Typical Homeowners Insurance Cost
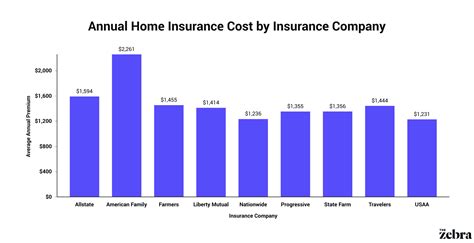
Homeowners insurance is a crucial aspect of homeownership, providing financial protection and peace of mind for millions of individuals and families across the United States. However, the cost of this essential coverage can vary significantly depending on numerous factors. Understanding the typical expenses associated with homeowners insurance is vital for prospective buyers and current homeowners alike. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of homeowners insurance costs, offering an in-depth analysis of the key factors that influence these expenses and providing valuable insights to help readers navigate this complex landscape.
Understanding the Basics of Homeowners Insurance
Before diving into the cost considerations, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of homeowners insurance. This type of insurance is designed to protect homeowners from financial losses resulting from damage to their property, liability claims, and, in some cases, additional living expenses if the home becomes uninhabitable due to an insured event.
The coverage offered by homeowners insurance typically includes:
- Dwelling Coverage: Protects the physical structure of the home, including walls, roofs, and permanent fixtures.
- Personal Property Coverage: Covers personal belongings such as furniture, electronics, and clothing.
- Liability Coverage: Provides protection against lawsuits and medical payments if someone is injured on the insured property.
- Additional Living Expenses: Covers temporary living expenses if the home is uninhabitable due to a covered event.
Factors Influencing Homeowners Insurance Costs
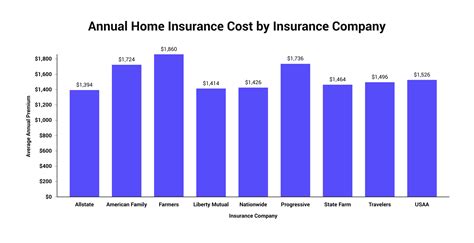
The cost of homeowners insurance is determined by a multitude of factors, each playing a unique role in the overall premium calculation. Understanding these factors is crucial for homeowners to assess their coverage needs accurately and make informed decisions about their insurance policies.
Location and Geographical Factors
One of the most significant determinants of homeowners insurance costs is the location of the property. Insurance companies carefully evaluate the geographical characteristics of an area, considering factors such as:
- Natural Disasters: Regions prone to natural disasters like hurricanes, tornadoes, earthquakes, or wildfires often have higher insurance premiums. These events can result in extensive property damage, leading to increased risk for insurance providers.
- Crime Rates: Areas with higher crime rates may experience elevated insurance costs due to the potential for theft, vandalism, or other property-related crimes.
- Proximity to Fire Stations: Homes located closer to fire stations may benefit from lower premiums, as the proximity to emergency services can reduce the response time in the event of a fire.
- Distance from Coastlines: Coastal regions are often susceptible to hurricanes and flooding, leading to higher insurance rates.
For example, a home located in a hurricane-prone area along the Gulf Coast may incur significantly higher insurance costs compared to a similar property in a low-risk inland region.
Home Value and Replacement Cost
The value of the home itself is a critical factor in determining insurance premiums. Insurance companies assess the replacement cost of the home, which is the estimated cost to rebuild the property if it were completely destroyed. Factors influencing home value include:
- Size and Square Footage: Larger homes generally have higher replacement costs and, consequently, higher insurance premiums.
- Construction Materials: Homes built with high-quality, durable materials may have lower insurance costs as they are more resistant to damage.
- Age of the Home: Older homes may require more extensive repairs or use of specialty materials, which can increase insurance costs.
- Special Features: Homes with unique architectural features, pools, or other amenities may have higher insurance costs due to the potential for increased risk or specialized repairs.
It's important to note that the replacement cost may differ from the market value of the home. The market value considers factors like location and real estate trends, while the replacement cost focuses solely on rebuilding the physical structure.
Coverage Limits and Deductibles
The level of coverage chosen by the homeowner also plays a significant role in determining insurance costs. Homeowners can opt for higher or lower coverage limits, which impact the premium. Additionally, the deductible—the amount the homeowner pays out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in—can affect the overall cost.
- Coverage Limits: Choosing higher coverage limits provides more extensive protection but typically results in higher premiums. It's crucial to strike a balance between adequate coverage and affordable premiums.
- Deductibles: Opting for a higher deductible can lead to lower insurance premiums. However, it's essential to consider the financial implications of paying a higher deductible in the event of a claim.
Policy Add-Ons and Endorsements
Homeowners may choose to enhance their insurance coverage with policy add-ons or endorsements. These additional coverages cater to specific needs and can include:
- Water Backup Coverage: Protects against damage caused by water backup from sewers or drains.
