Calculating Private Mortgage Insurance

Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI) is an essential aspect of homeownership for many individuals, especially those making a down payment of less than 20% on their property. It's a crucial financial consideration that can significantly impact your monthly expenses and overall borrowing costs. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of PMI, providing you with a detailed understanding of how it works, when it's required, and strategies to manage and potentially eliminate it.
Understanding Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)
Private Mortgage Insurance is a policy that protects lenders in the event of borrower default. It's typically required when the borrower's down payment is less than 20% of the home's purchase price. PMI ensures that the lender can recover a portion of their losses if the borrower fails to repay the loan. This insurance provides a safety net for lenders, making them more willing to approve mortgages for borrowers who may not have the financial cushion of a substantial down payment.
The cost of PMI is added to the borrower's monthly mortgage payments until it is no longer required. This insurance premium is calculated based on various factors, including the borrower's credit score, loan-to-value ratio, and the size of the loan. It's an additional expense that borrowers must consider when budgeting for their mortgage.
The Role of PMI in Homeownership
PMI plays a critical role in the housing market by enabling individuals with limited savings to become homeowners. It provides an opportunity for buyers to enter the property market earlier in their financial journey, even if they haven't yet amassed a large down payment. This insurance also helps to stabilize the mortgage market by reducing the risk of default and ensuring that lenders can continue to offer competitive mortgage products.
When is PMI Required?
The need for PMI depends primarily on the borrower's down payment and the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. Lenders generally require PMI when the LTV ratio exceeds 80%. This means if your down payment is less than 20% of the home's purchase price, you'll likely need to pay for PMI.
For example, if you're buying a home valued at $300,000 and your down payment is $60,000 (20%), you won't need PMI. However, if your down payment is $45,000 (15%), you'll likely be required to pay for PMI until your loan balance reaches 80% of the home's original value.
| Down Payment | LTV Ratio | PMI Required |
|---|---|---|
| $60,000 (20%) | 80% | No |
| $45,000 (15%) | 85% | Yes |
| $30,000 (10%) | 90% | Yes |
Factors Affecting PMI Requirements
While the LTV ratio is a key determinant, other factors can also influence the requirement for PMI. These include:
- Credit Score: Borrowers with higher credit scores may have more flexibility in negotiating PMI requirements.
- Loan Type: Different loan types, such as FHA or conventional loans, have varying PMI rules.
- Property Type: Certain property types, like condominiums, may have specific PMI requirements.
- Lender Policies: Individual lenders may have unique guidelines for when PMI is necessary.
Calculating PMI Costs
The cost of PMI varies depending on several factors, including the loan amount, loan term, credit score, and the borrower's specific circumstances. PMI is typically expressed as a percentage of the loan amount and is added to the borrower's monthly mortgage payment.
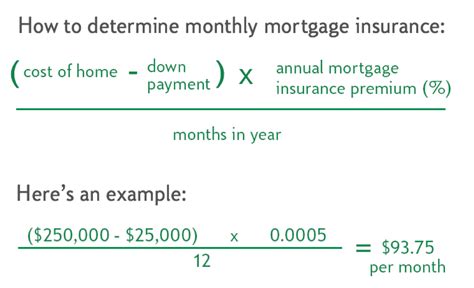
PMI Calculation Formula
The formula for calculating PMI is as follows:
PMI = (Loan Amount * PMI Rate) / 12
For example, if your loan amount is $200,000 and the PMI rate is 0.5% (or 0.005), your monthly PMI payment would be:
PMI = ($200,000 * 0.005) / 12 = $83.33
This means you would pay an additional $83.33 each month for PMI, on top of your regular mortgage payment.
Factors Influencing PMI Rates
Several factors can influence the PMI rate a borrower is offered, including:
- Credit Score: Higher credit scores often result in lower PMI rates.
- Loan-to-Value Ratio: Lenders may offer lower PMI rates for loans with lower LTV ratios.
- Loan Term: Shorter loan terms may attract lower PMI rates.
