Gov Health Insurance
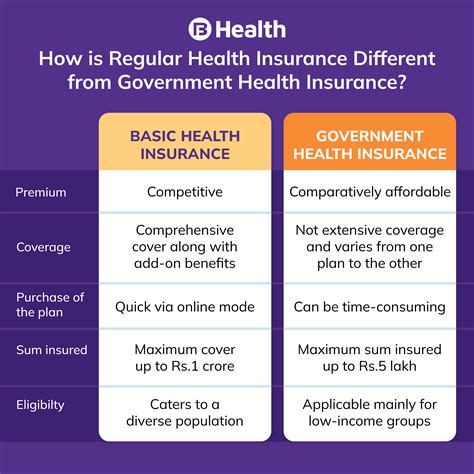
Health insurance is a crucial aspect of modern healthcare systems, ensuring individuals have access to essential medical services and financial protection in times of illness or injury. In many countries, governments play a significant role in providing and regulating health insurance, aiming to make healthcare more accessible and affordable for their citizens. This article delves into the world of government-sponsored health insurance, exploring its significance, various models, and the impact it has on healthcare systems and individuals.
The Importance of Government Health Insurance
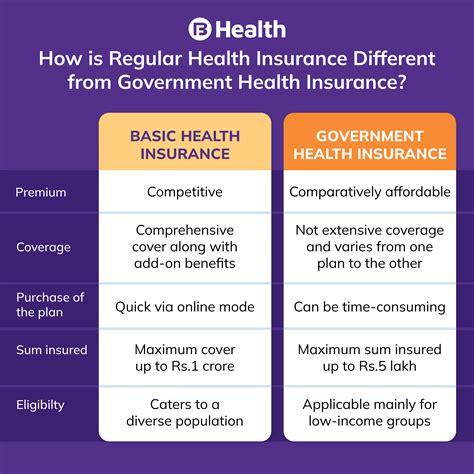
Government health insurance programs are designed to address the fundamental need for equitable and universal healthcare coverage. They aim to provide a safety net for individuals and families, ensuring they can access necessary medical care without facing financial hardship. Here are some key reasons why government-led health insurance initiatives are vital:
- Financial Protection: Government health insurance shields individuals from the potentially devastating financial consequences of unexpected medical expenses. It helps ensure that necessary treatments, surgeries, and medications are accessible without plunging people into debt.
- Equitable Access: These programs strive to make healthcare services available to all, regardless of income, social status, or pre-existing health conditions. This promotes equality and ensures that no one is denied care due to their financial circumstances.
- Public Health: By encouraging regular check-ups, screenings, and preventive measures, government health insurance contributes to improved public health outcomes. Early detection and management of health issues can lead to better long-term health for individuals and reduce the burden on the healthcare system.
- Economic Stability: Well-designed health insurance schemes can provide economic stability for both individuals and the healthcare industry. They reduce the financial strain on hospitals and healthcare providers, allowing them to focus on delivering quality care.
Models of Government Health Insurance

The landscape of government health insurance is diverse, with countries adopting various approaches based on their unique socio-economic conditions and healthcare traditions. Here are some of the primary models:
Single-Payer Systems
In a single-payer system, the government acts as the sole financier of healthcare services, covering the cost of medical care for all citizens. This model is often associated with universal healthcare coverage and is known for its simplicity and efficiency. Notable examples include the National Health Service (NHS) in the United Kingdom and the Canada Health Act.
Key characteristics of single-payer systems include:
- Universal Coverage: All citizens are entitled to the same level of healthcare, regardless of their ability to pay.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By streamlining payment processes and negotiating with healthcare providers, single-payer systems can control costs effectively.
- Reduced Administrative Burden: With a single payer, administrative overhead is minimized, allowing more resources to be directed towards patient care.
Public Insurance Programs
Public insurance programs are typically offered alongside private insurance options, often targeting specific population segments such as low-income individuals, seniors, or those with disabilities. These programs are funded by the government but may have varying levels of cost-sharing and eligibility criteria.
