Average Price For Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance is a crucial aspect of protecting one's home and assets. It provides financial coverage for various risks and liabilities associated with owning a property. The average price for homeowners insurance varies depending on several factors, including the location, type of home, and the level of coverage chosen. Understanding the average cost and the factors influencing it can help homeowners make informed decisions when selecting an insurance policy.
Factors Influencing Homeowners Insurance Costs
Several key factors play a significant role in determining the average price of homeowners insurance. These factors can vary across different regions and insurance providers, but they generally include:
- Location: The geographic location of the property is a critical factor. Areas prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, tornadoes, or earthquakes, typically have higher insurance costs. Regions with high crime rates or a history of severe weather events may also experience increased premiums.
- Home Value and Size: The value and size of the home are essential considerations. Larger homes with higher replacement costs will generally require more extensive coverage, resulting in higher premiums. The type of construction and the materials used can also impact the insurance rate.
- Coverage Limits: The level of coverage chosen by the homeowner directly affects the insurance cost. Higher coverage limits provide more financial protection but also increase the premium. It's crucial to strike a balance between adequate coverage and affordable premiums.
- Deductibles: The deductible is the amount the homeowner pays out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. Choosing a higher deductible can lower the insurance premium, but it means the homeowner assumes more financial responsibility in the event of a claim.
- Age and Condition of the Home: Older homes may have outdated electrical systems, plumbing, or roofing, which can increase the risk of accidents and claims. As a result, insurance providers may charge higher premiums for older homes. Regular maintenance and updates can help mitigate these risks and potentially lower insurance costs.
- Claims History: Insurance providers consider the homeowner's claims history when calculating premiums. Multiple claims within a short period can indicate a higher risk, leading to increased insurance costs. Maintaining a clean claims history can help keep premiums lower.
- Discounts and Bundling: Many insurance companies offer discounts for various reasons. These can include loyalty discounts for long-term customers, safety discounts for homes with security systems or fire prevention measures, or multi-policy discounts when homeowners bundle their insurance policies (e.g., home and auto insurance) with the same provider.
Average Homeowners Insurance Costs by Region
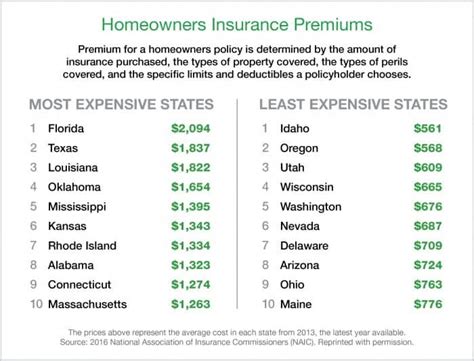
The average cost of homeowners insurance can vary significantly across different regions within the United States. Here’s a breakdown of average premiums based on regional data:
| Region | Average Annual Premium |
|---|---|
| Northeast | $1,500 - $2,000 |
| Midwest | $1,000 - $1,500 |
| Southeast | $1,200 - $1,800 |
| West | $1,100 - $1,600 |

It's important to note that these averages are general estimates and can vary widely based on the specific factors mentioned earlier. For instance, a homeowner in a high-risk area for hurricanes may pay significantly more than the regional average, while a homeowner with a well-maintained home and a clean claims history could pay considerably less.
Understanding Coverage Options and Add-ons
Homeowners insurance policies typically offer a range of coverage options and add-ons to tailor the policy to the specific needs of the homeowner. Some common coverage options include:
- Dwelling Coverage: This covers the structure of the home, including the main house, attached structures like garages, and any outbuildings on the property.
- Personal Property Coverage: Provides financial protection for the homeowner's personal belongings, such as furniture, electronics, and clothing. It typically covers both damage and theft.
- Liability Coverage: Protects the homeowner from financial liability if someone is injured on their property or if their actions cause damage to others' property. This coverage is crucial for legal protection.
- Additional Living Expenses (ALE): In the event of a covered loss that makes the home uninhabitable, ALE coverage reimburses the homeowner for additional living expenses incurred during the repair or rebuilding process.
