Deductible Meaning In Insurance
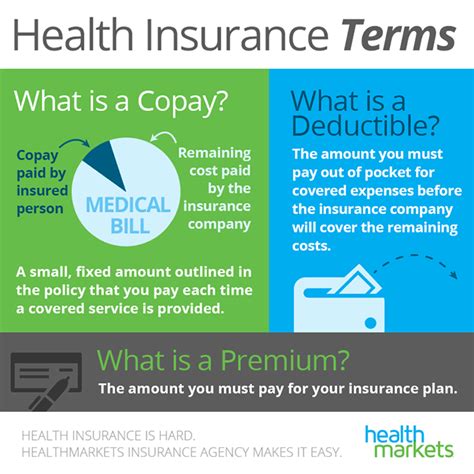
The concept of deductibles is an integral part of the insurance industry, playing a significant role in how insurance policies are structured and how policyholders interact with their coverage. A deductible, in the context of insurance, is a predetermined amount that the policyholder agrees to pay out of pocket before the insurance company steps in to cover the remaining costs of a claim.
Understanding deductibles is crucial for anyone looking to purchase insurance, as it can significantly impact the cost and coverage of a policy. This article will delve into the intricacies of deductibles, exploring their various types, how they work, and their impact on insurance policies. We'll also provide real-world examples and insights to help you make informed decisions when choosing an insurance plan.
Types of Deductibles

Deductibles come in several forms, each designed to suit different insurance needs and preferences. Here’s an overview of the most common types of deductibles:
Fixed Deductibles
Fixed deductibles, also known as flat deductibles, are the most straightforward type. They are a predetermined, fixed amount that remains constant for all claims within a specific policy period. For instance, if your auto insurance policy has a 500 fixed deductible, you'll need to pay 500 out of pocket for each accident or claim during that policy year. Fixed deductibles are typically used in auto and property insurance policies.
Percentage Deductibles
Percentage deductibles are calculated as a percentage of the insured amount or the total value of the property. These deductibles are often used in homeowners’ insurance and business insurance policies. For example, if your homeowners’ insurance policy has a 2% deductible and your home is insured for 500,000, your deductible would be 10,000. Percentage deductibles can significantly impact the out-of-pocket costs for policyholders, especially for high-value properties.
Per-Occurrence Deductibles
Per-occurrence deductibles, as the name suggests, apply to each individual occurrence or event that triggers a claim. This means that if you have multiple claims in a policy period, you’ll have to pay the deductible for each claim separately. This type of deductible is commonly used in liability insurance, such as general liability insurance for businesses.
Aggregate Deductibles
Aggregate deductibles, also referred to as annual deductibles, are the total amount a policyholder must pay in a given policy period before the insurance company starts covering costs. Once the aggregate deductible is met, the insurer pays the full amount for all subsequent claims within that policy period. Aggregate deductibles are often seen in health insurance plans and can be a significant financial consideration for policyholders.
Deductible Waivers
In some cases, insurance companies may offer deductible waivers as an add-on feature to certain policies. These waivers allow policyholders to opt out of paying their deductible for a specific claim or a set number of claims. Deductible waivers are often available for an additional premium and are typically used in auto insurance policies.
How Deductibles Work
Deductibles are a key component of the insurance claim process. When a policyholder experiences a covered loss or an event that triggers a claim, they must first pay the deductible amount before the insurance company starts covering the remaining costs. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how deductibles work in the claim process:
- Loss or Damage Occurs: An insured event, such as an accident, theft, or natural disaster, takes place.
- Report the Claim: The policyholder contacts their insurance company to report the loss and initiate the claim process.
- Determine the Amount of Loss: The insurance company assesses the extent of the damage and calculates the total cost of the claim.
- Pay the Deductible: The policyholder pays the agreed-upon deductible amount to the insurance company.
- Insurance Company Pays the Rest: Once the deductible is paid, the insurance company steps in to cover the remaining costs of the claim, up to the policy limits.
