Cost Of Individual Health Insurance
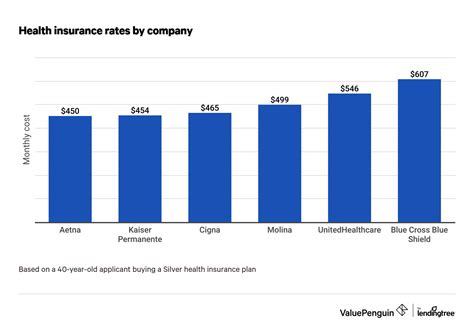
Health insurance is a vital aspect of personal financial planning and healthcare access. As the cost of healthcare continues to rise, understanding the expenses associated with individual health insurance plans becomes increasingly crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the factors influencing the cost of individual health insurance, offering insights to help individuals make informed decisions about their coverage.
Understanding the Cost Structure

The cost of individual health insurance plans is determined by a multitude of factors, each playing a unique role in shaping the overall price. These factors include:
- Age: Typically, younger individuals pay lower premiums, as they are generally healthier and less likely to require extensive medical care. However, as we age, the risk of health issues increases, leading to higher insurance costs.
- Health Status: Pre-existing medical conditions or chronic illnesses can significantly impact insurance premiums. Insurers may charge higher rates for individuals with known health issues, reflecting the potential for increased healthcare utilization.
- Smoking Status: Smoking is a major risk factor for various health conditions. Insurance companies often charge smokers higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of developing smoking-related illnesses.
- Location: The cost of living and healthcare expenses vary significantly across different regions. Consequently, insurance premiums can be higher in areas with higher healthcare costs or a greater demand for medical services.
- Plan Type and Coverage: The type of health insurance plan and the level of coverage chosen also influence costs. Plans with more comprehensive benefits and lower deductibles tend to be more expensive.
- Deductibles and Out-of-Pocket Limits: Higher deductibles and out-of-pocket limits can reduce monthly premiums, but individuals may pay more when accessing healthcare services.
- Family Size: The cost of insurance increases with the number of family members covered under the plan. Family plans cater to the diverse healthcare needs of each member, leading to higher overall expenses.
- Provider Networks: Choosing a plan with a narrow provider network may result in lower premiums, but it could limit access to specific healthcare providers or facilities.
Impact of Policy and Regulation
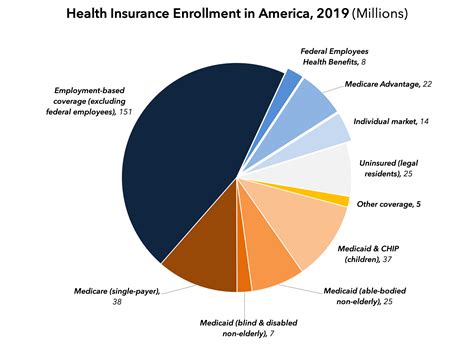
The cost of individual health insurance is also influenced by various policy and regulatory factors, including:
- Government Programs and Subsidies: Government initiatives like the Affordable Care Act (ACA) can provide subsidies to reduce the cost of insurance for eligible individuals, making healthcare more affordable.
- State-Level Mandates: Some states impose additional requirements on insurance companies, such as covering specific services or pre-existing conditions, which can impact insurance costs.
- Market Competition: In regions with a competitive insurance market, consumers may benefit from lower premiums as insurers strive to offer more affordable plans.
- Community Rating: This policy ensures that insurance companies cannot charge higher premiums based solely on an individual's health status. Instead, premiums are based on the overall health of the community, promoting fairness.
Strategies for Managing Costs
Understanding the factors that affect insurance costs empowers individuals to make strategic choices to manage their healthcare expenses effectively. Here are some strategies to consider:
Evaluate Plan Options
Compare different plan types, such as Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs). Each offers varying levels of coverage and cost structures. Assess your healthcare needs and choose a plan that provides the right balance of benefits and affordability.
Assess Your Health Status
If you have pre-existing conditions or anticipate high healthcare utilization, consider plans with more comprehensive coverage and lower out-of-pocket costs. However, if you are generally healthy, a plan with higher deductibles and lower premiums may be a cost-effective option.
Consider High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
HDHPs often come with lower premiums, making them an attractive option for those who prioritize lower monthly expenses. These plans are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), allowing individuals to save pre-tax dollars for future healthcare expenses.
