When Did Health Insurance Start
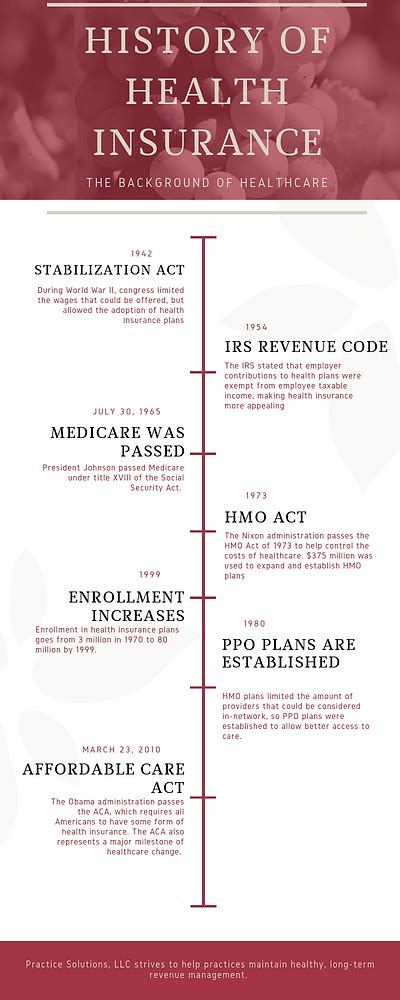
The concept of health insurance, as we know it today, has a long and complex history, evolving over centuries to become an integral part of modern healthcare systems worldwide. While the idea of insurance dates back to ancient times, the specific notion of protecting oneself against medical expenses is a relatively modern development. This article delves into the fascinating journey of health insurance, from its early beginnings to its modern-day forms, exploring key milestones and the impact it has had on healthcare accessibility and financial protection.
The Early Foundations of Health Insurance

The origins of health insurance can be traced back to various early societies, where communities recognized the need for mutual aid and support during times of illness or injury. Here are some of the earliest forms of health-related insurance-like practices:
- Ancient Greece and Rome: In ancient Greece, a system called prosiggia was established, where individuals or families provided mutual aid and support during difficult times, including illness. Similarly, in ancient Rome, collegia were formed, which were essentially burial societies that also provided financial assistance to members facing illness.
- Medieval Europe: During the Middle Ages, religious orders and guilds played a significant role in providing healthcare and financial support to their members. These organizations often had funds set aside to cover the costs of medical care and burial expenses.
- The Fraternal Benefit Societies: In the 17th and 18th centuries, mutual aid societies and friendly societies emerged in Europe and the United States. These societies offered various benefits to their members, including sickness and funeral benefits. Members paid regular contributions, and in return, they received financial support during times of illness or death.
The Birth of Modern Health Insurance