Impact on Premiums
Deductibles have a direct correlation with insurance premiums. In general, choosing a higher deductible can lead to lower premiums, while opting for a lower deductible may result in higher premiums. This is because a higher deductible means the policyholder is taking on more financial responsibility, which can reduce the risk and potential costs for the insurance company. Conversely, a lower deductible shifts more of the financial burden to the insurer, leading to higher premiums.
| Deductible Amount | Premium Impact |
|---|---|
| High Deductible | Lower Premiums |
| Low Deductible | Higher Premiums |
Real-World Examples
Let’s look at some practical scenarios to better understand how deductibles work in different insurance contexts.
Auto Insurance
Suppose you have an auto insurance policy with a 500 deductible</strong>. You're involved in a minor accident where the repairs are estimated at 3,000. In this case, you would pay the 500 deductible, and your insurance company would cover the remaining 2,500.
Health Insurance
In a health insurance plan, deductibles often work on an annual basis. For instance, if your plan has a $2,000 annual deductible, you’ll need to pay for medical expenses up to that amount before your insurance coverage kicks in. Once you’ve met the deductible, your insurance company will cover the agreed-upon percentage of the costs for the rest of the year.
Homeowners’ Insurance
Consider a homeowners’ insurance policy with a 2% deductible and a home insured for 400,000. In this scenario, your deductible would be 8,000. If a storm causes 20,000 worth of damage to your home, you would pay the first 8,000, and your insurance company would cover the remaining $12,000.
Choosing the Right Deductible
Selecting the appropriate deductible for your insurance policy is a crucial decision that can impact your financial well-being. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a deductible:
- Financial Ability: Assess your financial situation and determine how much you can afford to pay out of pocket in the event of a claim. A higher deductible can save you money on premiums, but it also means you'll need to have the funds available to cover the deductible.
- Claim Frequency: Consider how often you anticipate making claims. If you have a history of frequent claims, a lower deductible may be more suitable to minimize your out-of-pocket costs.
- Risk Tolerance: Think about your risk tolerance. Are you comfortable taking on more financial responsibility to save on premiums? Or do you prefer to have lower out-of-pocket costs in the event of a claim?
- Policy Coverage: Review your insurance policy's coverage limits and exclusions. Ensure that your deductible aligns with the coverage you need and that you're not left with unexpected expenses.
The Impact of Deductibles on Claims

Deductibles can significantly influence the claim settlement process and the overall experience for policyholders. Here’s how:
Discouraging Small Claims
Higher deductibles can deter policyholders from making small claims that may not significantly impact their financial situation. This is particularly relevant in auto insurance, where minor accidents might not warrant a claim if the deductible is substantial.
Encouraging Preventive Measures
Policyholders with higher deductibles may be more inclined to take proactive measures to prevent losses. For instance, homeowners with high deductibles may invest in home maintenance and security to reduce the likelihood of claims.
Impact on Claim Settlement Time
The presence of a deductible can also affect the time it takes to settle a claim. Policyholders must first pay the deductible, which can delay the claim settlement process, especially if the deductible amount is substantial.
FAQs
How do deductibles affect my insurance premium?
+Choosing a higher deductible typically leads to lower insurance premiums, as it shifts more financial responsibility to the policyholder. Conversely, a lower deductible often results in higher premiums.
Can I change my deductible after purchasing an insurance policy?
+In most cases, you can adjust your deductible when you renew your insurance policy. However, it’s essential to check with your insurance provider, as some policies may allow for mid-term changes.
Are there any disadvantages to having a high deductible?
+A high deductible can save you money on premiums, but it means you’ll have to pay more out of pocket if you need to make a claim. This can be a significant financial burden if you’re not prepared.
Do all insurance policies have deductibles?
+Not all insurance policies have deductibles. Some policies, like certain life insurance plans, do not include deductibles. However, deductibles are common in auto, homeowners’, and health insurance policies.