- Medical Payments Coverage: Covers medical expenses for injuries sustained by visitors on the insured property, regardless of fault.
Homeowners can also opt for additional coverage add-ons, such as:
- Flood Insurance: Standard homeowners insurance policies do not cover flood damage. Homeowners in high-risk flood zones should consider purchasing separate flood insurance through the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) or private insurers.
- Earthquake Insurance: Similarly, homeowners in earthquake-prone areas may need to purchase additional coverage to protect against seismic activity.
- Personal Articles Floater: This add-on provides extra coverage for high-value items like jewelry, artwork, or collectibles that may exceed the limits of standard personal property coverage.
Tips for Lowering Homeowners Insurance Costs
While the average price of homeowners insurance can be influenced by various factors, there are strategies homeowners can employ to potentially reduce their insurance costs:
- Shop Around: Compare quotes from multiple insurance providers. Rates can vary significantly between companies, so obtaining several quotes can help homeowners find the most competitive pricing.
- Increase Deductibles: Choosing a higher deductible can lower premiums. However, it's important to ensure the deductible amount is manageable in the event of a claim.
- Bundle Policies: Bundling home and auto insurance policies with the same provider can often result in substantial discounts.
- Maintain a Clean Claims History: Avoid making small claims that may not significantly impact your finances. Frequent claims can lead to increased premiums or even policy cancellations.
- Improve Home Security: Investing in home security measures like burglar alarms, smoke detectors, and fire sprinklers can lead to safety discounts from insurance providers.
- Review Coverage Annually: Regularly review your insurance policy to ensure it aligns with your current needs. As your home and lifestyle change, your coverage requirements may also evolve.
- Consider Renovations: Upgrading outdated systems, such as electrical wiring or plumbing, can reduce the risk of accidents and potentially lower insurance costs.
Future Implications and Industry Trends

The homeowners insurance industry is constantly evolving, and several trends and factors may impact the average price of policies in the future:
- Climate Change and Natural Disasters: As extreme weather events become more frequent and severe due to climate change, insurance providers may adjust their rates to account for increased risks. This could lead to higher premiums, particularly in regions vulnerable to hurricanes, wildfires, or flooding.
- Technological Advancements: The adoption of smart home technology and Internet of Things (IoT) devices can potentially reduce insurance costs. These technologies can enhance home security and provide real-time data, allowing insurance companies to offer more precise risk assessments and potentially lower premiums.
- Data Analytics and Underwriting: Advanced data analytics and underwriting techniques enable insurance providers to more accurately assess risks and set premiums. This can lead to a more personalized and fair pricing structure for homeowners.
- Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance: Similar to auto insurance, homeowners insurance may adopt usage-based models where premiums are based on actual usage and risk factors. This could incentivize homeowners to take proactive measures to reduce risks and potentially lower their insurance costs.
In conclusion, the average price for homeowners insurance is influenced by a variety of factors, including location, home characteristics, coverage limits, and claims history. By understanding these factors and exploring the available coverage options and add-ons, homeowners can make informed decisions to protect their assets while managing insurance costs effectively. Staying informed about industry trends and taking proactive measures to mitigate risks can also help homeowners navigate the evolving landscape of homeowners insurance.
How often should I review my homeowners insurance policy?
+It is recommended to review your homeowners insurance policy annually or whenever significant changes occur in your life or home situation. This ensures that your coverage remains adequate and up-to-date.
What factors can lead to homeowners insurance claims being denied?
+Insurance claims can be denied for various reasons, including failure to disclose pre-existing conditions, intentional damage, or violations of policy terms. It’s crucial to understand your policy’s terms and conditions to avoid potential denials.
Are there any tax benefits associated with homeowners insurance premiums?
+In some cases, homeowners insurance premiums may be tax-deductible, especially if the insurance is required for a mortgage or if the home is used for business purposes. It’s advisable to consult a tax professional for specific guidance.