Insurance Premiums Definition

Insurance premiums are an essential aspect of the insurance industry, playing a crucial role in the financial stability and risk management of both policyholders and insurance providers. Understanding the concept of insurance premiums is fundamental to navigating the world of insurance and making informed decisions about coverage.
Understanding Insurance Premiums

At its core, an insurance premium is the amount of money an individual or entity pays to an insurance company in exchange for a specific level of coverage. This monetary exchange is the foundation of the insurance contract, representing the policyholder’s commitment to the insurer and vice versa. The premium is typically paid at regular intervals, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, and is determined by various factors that assess the level of risk associated with the insured individual or entity.
Insurance premiums are not a one-size-fits-all arrangement. They are tailored to the unique circumstances and needs of the policyholder. The premium calculation considers a range of variables, including the type of insurance (e.g., auto, health, life, property), the level of coverage desired, the policyholder's personal characteristics and history (age, health status, driving record), and the geographical location. These factors collectively influence the insurer's assessment of the risk associated with providing coverage and, consequently, the premium amount.
From the perspective of the policyholder, insurance premiums represent a financial investment in their future security and peace of mind. By paying premiums, individuals secure protection against potential losses or damages. This protection can cover a wide range of scenarios, from medical emergencies and property damage to liability claims and even death benefits. The insurance premium essentially transfers the financial burden of unforeseen events from the policyholder to the insurer, providing a safety net against the unpredictability of life.
The Dynamics of Premium Calculation
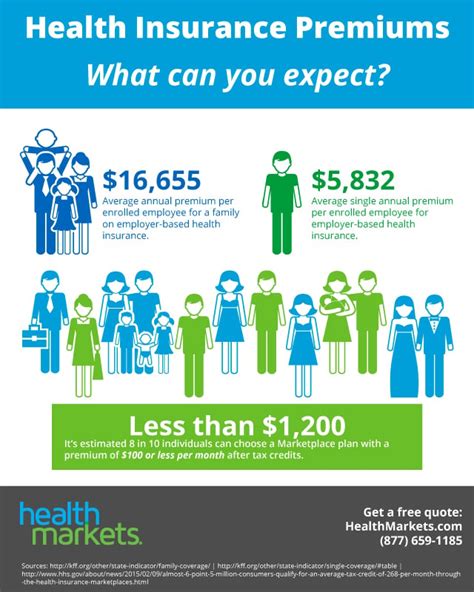
The process of determining insurance premiums is intricate and involves a deep understanding of risk assessment and actuarial science. Actuaries, professionals specializing in this field, employ sophisticated mathematical and statistical models to predict the likelihood of various events and the potential costs associated with them. By analyzing vast datasets and historical trends, actuaries can make informed estimates about the risks faced by different policyholders and adjust premiums accordingly.
One key factor in premium calculation is the law of large numbers, a statistical principle that suggests the more data points available, the more accurate the predictions can be. Insurance companies pool data from a large number of policyholders, allowing them to identify patterns and predict with greater precision the likelihood of claims. This collective data helps insurers set premiums that accurately reflect the level of risk for the average policyholder within a specific demographic or risk category.
Additionally, insurance companies utilize risk classification to further refine their premium calculations. This process involves grouping policyholders based on shared characteristics that impact risk. For example, in auto insurance, risk classification might consider factors such as driving history, age, gender, and the type of vehicle insured. By categorizing policyholders into different risk classes, insurers can more accurately assess and price the risk associated with each individual or entity.
Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums
- Risk Assessment: The primary factor influencing insurance premiums is the level of risk associated with the insured individual or entity. Higher-risk policyholders typically pay higher premiums to account for the increased likelihood of claims.
- Coverage Type and Amount: Different types of insurance policies (e.g., health, auto, home) carry varying levels of risk and cost. Additionally, the level of coverage desired, such as the policy limits and deductibles, can significantly impact the premium.
- Personal Characteristics: Factors such as age, gender, health status, and lifestyle can influence the risk assessment and, consequently, the premium. For instance, younger individuals may pay higher premiums for certain types of insurance due to their higher propensity for risk.
- Geographical Location: The location where the policyholder resides or operates can impact the premium. Areas with higher crime rates, natural disaster risks, or dense populations may result in higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of claims.
- Claims History: A policyholder’s claims history is a critical factor in premium calculation. Those with a history of frequent claims may be considered higher-risk and face higher premiums, as they are more likely to require compensation in the future.
The Role of Insurance Premiums in Risk Management
Insurance premiums are a critical component of the risk management strategy for both policyholders and insurance companies. For policyholders, paying premiums provides a sense of security and financial protection against unforeseen events. It allows individuals and entities to transfer the burden of potential losses to the insurer, ensuring they have the resources to recover and rebuild in the event of a claim.
From the insurer's perspective, premiums are the lifeblood of the business. They provide the financial resources necessary to pay out claims, cover administrative costs, and maintain the insurer's financial stability. By accurately assessing and pricing risk through premiums, insurance companies can ensure they have sufficient funds to meet their obligations to policyholders while also generating a profit to sustain their operations.
The Premium-Risk Balance
Achieving the right balance between premiums and risk is a delicate task for insurance companies. On the one hand, setting premiums too high may deter potential policyholders, limiting the insurer’s customer base and revenue. On the other hand, setting premiums too low can lead to financial strain if claims exceed expectations, potentially threatening the insurer’s solvency.
To strike this balance, insurance companies employ a variety of strategies. They continuously refine their risk assessment models, incorporating new data and analytical techniques to improve accuracy. They also offer a range of policy options and discounts to cater to different risk profiles and budget constraints. By providing flexible coverage options and personalized premiums, insurers can attract a diverse customer base while managing their risk exposure effectively.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Premiums |
|---|---|
| Age | Younger individuals may pay higher premiums due to their increased risk propensity. |
| Gender | In some cases, gender can influence premiums, with certain types of insurance policies considering gender as a risk factor. |
| Health Status | Pre-existing health conditions or high-risk lifestyles can result in higher premiums for health and life insurance. |
| Location | Areas with higher crime rates or natural disaster risks often have higher premiums. |

