What Is Health Insurance

The Comprehensive Guide to Health Insurance: Understanding Coverage and Benefits

Health insurance is an essential aspect of modern healthcare systems, offering individuals and families protection and financial security in the face of unexpected medical expenses. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the concept of health insurance, shedding light on its various facets, benefits, and how it functions in the healthcare landscape.
In an era where medical costs can be prohibitively high, health insurance provides a safety net, ensuring that individuals have access to necessary medical services without facing financial ruin. It is a vital component of healthcare management, influencing everything from the quality of care received to the overall health and well-being of a population.
With the rise of awareness about personal health and the importance of preventative care, health insurance has evolved to cater to a wide range of needs. From basic coverage for emergencies to comprehensive plans covering preventive care, chronic illness management, and even mental health services, the scope of health insurance has expanded significantly.
Understanding Health Insurance Coverage

Health insurance coverage is a contractual agreement between an individual or a group (such as an employer) and an insurance company. This agreement outlines the terms and conditions under which the insurance company agrees to provide financial protection against medical costs. The coverage details the specific medical services, treatments, and procedures that are included in the plan, as well as any associated costs, such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
The level of coverage varies widely between different health insurance plans. Some plans offer a broad range of services with minimal out-of-pocket costs, while others may have more limited coverage and higher deductibles. The choice of a health insurance plan depends on an individual's or family's unique healthcare needs and financial circumstances.
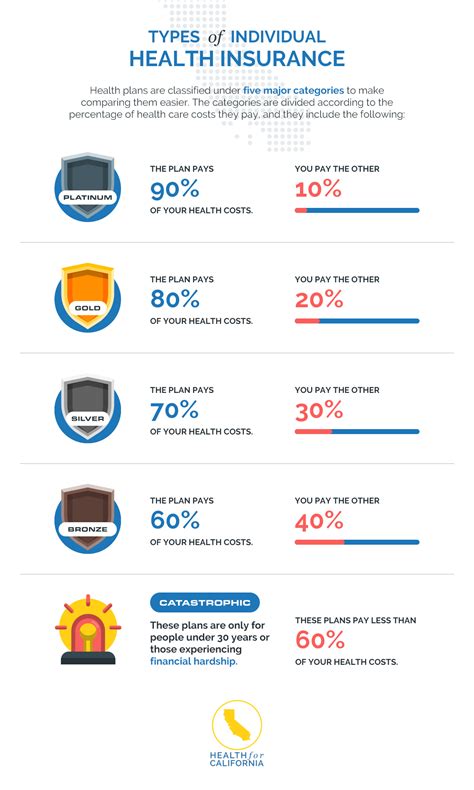
Key components of health insurance coverage include:
- Premium: The amount paid regularly (usually monthly) to maintain the insurance coverage.
- Deductible: The amount an individual must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance company starts covering the costs.
- Copayment: A fixed amount paid by the insured at the time of receiving a medical service, often for specific services like doctor visits or prescription drugs.
- Coinsurance: The percentage of costs that the insured must pay after the deductible is met, often for more extensive or specialized treatments.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The limit on the amount an individual will have to pay out-of-pocket in a year for covered services.
Understanding these components is crucial when choosing a health insurance plan, as they directly impact the cost and coverage an individual receives.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Health insurance plans come in various forms, each designed to cater to different healthcare needs and preferences. Here's an overview of some common types of health insurance plans:
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
HMOs are a type of managed care plan that typically offers a lower cost option for health insurance. In an HMO, members choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates their healthcare needs. Referrals are often required to see specialists, and members must use providers within the HMO's network to receive coverage.
Key features of HMOs include:
- Lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to other plans.
- Emphasis on preventative care and wellness programs.
- Typically, no coverage for out-of-network services, except in emergencies.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
PPOs offer more flexibility than HMOs, allowing members to choose their healthcare providers, both inside and outside the network. While in-network services are generally less expensive, out-of-network services are also covered, albeit at a higher cost.
Key features of PPOs include:
- Greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
- Usually, no need for referrals to see specialists.
- Higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to HMOs.
Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs)
EPOs are similar to PPOs in that members can choose their healthcare providers. However, EPOs do not cover out-of-network services, except in emergencies or for specialist care when a referral is provided.
Key features of EPOs include:
- Lower premiums compared to PPOs.
- No coverage for out-of-network services, except in specific cases.
- Emphasis on cost-effective, quality healthcare.
Point-of-Service (POS) Plans
POS plans combine features of both HMOs and PPOs. Members typically choose a primary care physician and receive coordinated care within the network. However, they can also choose to receive out-of-network services at a higher cost.
Key features of POS plans include:
- Flexibility to choose between in-network and out-of-network providers.
- Usually, lower out-of-pocket costs for in-network services.
- Referrals are often required to see specialists.
High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
HDHPs are a type of health insurance plan with higher deductibles than traditional plans. These plans are often paired with health savings accounts (HSAs), allowing individuals to save money tax-free to cover medical expenses.
Key features of HDHPs include:
- Lower premiums compared to traditional plans.
- High deductibles, meaning members pay more out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in.
- Eligibility to open an HSA, providing tax benefits and a way to save for future medical expenses.
The Role of Health Insurance in Preventative Care
Health insurance plays a critical role in promoting preventative care, which is an essential aspect of maintaining good health and well-being. Many health insurance plans now cover a wide range of preventative services, from annual check-ups and screenings to immunizations and counseling services, often at no additional cost to the insured.
By covering preventative care, health insurance plans aim to catch potential health issues early, when they are often more treatable and less costly. This approach not only benefits individuals by improving their health outcomes but also helps to reduce overall healthcare costs by preventing more serious, costly conditions from developing.
Covered Preventative Services
The scope of preventative services covered by health insurance plans can vary, but many plans now include the following:
- Annual physical exams and wellness checks.
- Immunizations, including flu shots and childhood vaccines.
- Cancer screenings, such as mammograms, colonoscopies, and Pap smears.
- Prenatal and postpartum care.
- Mental health and substance abuse screenings and counseling.
- Certain laboratory services and diagnostic tests.
The Future of Health Insurance: Innovations and Trends

