Health Insurance Deduction For Self Employed

The Complete Guide to Health Insurance Deductions for the Self-Employed

As a self-employed individual, managing your finances and maximizing tax deductions is crucial to ensure a healthy financial future. One significant expense for many self-employed individuals is health insurance, which can be a substantial financial burden. However, the good news is that there are tax benefits available to help offset these costs. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of health insurance deductions for the self-employed, providing you with all the information you need to navigate this complex yet rewarding aspect of financial management.
Understanding Health Insurance Deductions for the Self-Employed
When you are self-employed, you are responsible for providing your own health insurance coverage. The good news is that the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) recognizes this expense as a tax-deductible item, allowing you to reduce your taxable income and, consequently, your tax liability. This deduction applies to a wide range of health insurance plans, including individual policies, family plans, and even certain types of long-term care insurance.
By taking advantage of this deduction, you can significantly lower your tax burden and ensure that you are not paying more in taxes than necessary. It is an essential financial strategy for any self-employed individual, as it can provide a much-needed boost to your overall financial health.
Qualifying for the Health Insurance Deduction
To qualify for the health insurance deduction as a self-employed individual, you must meet a few key criteria. First and foremost, you must have a valid health insurance policy in place for yourself, your spouse, or your dependents. This policy can be obtained through various sources, such as the Health Insurance Marketplace, private insurance companies, or even through certain professional organizations.
Additionally, you must meet the requirements for being self-employed. This generally means that you are operating your own business or working as an independent contractor, and your income is primarily derived from these self-employment activities. It is important to note that certain income sources, such as rental income or investment gains, may not qualify for this deduction.
| Health Insurance Coverage | Qualifying Criteria |
|---|---|
| Individual Policy | Covers the self-employed individual |
| Family Plan | Covers the self-employed individual and their dependents |
| Long-Term Care Insurance | Provides coverage for extended care needs |

When selecting your health insurance plan, it is crucial to choose one that best suits your needs and ensures comprehensive coverage. This includes considering factors such as deductibles, co-pays, and the specific medical services covered by the plan. It is always advisable to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure that your chosen plan aligns with your financial goals and qualifies for the health insurance deduction.
Calculating Your Health Insurance Deduction
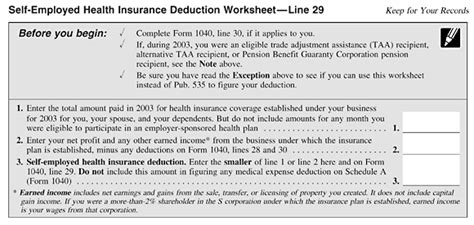
Calculating your health insurance deduction involves a straightforward process, but it is essential to understand the nuances to ensure accuracy. The deduction is calculated based on the amount you spend on health insurance premiums during the tax year. This includes premiums for yourself, your spouse, and any qualifying dependents.
Determining Your Premium Amounts
To calculate your health insurance deduction, you must first determine the total amount of premiums you paid during the tax year. This includes both monthly and annual premiums for your health insurance plan. It is crucial to include all premiums paid, regardless of whether they were paid directly to the insurance provider or through a third-party administrator.
Additionally, if you have a Health Savings Account (HSA) or a Flexible Spending Account (FSA) linked to your health insurance plan, you should include any contributions made to these accounts as part of your premium expenses. These contributions are tax-deductible and can further reduce your taxable income.
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) and the Deduction Limit
The health insurance deduction is subject to certain limitations based on your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI). Your AGI is calculated by taking your total income and subtracting certain deductions and adjustments. The specific deduction limit for health insurance premiums is determined annually by the IRS and may vary depending on your filing status and income level.
It is important to note that the health insurance deduction is considered an "above-the-line" deduction, which means it is taken before calculating your taxable income. This makes it a valuable tool for reducing your overall tax liability, as it effectively lowers your taxable income and can result in a lower tax rate.
| Tax Year | Deduction Limit for Self-Employed Individuals |
|---|---|
| 2022 | $10,500 for individuals; $21,000 for families |
| 2023 | To be determined by the IRS |
When calculating your health insurance deduction, it is crucial to stay updated with the latest IRS guidelines and deduction limits. Consulting with a tax professional can help ensure that you are taking full advantage of this deduction while staying compliant with tax regulations.