The Future of Insurance Premiums
The insurance industry is experiencing a period of significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. These shifts are expected to have a profound impact on the way insurance premiums are calculated and managed.
Technological Innovations
The advent of digital technologies and data analytics is revolutionizing the insurance industry. Insurers are leveraging big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to enhance their risk assessment capabilities and improve the accuracy of premium calculations. By analyzing vast datasets and employing advanced predictive modeling, insurers can identify new patterns and correlations, leading to more precise risk assessments and premium pricing.
Furthermore, the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices and telematics is enabling insurers to gather real-time data on policyholders' behavior and environment. For instance, in auto insurance, telematics devices can track driving habits, allowing insurers to offer usage-based insurance (UBI) policies. These policies adjust premiums based on actual driving behavior, rewarding safe drivers with lower premiums.
Personalized Insurance
The traditional one-size-fits-all approach to insurance is giving way to a more personalized model. Insurers are recognizing the unique needs and risk profiles of individual policyholders and are tailoring their products and premiums accordingly. This shift towards personalized insurance is driven by the desire to provide more relevant coverage options and competitive pricing, while also enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Personalized insurance involves offering a wide range of policy options, including customizable coverage levels, flexible deductibles, and various add-ons. Policyholders can choose the level of coverage that best suits their needs and budget, resulting in premiums that are more aligned with their individual risk profile. Additionally, insurers are exploring new ways to reward policyholders for positive behaviors, such as offering discounts for maintaining a healthy lifestyle or practicing safe driving habits.
Regulatory and Market Dynamics
The insurance industry is heavily regulated, and changes in regulatory frameworks can have a significant impact on premium calculations. Governments and regulatory bodies often implement measures to protect consumers and ensure the financial stability of the industry. These measures may include setting minimum capital requirements for insurers, regulating premium pricing, and introducing consumer protection laws.
Market dynamics also play a crucial role in shaping the future of insurance premiums. Changes in consumer preferences, economic conditions, and industry competition can influence the pricing strategies of insurers. For example, in a highly competitive market, insurers may be more inclined to offer lower premiums or innovative coverage options to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
Emerging Risks and Challenges
As society and technology evolve, new risks emerge that were previously unforeseen. Insurers must continually adapt their risk assessment models and premium calculations to address these emerging risks. For instance, with the rise of autonomous vehicles and artificial intelligence, insurers are grappling with the challenge of assessing and pricing the risks associated with these new technologies.
Additionally, climate change and the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters present significant challenges for the insurance industry. Insurers must incorporate these changing risk landscapes into their premium calculations, ensuring they remain financially resilient while continuing to provide adequate coverage to policyholders.
Conclusion
Insurance premiums are a fundamental component of the insurance industry, serving as the financial bridge between policyholders and insurers. The intricate process of premium calculation involves a delicate balance between risk assessment and financial stability. As the insurance landscape continues to evolve, insurers must embrace technological innovations, adapt to changing market dynamics, and address emerging risks to ensure the sustainability and relevance of their products and services.
How are insurance premiums determined?
+Insurance premiums are determined through a complex process that involves risk assessment, actuarial science, and statistical analysis. Factors such as risk level, coverage type and amount, personal characteristics, geographical location, and claims history are considered. Insurers use advanced models and datasets to predict the likelihood of claims and set premiums accordingly.
What happens if I can’t afford my insurance premiums?
+If you’re struggling to afford your insurance premiums, it’s important to explore options that can help make insurance more affordable. Some insurers offer payment plans or premium discounts for policyholders who meet certain criteria, such as safe driving records or maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Additionally, you can review your coverage and consider reducing the level of coverage or increasing your deductible to lower your premiums.
Are insurance premiums negotiable?
+In general, insurance premiums are not negotiable as they are based on standardized risk assessment models. However, insurers may offer discounts or flexible payment plans to attract new customers or retain existing ones. It’s worth shopping around and comparing quotes from different insurers to find the best coverage and premium combination for your needs.