The landscape of health insurance is continually evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changing healthcare needs, and policy reforms. Here are some key trends and innovations shaping the future of health insurance:
Telehealth and Virtual Care
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth services, which allow patients to access healthcare remotely through video conferencing, phone calls, or secure messaging. Many health insurance plans now cover a range of telehealth services, offering convenience and accessibility to members, especially for non-emergency care.
Value-Based Care and Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs)
Value-based care models focus on providing high-quality, cost-effective healthcare by rewarding healthcare providers for keeping patients healthy and managing chronic conditions effectively. ACOs are groups of healthcare providers, such as doctors and hospitals, that come together to give coordinated high-quality care to Medicare patients.
Health Insurance Marketplaces
The establishment of health insurance marketplaces, as mandated by the Affordable Care Act (ACA), has made it easier for individuals and small businesses to compare and purchase health insurance plans. These marketplaces offer a range of plans with varying levels of coverage and costs, providing a transparent and competitive environment for consumers.
Consumer-Driven Health Plans (CDHPs)
CDHPs, including HDHPs, continue to gain popularity, especially among younger and healthier individuals. These plans put more financial control in the hands of consumers, encouraging them to make cost-conscious healthcare decisions while also providing tax advantages through HSAs.
Integration of Wellness and Lifestyle Programs
Health insurance companies are increasingly integrating wellness and lifestyle programs into their offerings. These programs focus on promoting healthy behaviors, such as regular exercise, healthy eating, stress management, and smoking cessation, often with incentives and rewards for members who participate.
Conclusion
Health insurance is a complex but essential aspect of modern healthcare. By understanding the various types of plans, coverage options, and the role of health insurance in promoting preventative care, individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends and innovations in health insurance will be crucial for making the best choices for one's health and financial well-being.
What is the difference between a health insurance premium and a deductible?
+
A premium is the amount you pay regularly (usually monthly) to maintain your health insurance coverage, while a deductible is the amount you must pay out-of-pocket before your insurance company starts covering the costs of your medical services. In other words, the premium is the cost of having the insurance, while the deductible is the cost you pay before the insurance benefits kick in.
How do I choose the right health insurance plan for my needs?
+
Choosing the right health insurance plan depends on several factors, including your healthcare needs, your budget, and your preferred level of flexibility. Consider factors like the plan’s coverage for your specific medical needs, the cost of premiums and out-of-pocket expenses, the network of providers, and the plan’s focus on preventative care. It’s also helpful to read reviews and compare plans to find the best fit for your situation.
What is the significance of a health insurance plan’s network of providers?
+
A health insurance plan’s network of providers refers to the doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare professionals who have contracted with the insurance company to provide services at a discounted rate. Using in-network providers typically results in lower out-of-pocket costs compared to using out-of-network providers, who may not be covered or may require higher copayments or coinsurance.
How does health insurance coverage impact the cost of medical services?
+
Health insurance coverage can significantly impact the cost of medical services. With insurance, you typically pay a premium and have a deductible, copayments, and/or coinsurance. These costs are often much lower than the full price of medical services, making healthcare more affordable and accessible. Insurance also protects you from high medical bills in case of serious illness or injury.
What are some common challenges people face when navigating health insurance plans and coverage?
+
Navigating health insurance plans can be challenging due to the complexity of coverage, benefits, and costs. Common challenges include understanding the plan’s coverage limits, knowing which providers are in-network, managing out-of-pocket costs, and dealing with insurance claims and billing processes. Additionally, changes in healthcare policies and plans can make it difficult to keep up with the latest information.