- Ordinance or Law Coverage: Covers the cost of complying with updated building codes if the home is damaged and needs to be rebuilt.
- Personal Injury Coverage: Provides protection against lawsuits related to personal injury claims, such as libel or slander.
- Identity Theft Coverage: Offers assistance and reimbursement for expenses related to identity theft.
While these add-ons can provide valuable protection, they also contribute to higher insurance premiums.
Credit Score and Payment History
Insurance companies often consider an individual’s credit score and payment history when determining insurance premiums. A higher credit score may result in lower insurance costs, as it indicates a lower risk for the insurance provider.
Additionally, the method of payment can influence premiums. Some insurance companies offer discounts for paying the entire annual premium upfront, while others may charge slightly higher premiums for monthly payment plans.
Claim History and Risk Assessment
The insurance company evaluates the homeowner’s claim history to assess the risk associated with insuring the property. A history of frequent claims may lead to higher insurance premiums or even policy non-renewal.
Insurance companies also consider the overall risk assessment of the area, taking into account factors like the number of claims in the region and the potential for future losses.
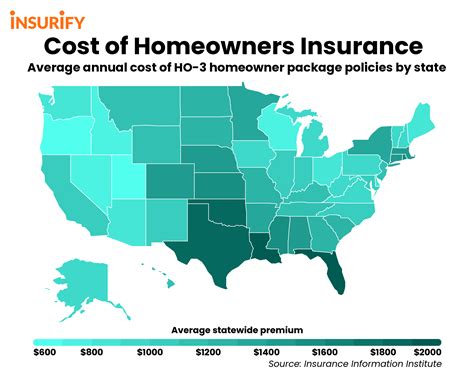
Average Cost of Homeowners Insurance
According to recent data, the average annual cost of homeowners insurance in the United States is approximately $1,300. However, it’s important to note that this figure is just an average, and the actual cost can vary significantly based on the factors discussed earlier.
| State | Average Annual Premium |
|---|---|
| Florida | $3,313 |
| Louisiana | $2,415 |
| Oklahoma | $2,370 |
| Alabama | $2,333 |
| Texas | $2,256 |
| ... | ... |
| Ohio | $839 |
| West Virginia | $837 |
| Maine | $810 |
| Vermont | $780 |
| Hawaii | $748 |
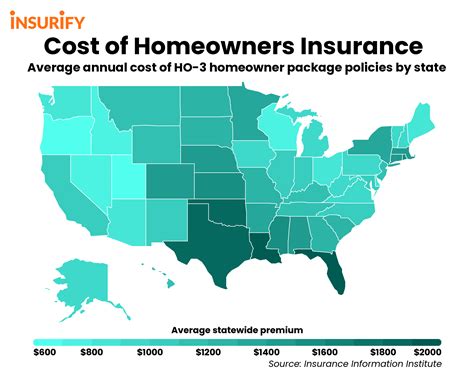
As illustrated in the table above, the average annual premium can vary widely from state to state, with states like Florida and Louisiana facing significantly higher costs due to their vulnerability to natural disasters.
Tips for Reducing Homeowners Insurance Costs
While the cost of homeowners insurance is influenced by various factors, there are strategies homeowners can employ to potentially reduce their insurance premiums. Here are some tips to consider:
- Shop Around: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance providers to compare rates and coverage options. Competition among insurers can lead to better deals.
- Bundle Policies: Many insurance companies offer discounts when homeowners bundle their insurance policies, such as combining homeowners and auto insurance.
- Improve Home Security: Installing security systems, smoke detectors, and fire extinguishers can reduce the risk of theft and fire, potentially leading to lower insurance premiums.
- Review Coverage Regularly: Regularly assess your insurance coverage to ensure it aligns with your needs. Avoid over-insuring or under-insuring your property.
- Consider Higher Deductibles: Opting for a higher deductible can lower insurance premiums, but it's important to ensure you have the financial means to cover the deductible in the event of a claim.
Conclusion: Navigating Homeowners Insurance Costs
Understanding the typical costs associated with homeowners insurance is a crucial step in making informed decisions about homeownership. By considering the various factors that influence insurance premiums, homeowners can better assess their coverage needs and explore strategies to potentially reduce their insurance expenses. Remember, the cost of homeowners insurance is a critical consideration when planning your financial future and protecting your most valuable asset.
What is the average annual increase in homeowners insurance premiums?
+The average annual increase in homeowners insurance premiums varies by state and can range from 2% to 10% or more. It’s important to review your policy annually to understand any changes in premiums.
Are there any discounts available for homeowners insurance?
+Yes, many insurance companies offer discounts for various reasons, such as bundling policies, installing security systems, or having certain safety features in your home. It’s worth exploring these discounts to potentially lower your premiums.
How often should I review my homeowners insurance policy?
+It’s recommended to review your homeowners insurance policy at least once a year, especially after significant life changes or home improvements. This ensures your coverage remains adequate and up-to-date.