Utilize Preventive Care
Many insurance plans offer free or low-cost preventive services, such as annual check-ups, immunizations, and screenings. Taking advantage of these services can help identify potential health issues early on, potentially reducing the need for more expensive treatments down the line.
Shop Around and Negotiate
Don’t settle for the first insurance quote you receive. Shop around and compare prices from different insurers. Additionally, consider negotiating with your current insurer to explore potential discounts or rate adjustments.
The Role of Technology and Digital Health
Advancements in technology and the rise of digital health solutions are transforming the insurance landscape. These innovations offer new opportunities for cost reduction and improved healthcare access.
Telehealth Services
Telehealth platforms enable individuals to access medical consultations and advice remotely. This not only improves convenience but also reduces the need for in-person visits, cutting down on transportation and facility costs.
Digital Health Monitoring
Wearable devices and digital health apps can track vital health metrics, empowering individuals to manage their health more effectively. By promoting preventive care and early intervention, these technologies can reduce the need for costly treatments and hospitalizations.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Healthcare
AI-powered tools are revolutionizing healthcare delivery, from improving diagnostic accuracy to optimizing treatment plans. By enhancing efficiency and reducing errors, AI has the potential to lower healthcare costs over time.
The Future of Individual Health Insurance

The healthcare industry is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements, policy changes, and shifting consumer expectations. As we look to the future, several key trends and developments are poised to shape the cost and accessibility of individual health insurance.
Personalized Medicine and Precision Health
Advances in genomics and personalized medicine are enabling healthcare providers to tailor treatments to individual genetic profiles. This precision approach has the potential to improve treatment outcomes and reduce the need for costly trial-and-error methods, ultimately lowering healthcare costs.
Value-Based Care Models
Value-based care models focus on delivering high-quality healthcare outcomes while controlling costs. These models incentivize healthcare providers to deliver efficient, effective care, as they are reimbursed based on patient outcomes rather than the volume of services provided. This shift towards value-based care has the potential to drive down healthcare costs and improve patient experiences.
Expanded Telehealth Adoption
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth services, and this trend is expected to continue. Telehealth offers convenient and cost-effective access to healthcare, particularly for individuals in rural or underserved areas. By reducing the need for in-person visits, telehealth can lower healthcare costs and improve access to care.
Digital Health Innovations
Digital health technologies, such as wearable devices, mobile health apps, and remote patient monitoring systems, are transforming the way healthcare is delivered and consumed. These innovations enable individuals to actively manage their health, promote preventive care, and reduce the need for costly hospitalizations. As these technologies become more prevalent and accessible, they have the potential to drive down healthcare costs and improve overall health outcomes.
Integration of Social Determinants of Health
Recognizing the significant impact of social and economic factors on health outcomes, healthcare providers and insurers are increasingly integrating social determinants of health into their strategies. By addressing issues such as food insecurity, housing instability, and access to education and employment opportunities, healthcare stakeholders can improve population health and reduce healthcare costs in the long run.
Policy and Regulatory Changes
Policy and regulatory changes will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the cost and accessibility of individual health insurance. The future may see further implementation of value-based care models, increased focus on preventive care, and continued efforts to address healthcare disparities. Additionally, the ongoing debate around universal healthcare and single-payer systems will influence the landscape of individual health insurance, potentially impacting costs and coverage options.
How do I choose the right health insurance plan for my needs?
+When selecting a health insurance plan, consider your healthcare needs, budget, and preferences. Assess the coverage provided, including deductibles, copays, and out-of-pocket limits. Evaluate the plan’s provider network to ensure access to your preferred healthcare providers. Additionally, review any additional benefits or perks offered by the plan, such as wellness programs or prescription drug coverage.
Are there any tax benefits associated with individual health insurance plans?
+Yes, in some cases, there are tax benefits associated with individual health insurance plans. For example, if you purchase insurance through the Health Insurance Marketplace and meet certain income requirements, you may be eligible for premium tax credits to reduce your monthly premiums. Additionally, if you have a High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) and a Health Savings Account (HSA), you can contribute pre-tax dollars to the HSA, offering tax advantages.
What should I do if I can’t afford the insurance premiums?
+If you’re struggling to afford insurance premiums, consider exploring options like government-subsidized plans, Medicaid (if eligible), or employer-sponsored plans, which may offer more affordable coverage. Additionally, review your budget and explore ways to reduce expenses in other areas to free up funds for insurance.



