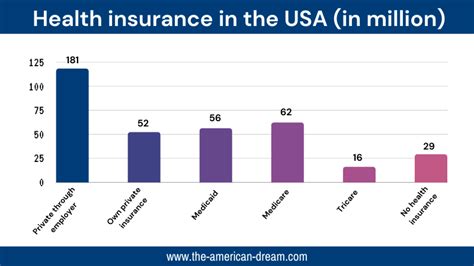
Health insurance in the US is a multifaceted system, influenced by federal and state regulations, market dynamics, and individual needs. At its core, health insurance provides financial protection against the high costs of medical care, ensuring individuals can access necessary healthcare services without facing devastating financial burdens.
The history of health insurance in America dates back to the early 20th century when the concept of insurance began to gain traction. However, it was the introduction of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) in 1974 that significantly shaped the industry, establishing standards for private health plans offered by employers. This legislation paved the way for the growth of employer-sponsored health insurance, which remains a dominant force in the market today.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare, further revolutionized the health insurance landscape in 2010. The ACA aimed to increase the quality and affordability of health insurance, making significant changes to the industry, including the establishment of health insurance marketplaces and the expansion of Medicaid. This landmark legislation has had a lasting impact on the availability and accessibility of health insurance for millions of Americans.
Understanding Coverage Options
Health insurance coverage in America comes in various forms, catering to different needs and budgets. Here’s an overview of the primary types of health insurance plans:
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
The majority of working Americans receive health insurance through their employers. These plans are typically offered as part of an employee benefits package and are often partially subsidized by the employer. Employer-sponsored plans vary widely in terms of coverage, deductibles, and premiums, with options ranging from comprehensive plans to more basic coverage.
One of the key advantages of employer-sponsored insurance is the potential for group purchasing power, which can lead to more affordable premiums. Additionally, these plans often include additional benefits such as dental, vision, and prescription drug coverage.
Individual and Family Plans
Individuals and families who do not have access to employer-sponsored insurance can purchase health insurance plans directly from insurance providers. These plans are available through the Health Insurance Marketplace, also known as the exchange, which was established under the ACA. Marketplace plans offer a range of options, from bronze to platinum, with varying levels of coverage and cost.
The Marketplace provides an essential platform for individuals and families to compare and select health insurance plans that best suit their needs. Eligibility for premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions is determined based on income, making health insurance more affordable for many.
Medicaid and Medicare
Medicaid and Medicare are government-funded health insurance programs designed to provide coverage for specific populations. Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that offers health coverage to low-income individuals and families. It plays a critical role in covering the health needs of vulnerable populations, including children, pregnant women, the elderly, and individuals with disabilities.
On the other hand, Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, as well as younger individuals with certain disabilities. Medicare is divided into several parts, each covering different aspects of healthcare, such as hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs.
Short-Term Health Insurance
Short-term health insurance plans provide temporary coverage for individuals between jobs or those who are not eligible for other types of insurance. These plans typically offer more limited coverage and have shorter durations, ranging from a few months to a year. While they can be a cost-effective solution for short-term needs, they often come with higher out-of-pocket costs and may not cover pre-existing conditions.
Key Considerations for Choosing Health Insurance
Selecting the right health insurance plan involves careful consideration of several factors. Here are some key aspects to keep in mind when evaluating your options:
Coverage and Benefits
Assess your healthcare needs and choose a plan that covers the services you anticipate requiring. Consider the plan’s network of providers, including doctors, hospitals, and specialists, to ensure access to your preferred healthcare professionals. Additionally, review the plan’s coverage for prescription drugs, mental health services, and other essential benefits.
Cost and Affordability
Premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs are crucial factors in determining the affordability of a health insurance plan. Evaluate your budget and select a plan that fits within your financial means. Remember that higher premiums may result in lower out-of-pocket costs, while lower premiums could mean higher deductibles and copays.