Filing Your Taxes and Claiming the Deduction
When it comes to filing your taxes and claiming the health insurance deduction, it is essential to follow the proper procedures to ensure accuracy and compliance. The process involves completing the appropriate tax forms and providing supporting documentation to substantiate your claims.
Preparing Your Tax Documents
To claim the health insurance deduction, you will need to gather all relevant tax documents related to your health insurance premiums. This includes insurance statements, premium payment receipts, and any other documentation that verifies your payments. It is crucial to keep these documents organized and easily accessible, as they may be required during the tax filing process or if your return is selected for an audit.
Additionally, if you have an HSA or FSA, you will need to provide documentation of your contributions to these accounts. This includes contribution statements and any receipts for eligible expenses incurred during the tax year.
Completing the Tax Forms
The health insurance deduction is claimed on Schedule C (Form 1040) for self-employed individuals. Schedule C is used to report income and expenses related to your business activities. Within Schedule C, you will find a section dedicated to health insurance deductions, where you can enter the total amount of premiums paid during the tax year.
It is important to carefully review and complete all sections of Schedule C, ensuring that you accurately report your business income and expenses. This includes not only your health insurance premiums but also other deductible expenses such as business travel, supplies, and equipment.
Submitting Your Tax Return
Once you have completed Schedule C and all other necessary tax forms, you can submit your tax return to the IRS. This can be done electronically or by mail, depending on your preference and the requirements of your tax preparer or software.
It is crucial to double-check your tax return for accuracy before submission. This includes reviewing all calculations, ensuring that you have included all relevant forms and schedules, and verifying that your personal information is correct. By taking the time to thoroughly review your return, you can minimize the risk of errors and potential issues with the IRS.
Maximizing Your Health Insurance Deduction
While the health insurance deduction provides a valuable opportunity to reduce your tax liability, there are additional strategies you can employ to maximize its benefits. By implementing these strategies, you can further optimize your financial position and ensure that you are taking full advantage of this tax deduction.
Consider High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
One effective strategy to maximize your health insurance deduction is to enroll in a High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP). HDHPs are designed to have higher deductibles and lower premiums compared to traditional health insurance plans. This means that while you may incur higher out-of-pocket costs for medical expenses, you can benefit from a lower premium and a higher tax-deductible amount.
By opting for an HDHP, you can potentially increase your health insurance deduction, as the premium amount is generally higher for these plans. Additionally, HDHPs are eligible for Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), which offer further tax advantages. HSAs allow you to contribute pre-tax dollars to a dedicated savings account specifically for medical expenses, providing an additional layer of tax savings.
Utilize Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs)
Another valuable tool to maximize your health insurance deduction is a Flexible Spending Account (FSA). FSAs are employer-sponsored plans that allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars for eligible medical expenses. While self-employed individuals do not have access to employer-sponsored FSAs, there are FSA options specifically designed for the self-employed.
By contributing to an FSA, you can reduce your taxable income and lower your tax liability. FSAs cover a wide range of medical expenses, including copayments, prescription drugs, and even certain over-the-counter medications. It is important to note that FSAs operate on a "use-it-or-lose-it" basis, meaning any funds remaining in the account at the end of the plan year may be forfeited. Therefore, it is crucial to plan your contributions carefully to maximize the benefits of this tax-advantaged account.
Explore Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
If you have enrolled in a High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP), you may be eligible to open a Health Savings Account (HSA). HSAs are tax-advantaged accounts that allow you to save for current and future medical expenses. Contributions to HSAs are made with pre-tax dollars, which means you can reduce your taxable income and potentially lower your tax liability.