Examples of public insurance programs include:
- Medicare (USA): A federal program providing health insurance for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as those with certain disabilities.
- Medicaid (USA): A joint federal and state program offering health coverage to low-income individuals and families.
- National Health Insurance (Taiwan): A system that covers all citizens and foreign nationals residing in Taiwan, with premiums based on income.
Social Health Insurance
Social health insurance (SHI) is a common model in many European countries. It is a compulsory insurance scheme funded by contributions from employees, employers, and the government. SHI aims to provide comprehensive coverage for a range of healthcare services, with premiums adjusted based on income.
Key features of social health insurance include:
- Compulsory Participation: All individuals are required to participate in the scheme, ensuring a large pool of contributors.
- Solidarity Principle: The system operates on the principle of solidarity, where healthier individuals contribute to support those with higher healthcare needs.
- Comprehensive Benefits: SHI often covers a wide range of services, including hospitalization, physician visits, prescription drugs, and preventive care.
Impact and Performance Analysis
The effectiveness of government health insurance programs can be evaluated based on several key metrics:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Coverage Rate | The percentage of the population covered by the insurance program. |
| Access to Care | Measures the ease with which individuals can access necessary healthcare services. |
| Out-of-Pocket Expenses | The amount individuals pay directly for healthcare services, indicating the financial burden on patients. |
| Healthcare Quality | Assesses the overall quality of healthcare provided, including patient satisfaction and clinical outcomes. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Evaluates the efficiency of the program in delivering healthcare services within available resources. |

The performance of government health insurance programs can vary significantly based on the model adopted and the specific implementation. While single-payer systems often excel in cost-effectiveness and equitable access, they may face challenges in managing long waiting times for certain procedures. Public insurance programs, on the other hand, can be more flexible in catering to specific population needs but may have higher administrative costs.
Future Implications and Innovations
As healthcare landscapes continue to evolve, government health insurance programs must adapt to address emerging challenges and opportunities. Here are some key areas of focus for the future:
Addressing Healthcare Disparities
Despite the efforts of government health insurance programs, disparities in healthcare access and outcomes persist. Future initiatives should aim to reduce these disparities by improving access to care in underserved areas, enhancing cultural competency in healthcare delivery, and addressing social determinants of health.
Digital Health and Technology
The integration of digital health technologies offers significant potential for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of government health insurance programs. Electronic health records, telemedicine, and mobile health apps can enhance patient engagement, improve data management, and reduce administrative burdens.
Value-Based Care
Shifting from a volume-based to a value-based care model can help improve the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery. Government health insurance programs can incentivize healthcare providers to focus on outcomes and patient satisfaction rather than the sheer number of services delivered.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The use of advanced analytics and data science can help government health insurance programs make more informed decisions. By leveraging data on population health, utilization patterns, and cost drivers, these programs can identify areas for improvement and target interventions more effectively.
Global Collaboration
Learning from international best practices and sharing knowledge across borders can help governments enhance their health insurance programs. Collaborative efforts can lead to the development of innovative solutions and the exchange of successful strategies.
Conclusion
Government health insurance programs play a pivotal role in shaping the healthcare landscape, ensuring that individuals have access to necessary medical care and financial protection. The diverse models and approaches taken by different countries demonstrate the complexity and importance of this field. As healthcare continues to evolve, governments and healthcare stakeholders must remain committed to innovation, collaboration, and equitable access to create a brighter and healthier future for all.
What is the difference between public and private health insurance?
+
Public health insurance is typically government-funded and often aims to provide universal coverage, while private health insurance is purchased by individuals or provided by employers, offering more flexibility in terms of coverage and cost.
Are government health insurance programs sustainable in the long term?
+
The sustainability of government health insurance programs depends on various factors, including efficient administration, adequate funding, and the ability to adapt to changing healthcare needs and technologies.
How can government health insurance improve access to care for underserved populations?
+
To improve access for underserved populations, government health insurance programs can focus on initiatives such as expanding provider networks in underserved areas, offering financial incentives for providers to serve these communities, and implementing targeted outreach and enrollment campaigns.