If you're eligible, take advantage of premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions available through the Health Insurance Marketplace. These subsidies can significantly reduce the cost of your insurance premiums, making health insurance more accessible.
Provider Network and Accessibility
Review the plan’s provider network to ensure it includes your preferred doctors and specialists. Consider the plan’s coverage for out-of-network care, as well as any additional costs associated with seeking care outside the network. Additionally, evaluate the plan’s accessibility in terms of convenience and proximity to your home or workplace.
Plan Type and Flexibility
Different health insurance plans offer varying levels of flexibility and control over your healthcare decisions. Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) typically require you to choose a primary care physician and obtain referrals for specialist care, while Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs) offer more flexibility in choosing providers and specialists. Consider your personal preferences and healthcare needs when selecting the right plan type.
The Future of Health Insurance in America
The landscape of health insurance in America is constantly evolving, driven by changing demographics, advancements in healthcare technology, and shifting policy priorities. Here are some key trends and developments shaping the future of health insurance:
Digital Transformation
The digital revolution is transforming the health insurance industry, with insurers increasingly adopting digital technologies to enhance customer experiences and streamline operations. From online enrollment and claims processing to digital health records and telemedicine, the industry is embracing a more efficient and convenient approach to healthcare delivery.
The use of artificial intelligence and data analytics is also gaining traction, enabling insurers to make more informed decisions, identify cost-saving opportunities, and improve overall efficiency. These technological advancements are poised to revolutionize the way health insurance is delivered and accessed.
Focus on Value-Based Care
The shift towards value-based care is a significant trend in the health insurance industry. This approach emphasizes the quality and outcomes of healthcare services, rather than solely focusing on the quantity of services provided. By incentivizing healthcare providers to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care, value-based models aim to improve patient outcomes and reduce overall healthcare costs.
Insurers are increasingly partnering with healthcare providers to develop value-based care models, such as Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs), which coordinate care and share financial risks and rewards. This collaborative approach has the potential to enhance the patient experience and improve population health outcomes.
Expanding Access and Affordability
Efforts to expand access to health insurance and improve affordability remain a top priority. The ongoing debate surrounding the future of the Affordable Care Act continues to shape the industry, with potential changes impacting millions of Americans. Additionally, states are exploring innovative approaches, such as public option plans and reinsurance programs, to make health insurance more accessible and affordable for their residents.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further highlighted the importance of universal access to healthcare. As the country recovers from the pandemic, policymakers and industry leaders are examining ways to ensure equitable access to healthcare services and address the underlying disparities that impact health outcomes.
Conclusion
Health insurance in America is a complex and ever-evolving landscape, shaped by federal and state regulations, market dynamics, and the evolving needs of the population. As an essential component of the healthcare system, health insurance plays a vital role in ensuring Americans can access the medical care they need without facing financial hardship.
By understanding the various coverage options, key considerations, and emerging trends, individuals and families can make informed decisions about their health insurance. As the industry continues to adapt and innovate, the future of health insurance in America holds the promise of improved access, affordability, and quality of care for all.
What is the average cost of health insurance in the US?
+The average cost of health insurance in the US varies significantly based on factors such as age, location, and the type of plan. As of 2021, the average monthly premium for an individual was around 452, while the average for a family was approximately 1,142. However, these averages can be misleading as premiums can range widely, from a few hundred dollars to over $1,000 per month.
Can I switch health insurance plans during the year?
+In general, health insurance plans have specific enrollment periods, and switching plans outside of these periods is not typically allowed. However, there are certain qualifying life events, such as marriage, divorce, birth or adoption of a child, or loss of other coverage, that may allow you to enroll in a new plan outside of the open enrollment period.
How does pre-existing condition coverage work under the Affordable Care Act (ACA)?
+The ACA prohibits health insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions. This means that regardless of your health status, you have the right to purchase health insurance and receive the same coverage as anyone else. This protection ensures that individuals with pre-existing conditions can access affordable healthcare without facing discrimination.



