Do You Get Penalized For Not Having Health Insurance

In many countries, health insurance is a crucial aspect of personal and societal well-being, providing access to essential medical care and protecting individuals from the financial burden of unexpected health issues. However, there are places where health insurance is not a legal requirement, and individuals may choose to go without it. This raises an important question: are there consequences or penalties for opting out of health insurance coverage? In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the implications and potential repercussions of not having health insurance, shedding light on the legal, financial, and practical aspects involved.
Legal Implications and Penalties

The legal landscape surrounding health insurance varies significantly across different jurisdictions. While some countries mandate universal health coverage, others leave the decision of obtaining insurance to individual discretion.
Mandatory Health Insurance Countries
In countries with a universal healthcare system, such as the United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS) or Canada’s provincial healthcare plans, access to essential medical services is typically provided to all residents, regardless of insurance status. However, it’s important to note that these systems may have variations in coverage and eligibility criteria.
For instance, in the UK, the NHS offers free at the point of use healthcare, but certain services like dental care and prescriptions may have associated costs. Similarly, in Canada, while healthcare is generally covered, some provinces may require additional insurance for specific services.
While these countries may not impose direct penalties for not having health insurance, there can be indirect consequences. For example, in the UK, if you are not a resident or do not meet specific criteria, you may be charged for certain NHS services. In Canada, non-residents and visitors may also face out-of-pocket expenses for healthcare services.
Countries with No Mandatory Health Insurance
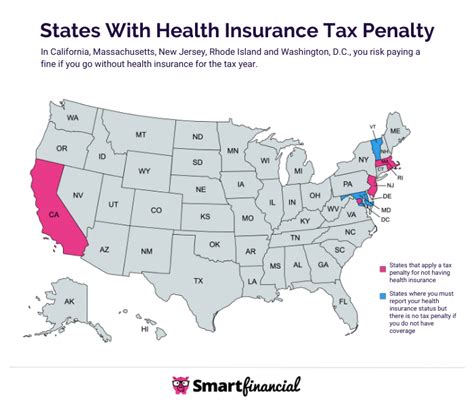
In countries where health insurance is not mandatory, such as the United States, individuals have the freedom to choose whether to obtain coverage. However, this choice comes with certain legal and financial considerations.
In the past, the Affordable Care Act (ACA), also known as Obamacare, imposed a penalty for not having health insurance, commonly referred to as the "individual mandate". This penalty was in effect from 2014 to 2018 and required individuals without qualifying health coverage to pay a fee when filing their federal taxes. However, as of 2019, the individual mandate penalty was eliminated, making it no longer a legal requirement to have health insurance in the US.
Despite the removal of the penalty, it's important to note that not having health insurance can still result in significant financial implications. Without insurance, individuals are responsible for paying the full cost of any medical services they receive. This can lead to substantial out-of-pocket expenses, especially in the case of emergencies or complex medical treatments.
Financial Implications
The financial impact of not having health insurance can be substantial and often unpredictable. Medical costs can vary widely depending on the nature of the treatment, the healthcare provider, and the individual’s location.
Emergency Medical Care
One of the most significant financial risks of going without health insurance is the potential need for emergency medical care. Whether it’s a sudden illness, an accident, or a medical condition that requires immediate attention, emergency treatments can result in astronomical bills.
| Emergency Treatment | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Appendicitis Surgery | $15,000 - $30,000 |
| Heart Attack Treatment | $20,000 - $100,000 |
| Broken Bone Repair | $3,000 - $15,000 |
| Stroke Treatment | $30,000 - $150,000 |
These costs can quickly become overwhelming, leading to financial strain and potentially long-term debt.
Routine and Preventive Care
Beyond emergencies, routine and preventive healthcare services can also be costly without insurance. Regular check-ups, screenings, and treatments for chronic conditions can accumulate significant expenses over time.
| Routine Care | Average Cost |
|---|---|
| Annual Physical Exam | $200 - $500 |
| Dental Cleaning | $75 - $200 |
| Eye Exam | $50 - $200 |
| Prescription Medications | Varies, but often $100+ per month |
Neglecting these routine services can lead to undetected health issues, potentially resulting in more severe and costly problems down the line.
Specialized Treatments
Certain specialized treatments, such as cancer care, organ transplants, or advanced surgeries, can incur enormous expenses. Without insurance coverage, these treatments may be financially out of reach for many individuals.
| Specialized Treatment | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Cancer Treatment (Chemotherapy) | $30,000 - $150,000 per cycle |
| Organ Transplant | $250,000 - $1,000,000 |
| Major Surgery (e.g., Open-Heart) | $50,000 - $200,000 |
These costs often include not only the procedure itself but also associated hospital stays, medications, and follow-up care.
Access to Healthcare
Beyond the financial implications, not having health insurance can also impact an individual’s access to healthcare services.
Healthcare Provider Networks
Many healthcare providers, especially specialists and high-quality facilities, may require patients to have insurance coverage. Without insurance, individuals may find it challenging to secure appointments with preferred doctors or access certain medical centers.