The concept of health insurance as we understand it today began to take shape in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Several key events and innovations paved the way for the establishment of formal health insurance systems:
The Rise of Industrialization and Medical Advances
The Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in society, including an increase in urbanization and the emergence of a new working class. This period also witnessed remarkable advancements in medicine, such as the discovery of anesthesia and the development of antiseptic techniques. These factors combined to create a growing need for accessible and affordable healthcare.
The First Health Insurance Plans
One of the earliest health insurance plans was introduced in Germany by Otto von Bismarck in the late 19th century. The Krankenversicherung (sickness insurance) program, implemented in 1883, provided workers with access to medical care and financial support during illness. This program served as a model for many other countries, inspiring the development of similar social insurance systems.
The Expansion of Health Insurance Globally
In the early 20th century, health insurance began to gain traction in various countries. For instance, the United Kingdom established the National Insurance Act in 1911, which provided sickness benefits to certain workers. Similarly, the United States saw the emergence of early health insurance plans, such as the Railroad Insurance Plan in 1875, which offered limited healthcare coverage to railroad workers.
Key Milestones in the Evolution of Health Insurance
The journey of health insurance has been marked by several significant milestones, each contributing to the development and refinement of healthcare coverage systems:
The Rise of Group Health Insurance
In the 1930s, during the Great Depression, group health insurance plans gained popularity. These plans, often sponsored by employers, offered a more affordable and accessible way for individuals to obtain healthcare coverage. Group insurance plans provided a level of financial protection and stability, particularly during a time of economic uncertainty.
The Establishment of Medicare and Medicaid
In the United States, two landmark programs, Medicare and Medicaid, were established in the 1960s. Medicare, introduced in 1965, provides health insurance for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as those with certain disabilities. Medicaid, also launched in 1965, offers healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families. These programs significantly expanded access to healthcare for vulnerable populations.
The Growth of Private Health Insurance
In many countries, private health insurance has become a significant component of the healthcare system. Private insurance companies offer a range of plans, providing individuals with the flexibility to choose coverage that suits their needs. The growth of private insurance has led to increased competition and innovation in the healthcare industry.
The Impact of Health Insurance on Healthcare
The introduction and evolution of health insurance have had a profound impact on healthcare systems worldwide. Here are some key ways in which health insurance has shaped the landscape of healthcare:
Increased Access to Healthcare
Health insurance has played a crucial role in making healthcare more accessible to a wider population. By providing financial protection against medical expenses, insurance plans ensure that individuals can seek necessary medical care without facing significant financial burden. This has led to improved health outcomes and reduced healthcare disparities.
Financial Protection for Individuals and Families
One of the primary goals of health insurance is to provide financial protection to policyholders. By spreading the risk across a large pool of individuals, insurance companies can offer coverage at more affordable rates. This protection is particularly beneficial for those with pre-existing conditions or chronic illnesses, as it ensures they can access the healthcare they need without facing unaffordable costs.
Encouraging Preventive Care
Many health insurance plans today emphasize the importance of preventive care. By covering routine check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings, insurance providers aim to promote early detection and prevention of diseases. This approach not only improves overall health outcomes but also reduces the long-term costs associated with treating advanced or chronic conditions.
Innovation and Quality Improvement
The competitive nature of the health insurance market has driven innovation and quality improvement in healthcare delivery. Insurance companies often partner with healthcare providers to offer enhanced services, improve patient experiences, and optimize healthcare processes. This collaboration has led to advancements in medical technology, improved patient safety, and more efficient healthcare systems.
The Future of Health Insurance

As healthcare continues to evolve, so too will the landscape of health insurance. Here are some potential trends and developments that may shape the future of health insurance:
Digital Health and Telemedicine
The integration of digital health technologies and telemedicine is likely to play a significant role in the future of health insurance. With the increasing availability of remote healthcare services, insurance companies may offer more flexible and convenient coverage options. Telemedicine can improve access to care, especially in rural or underserved areas, and reduce the need for in-person visits, thus lowering costs.
Value-Based Care and Payment Models
There is a growing shift towards value-based care, where healthcare providers are reimbursed based on the quality and outcomes of care, rather than the volume of services provided. This approach aligns with the goals of health insurance, as it encourages efficient and effective healthcare delivery. Value-based payment models may become more prevalent, incentivizing providers to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care.
Expanded Coverage for Mental Health and Wellness
Mental health and wellness are gaining increased recognition and importance in healthcare. Insurance companies are likely to expand their coverage to include more comprehensive mental health services and wellness programs. This shift towards holistic healthcare will benefit individuals by promoting overall well-being and early intervention for mental health issues.
Personalized and Precision Medicine
Advancements in genomics and personalized medicine are expected to have a significant impact on health insurance. With the ability to tailor treatments and interventions based on an individual’s genetic makeup, insurance companies may adjust their coverage to accommodate these personalized approaches. This could lead to more targeted and effective healthcare, improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The journey of health insurance is a testament to the continuous evolution of healthcare systems and the recognition of the importance of accessible and affordable medical care. From its early foundations in mutual aid societies to the sophisticated systems of today, health insurance has transformed the way we approach healthcare. As we move forward, the focus on innovation, quality, and accessibility will continue to shape the future of health insurance, ensuring that individuals around the world have the protection and care they need.
What is the purpose of health insurance?
+Health insurance aims to provide financial protection and access to healthcare services for individuals. It helps cover the costs of medical treatments, prescriptions, and preventive care, ensuring that people can receive necessary care without facing unaffordable expenses.
How does health insurance benefit society as a whole?
+Health insurance plays a crucial role in promoting public health and reducing healthcare disparities. By providing coverage to a wide range of individuals, it ensures that people can seek timely medical care, leading to better health outcomes and a healthier population overall.
What are the different types of health insurance plans available?
+There are various types of health insurance plans, including employer-sponsored group plans, individual plans purchased directly from insurance companies, government-funded programs like Medicare and Medicaid, and private insurance plans offered by for-profit companies. Each type has its own features and coverage options.