HSAs offer triple tax advantages: contributions are tax-deductible, earnings on the account grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. This makes HSAs an attractive option for self-employed individuals looking to maximize their health insurance deductions and save for future healthcare needs. It is important to note that there are annual contribution limits for HSAs, which are determined by the IRS and may vary based on your age and family status.
Take Advantage of Tax Credits and Subsidies
In addition to deductions, there are tax credits and subsidies available to help offset the cost of health insurance for certain self-employed individuals. These credits and subsidies are designed to make health insurance more affordable and accessible. It is important to explore these options and determine your eligibility to maximize your financial benefits.
For example, if you purchase your health insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace, you may be eligible for a premium tax credit. This credit is designed to lower the cost of your monthly premiums and is based on your income and family size. Additionally, there are cost-sharing reduction subsidies available for individuals with lower incomes, which can further reduce out-of-pocket costs for medical services.
Future Implications and Tax Strategies
As a self-employed individual, it is essential to stay informed about potential changes in tax laws and regulations that may impact your health insurance deductions. By staying updated and adapting your tax strategies, you can ensure that you continue to maximize your deductions and optimize your financial position.
Monitoring Tax Law Changes
Tax laws and regulations are subject to change, and it is crucial to stay abreast of any modifications that may affect your health insurance deductions. This includes monitoring updates from the IRS, consulting with tax professionals, and staying informed about relevant legislative developments. By being proactive and keeping up with the latest tax news, you can ensure that you are compliant with the latest regulations and take advantage of any new opportunities that may arise.
Long-Term Tax Planning
Beyond the immediate tax year, it is beneficial to engage in long-term tax planning to maximize your health insurance deductions and overall financial well-being. This involves developing a comprehensive financial strategy that takes into account your short-term and long-term goals. By working with a financial advisor or tax professional, you can create a personalized plan that considers your unique circumstances and maximizes your tax advantages.
Long-term tax planning may involve strategies such as optimizing your business structure, exploring retirement account options, and implementing effective wealth management strategies. By taking a proactive approach to your financial planning, you can ensure that you are making the most of your health insurance deductions and building a secure financial future.
Exploring Alternative Health Insurance Options
As the healthcare landscape evolves, it is important to explore alternative health insurance options that may offer greater flexibility and cost savings. This includes investigating innovative insurance models, such as direct primary care (DPC) plans or telemedicine services. These options may provide more affordable coverage and allow you to customize your healthcare benefits to meet your specific needs.
Additionally, keeping an eye on emerging trends and advancements in the healthcare industry can help you stay ahead of the curve. By staying informed about new technologies, treatment options, and insurance products, you can make informed decisions about your health insurance coverage and potentially reduce your overall healthcare costs.
FAQs
Can I deduct the entire amount of my health insurance premiums as a self-employed individual?
+Yes, as a self-employed individual, you can deduct the full amount of your health insurance premiums, including premiums for yourself, your spouse, and any qualifying dependents. This deduction is an important benefit to help offset the cost of health insurance coverage.
Are there any income limitations for claiming the health insurance deduction as a self-employed individual?
+The health insurance deduction for self-employed individuals is not subject to income limitations. However, there may be other tax implications based on your income level, such as phase-outs or adjustments to certain deductions and credits. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional to understand the full impact on your specific situation.
Can I deduct health insurance premiums for my entire family, including children who are not my dependents?
+When claiming the health insurance deduction, you can deduct premiums for yourself, your spouse, and any qualifying dependents. Qualifying dependents typically include your children who meet certain age and relationship criteria. However, it is important to consult with a tax professional to determine the specific qualifications and requirements for claiming dependents.
Are there any additional tax benefits or subsidies available for self-employed individuals with health insurance coverage?
+Yes, self-employed individuals may be eligible for additional tax benefits and subsidies to help offset the cost of health insurance. This includes the Premium Tax Credit, which can lower the cost of monthly premiums for those who purchase insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace. Additionally, there are cost-sharing reduction subsidies available for individuals with lower incomes, which can further reduce out-of-pocket costs for medical services. It is important to explore these options and determine your eligibility to maximize your financial benefits.