Limited Treatment Options
In some cases, uninsured individuals may face restricted treatment options. Certain advanced or experimental treatments may only be available to those with specific insurance plans or coverage. This can limit access to potentially life-saving or life-improving medical interventions.
Out-of-Pocket Negotiations
Without insurance, individuals may need to negotiate directly with healthcare providers regarding the cost of services. This can be a complex and stressful process, as providers often have set rates and may not offer significant discounts.
Medical Tourism
For those seeking more affordable options, medical tourism has become a viable alternative. Many individuals travel to countries with lower healthcare costs, such as Thailand, India, or Mexico, to receive medical treatments. However, this approach comes with its own set of risks and considerations, including language barriers, cultural differences, and potential quality of care concerns.
Health Insurance Alternatives
For individuals who choose not to have traditional health insurance, there are alternative options to consider:
Short-Term Health Insurance
Short-term health insurance plans offer temporary coverage for a specified period, typically ranging from one month to a year. These plans can be a cost-effective solution for those between jobs, traveling, or in transition. However, they often have limited coverage and may not cover pre-existing conditions.
Catastrophic Health Insurance
Catastrophic health insurance plans are designed to provide coverage for major medical events, such as accidents or serious illnesses. These plans typically have high deductibles and offer limited benefits for routine care. They can be a viable option for young and healthy individuals who want protection against unexpected emergencies.
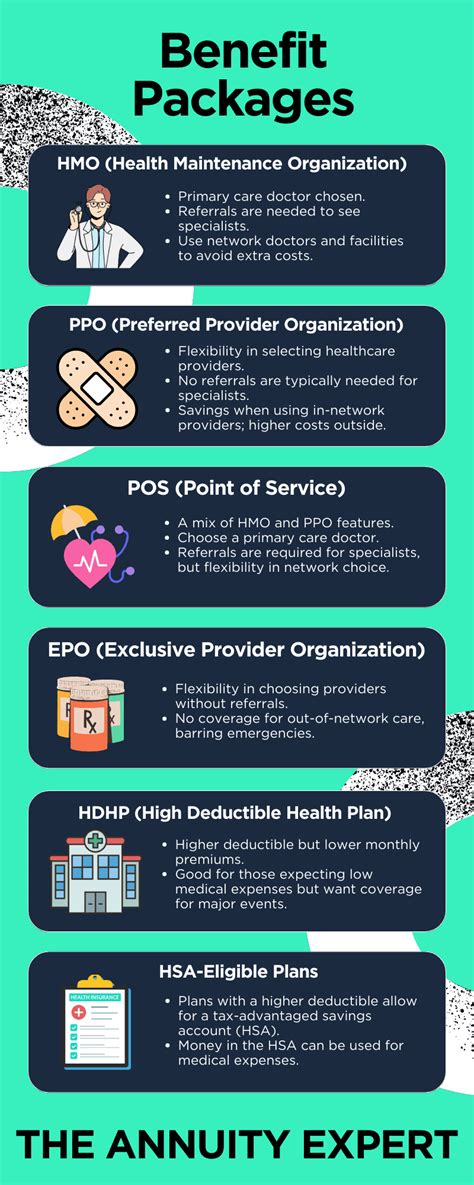
High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
HDHPs are traditional health insurance plans with high deductibles, meaning individuals must pay a significant portion of their medical expenses out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. These plans are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), allowing individuals to save money tax-free for medical expenses.
Healthcare Sharing Ministries
Healthcare sharing ministries are faith-based organizations where members contribute to a shared pool of funds to assist each other with medical expenses. These ministries operate outside of traditional insurance models and may have eligibility requirements and restrictions.
Conclusion
The decision to go without health insurance is a complex and personal one, with legal, financial, and practical considerations. While certain countries may not impose direct penalties, the financial and access-related implications can be significant. Understanding the potential risks and exploring alternative coverage options can help individuals make informed choices about their healthcare and financial well-being.
What are the potential legal consequences of not having health insurance in the US?
+While the individual mandate penalty has been eliminated, there are no direct legal consequences for not having health insurance in the US. However, uninsured individuals may face financial penalties through higher out-of-pocket medical expenses.
Can I still access emergency healthcare services without insurance?
+Yes, emergency healthcare services are typically provided to all individuals, regardless of insurance status. However, the cost of these services can be extremely high without insurance coverage.
Are there any affordable alternatives to traditional health insurance?
+Yes, alternatives like short-term health insurance, catastrophic plans, and high-deductible plans can provide coverage at a lower cost. Additionally, healthcare sharing ministries offer a faith-based approach to sharing medical expenses.
What happens if I can’t afford to pay my medical bills without insurance?
+Unpaid medical bills can have serious consequences, including damage to your credit score and potential collection actions. It’s essential to explore financial assistance programs, negotiate payment plans with providers, or seek legal advice if needed.