- Property Type: Certain property types may carry higher PMI rates.
Strategies to Manage PMI
While PMI is a necessary expense for many borrowers, there are strategies to manage and potentially eliminate it over time. Here are some approaches to consider:
1. Increase Your Down Payment
The most straightforward way to avoid or reduce PMI is to make a larger down payment. By increasing your down payment to 20% or more, you can often bypass the PMI requirement altogether. This strategy can save you significant money in the long run by eliminating the need for PMI.
2. Improve Your Credit Score
A higher credit score can lead to lower PMI rates. Lenders view borrowers with strong credit scores as less risky, which can result in more favorable PMI terms. Focus on improving your credit score by paying bills on time, reducing credit card balances, and regularly monitoring your credit report for errors.
3. Refinance Your Mortgage
If you've already purchased a home and are paying PMI, refinancing your mortgage could be an option to eliminate PMI. By refinancing, you may be able to reduce your loan-to-value ratio to below 80%, which could remove the PMI requirement. However, it's essential to consider the costs and benefits of refinancing, as there may be fees associated with the process.
4. Request a PMI Review
Some lenders offer reviews of PMI requirements after a certain period. If you've made significant progress in paying down your loan balance or your home's value has increased, you may be able to request a review to have PMI removed. Keep in mind that this process may involve a fee and a new appraisal.
The Impact of PMI on Your Mortgage

PMI can significantly impact your monthly mortgage payments and overall borrowing costs. Here's a closer look at how PMI affects your financial obligations:
Monthly Mortgage Payments
PMI is added to your monthly mortgage payment, increasing the overall cost. For example, if your mortgage payment without PMI is $1,500, and your PMI payment is $83.33 (as calculated above), your total monthly payment would be $1,583.33.
Total Borrowing Costs
Over the life of your loan, PMI can add up to a substantial amount. For a 30-year mortgage, even a relatively low PMI rate of 0.5% can result in tens of thousands of dollars in additional costs. It's essential to consider these long-term expenses when budgeting for your mortgage.
The Future of PMI
The landscape of PMI is continually evolving, and there are several factors that could impact its future. Here are some potential developments to consider:
1. Changing Lender Policies
Lenders may adjust their policies regarding PMI requirements in response to market conditions and regulatory changes. For example, some lenders have begun offering alternative forms of mortgage insurance, such as lender-paid mortgage insurance (LPMI), which is paid upfront as part of the loan closing costs.
2. Technological Innovations
Advancements in technology could also influence the future of PMI. For instance, the use of blockchain and smart contracts may streamline the mortgage process, potentially reducing the need for traditional PMI.
3. Economic Factors
Economic conditions, such as interest rates and housing market trends, can significantly impact PMI requirements. During periods of economic uncertainty, lenders may tighten their lending criteria, which could lead to more stringent PMI requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I get a mortgage without PMI?
+Yes, you can avoid PMI by making a down payment of 20% or more. This is often referred to as a “conventional loan” and does not require PMI.
How long do I have to pay PMI?
+The duration of PMI payments depends on various factors, including your loan type and lender policies. Typically, you’ll pay PMI until your loan balance reaches 80% of the original property value or until you refinance your mortgage.
Can I get a refund on my PMI payments?
+In most cases, PMI payments are non-refundable. However, if you’ve paid PMI for a significant portion of your loan term and your loan balance has dropped below 80% of the original property value, you may be able to request a refund.
Are there any alternatives to PMI?
+Yes, there are alternative mortgage insurance options, such as lender-paid mortgage insurance (LPMI) and mortgage insurance premium (MIP) for FHA loans. These alternatives have different payment structures and requirements, so it’s essential to understand your options and choose the best fit for your financial situation.
How can I reduce my PMI costs?
+To reduce PMI costs, consider increasing your down payment, improving your credit score, or refinancing your mortgage to remove PMI. Additionally, some lenders offer programs to reduce PMI over time based on your loan performance.