Cost Of Covid Vaccine Without Insurance
The cost of healthcare and access to medical treatments are topics of great importance, especially during unprecedented times like the COVID-19 pandemic. As the world navigated through this global health crisis, the development and distribution of vaccines became a pivotal aspect of public health strategies. For individuals without insurance coverage, understanding the financial implications of receiving the COVID-19 vaccine is crucial. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the cost of the COVID-19 vaccine for those without insurance, exploring the factors that influence pricing, the financial assistance available, and the impact on public health initiatives.
Understanding the Cost Structure of COVID-19 Vaccines
The pricing of COVID-19 vaccines is a multifaceted topic, influenced by various economic, logistical, and regulatory factors. While vaccine manufacturers play a pivotal role in setting initial prices, the cost to consumers can vary significantly based on their insurance status and the specific healthcare provider they choose.
For individuals with insurance, the cost of the COVID-19 vaccine is typically covered by their health plan, ensuring minimal out-of-pocket expenses. However, for those without insurance, the financial landscape is more complex. The lack of insurance coverage can lead to higher expenses, making it essential to understand the cost structure and available options.
Factors Influencing Vaccine Pricing
- Manufacturing and Distribution Costs: The development and production of vaccines are expensive endeavors, with significant investments required for research, clinical trials, and large-scale manufacturing. These costs are often passed on to consumers, influencing the final price.
- Government Subsidies and Contracts: Many governments have entered into agreements with vaccine manufacturers, providing financial support and securing doses at negotiated prices. These arrangements can impact the retail cost of vaccines for consumers.
- Healthcare Provider Pricing: Healthcare facilities and pharmacies set their own prices for administering vaccines, which can vary based on location, demand, and overhead costs.
- Market Competition: In regions with multiple vaccine options and competing providers, prices may be more competitive, benefiting consumers. However, in areas with limited options, prices can be higher.
- Vaccine Type and Dosage: Different COVID-19 vaccines have varying dosage requirements and administration schedules, which can affect the overall cost for individuals.
Real-World Vaccine Cost Examples
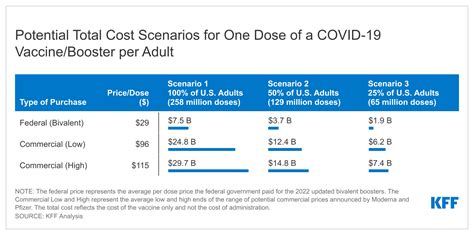
To illustrate the cost variations, let’s consider some real-world examples. In the United States, the COVID-19 vaccine prices can range from 0 to 150 per dose, depending on the vaccine type and the healthcare provider. For instance, the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine may cost around 150 for those without insurance, while the Moderna vaccine could be slightly lower, ranging from 0 to $100 per dose.
In contrast, countries with universal healthcare systems, such as the United Kingdom, often provide free COVID-19 vaccines to their citizens, ensuring equitable access regardless of insurance status. This highlights the significant impact of government policies and healthcare infrastructure on vaccine pricing and availability.
Financial Assistance and Programs for the Uninsured
Recognizing the financial challenges faced by individuals without insurance, various governments and healthcare organizations have implemented initiatives to provide affordable or free access to COVID-19 vaccines. These programs aim to ensure that financial barriers do not prevent people from receiving essential medical care.
Government-Funded Vaccination Programs
Many governments have allocated funds specifically for COVID-19 vaccination drives, making vaccines available at little to no cost for all citizens. These initiatives often cover the full cost of the vaccine and its administration, ensuring that financial status does not become a barrier to immunization.
For example, the United States government, through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), launched the COVID-19 Vaccination Program, which provides vaccines at no cost to all individuals living in the country, regardless of their insurance status. This program is a crucial component of the public health response, ensuring widespread vaccination and herd immunity.
Non-Profit and Community Initiatives
Non-profit organizations and community health centers have played a vital role in providing affordable or free COVID-19 vaccines to underserved populations. These initiatives often receive funding from government grants, philanthropic donations, or corporate sponsorships, enabling them to offer vaccines at reduced prices or no cost.
Community health centers, in particular, have been at the forefront of ensuring equitable access to vaccines. They often provide comprehensive healthcare services to underserved communities, including vaccination drives targeted at low-income individuals, the uninsured, and those facing language or cultural barriers.
Pharmaceutical Company Programs
Some pharmaceutical companies, in collaboration with governments and healthcare providers, have established patient assistance programs to support individuals who cannot afford the COVID-19 vaccine. These programs typically provide financial assistance or free vaccines to eligible individuals, ensuring that cost does not impede access to life-saving treatments.
For instance, Pfizer has implemented the Pfizer Patient Assistance Program, which offers free medications, including vaccines, to eligible individuals who lack insurance coverage or have limited financial means. Such initiatives are crucial in ensuring that everyone has an opportunity to receive essential healthcare, regardless of their financial circumstances.
The Impact on Public Health and Equity
The cost of COVID-19 vaccines without insurance has significant implications for public health and equity. Ensuring equitable access to vaccines is crucial for controlling the spread of the virus and achieving herd immunity. When financial barriers exist, it can lead to disparities in vaccination rates, impacting vulnerable communities disproportionately.
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy and Disparities
Vaccine hesitancy, or the reluctance or refusal to vaccinate despite the availability of vaccines, is a complex issue influenced by various factors, including cost. For individuals without insurance, the financial burden of vaccination can be a significant deterrent, contributing to lower vaccination rates.
To address vaccine hesitancy, it is essential to provide clear and transparent information about the cost of vaccines and the financial assistance available. By removing financial barriers, we can encourage more individuals to consider vaccination, improving overall public health outcomes.
Ensuring Equitable Access and Inclusion
Equitable access to healthcare, including COVID-19 vaccines, is a fundamental principle of public health. It ensures that all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status, have an equal opportunity to protect their health and well-being. When vaccines are readily available and affordable, it promotes a more inclusive society, where everyone can participate in community life without fear of illness.
By providing financial support and ensuring affordable or free access to vaccines, we can bridge the gap between the insured and uninsured, fostering a sense of unity and solidarity during challenging times. This approach not only benefits individuals but also strengthens the resilience of our communities and the overall healthcare system.
Conclusion: Navigating Financial Barriers to Vaccination
The cost of the COVID-19 vaccine without insurance presents a complex landscape, influenced by various economic and regulatory factors. However, it is essential to remember that financial barriers should not impede access to essential healthcare, especially during a global pandemic. Governments, healthcare providers, and community organizations have a crucial role in ensuring equitable access to vaccines, regardless of an individual’s financial status.
By understanding the cost structure, exploring available financial assistance programs, and advocating for inclusive healthcare policies, we can work towards a future where everyone has the opportunity to protect their health and contribute to a healthier society. As we navigate the ongoing challenges posed by COVID-19, let us continue to prioritize equitable access to vaccines and support those who may face financial hardships in accessing essential medical care.
FAQ
Are COVID-19 vaccines free for all individuals, regardless of insurance status?
+
In many countries, including the United States, COVID-19 vaccines are provided free of charge to all individuals, regardless of their insurance status. This initiative is part of the public health response to ensure widespread vaccination and control the spread of the virus.
What if I don’t have insurance and cannot afford the vaccine cost?
+
If you’re uninsured and facing financial challenges, there are government-funded programs and community initiatives that provide COVID-19 vaccines at little to no cost. You can also explore patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies, which may provide financial support or free vaccines.
Can I receive the COVID-19 vaccine if I have limited financial means or no insurance coverage?
+
Yes, financial barriers should not prevent anyone from receiving essential medical care, including COVID-19 vaccines. Governments and healthcare providers have implemented programs to ensure equitable access, and you can inquire about these initiatives at your local health department or community health center.