Insurance On

Insurance is a vital aspect of our modern world, providing financial protection and peace of mind to individuals, families, and businesses. With an ever-evolving landscape of risks and an increasing awareness of the importance of preparedness, understanding the intricacies of insurance has become more crucial than ever. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of insurance, exploring its various facets, benefits, and how it can be a powerful tool for safeguarding our lives and livelihoods.
The Evolution of Insurance: A Historical Perspective

The concept of insurance has its roots in ancient civilizations, where early forms of risk management were employed to protect against losses. From the maritime trade of ancient Greece to the mutual aid societies of medieval Europe, the idea of sharing risk has been an integral part of human civilization. However, it was during the 17th century in England that modern insurance practices began to take shape.
The Great Fire of London in 1666 served as a catalyst for the development of fire insurance, with Nicholas Barbon establishing the first fire insurance company, "The Fire Office," in 1680. This marked a significant shift towards more formalized insurance practices, where premiums were calculated based on risk assessments. The principles established during this period laid the foundation for the insurance industry we know today.
Understanding the Basics: Types of Insurance

Insurance is a broad term encompassing various types of coverage, each designed to address specific risks and needs. Here’s an overview of some of the most common types of insurance:
Life Insurance
Life insurance provides financial protection to beneficiaries upon the insured individual’s death. It offers a safety net for families, ensuring financial stability and covering expenses such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, and ongoing living expenses.
Health Insurance
Health insurance is crucial for accessing medical care without incurring significant financial burdens. It covers a range of healthcare services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and preventive care. With rising healthcare costs, health insurance is essential for maintaining good health and managing unexpected medical emergencies.
Auto Insurance
Auto insurance is mandatory in many jurisdictions and provides coverage for vehicle-related incidents. It typically includes liability coverage, which protects the insured against claims for bodily injury or property damage caused to others, as well as comprehensive and collision coverage, which covers damage to the insured vehicle.
Homeowners and Renters Insurance
Homeowners insurance is designed to protect the policyholder’s residence and its contents against damages caused by perils such as fire, theft, or natural disasters. Renters insurance, on the other hand, provides coverage for personal belongings and liability protection for renters.
Business Insurance
Business insurance is tailored to meet the unique needs of businesses, offering protection against a wide range of risks, including property damage, liability claims, and loss of income. It can include coverage for commercial property, product liability, professional indemnity, and business interruption.
How Insurance Works: The Underwriting Process
At the core of insurance lies the underwriting process, where insurance companies assess the risks associated with insuring an individual or entity. This process involves evaluating various factors, such as age, health status, driving record, property location, and business activities, to determine the likelihood of a claim and set appropriate premiums.
Underwriters use statistical data, actuarial science, and risk modeling to calculate premiums and establish policy terms. This ensures that insurance companies can accurately price the risk and maintain financial stability while providing coverage to policyholders.
Risk Assessment and Premium Calculation
Insurance companies employ sophisticated risk assessment tools to evaluate the probability of claims and determine appropriate premiums. Factors such as the insured’s age, health, and lifestyle can significantly impact the premium. For instance, younger individuals may pay lower premiums for life insurance due to their lower mortality risk, while older individuals may face higher premiums.
Similarly, health insurance premiums can be influenced by pre-existing conditions, lifestyle choices, and geographic location. Auto insurance premiums, on the other hand, consider factors like driving record, vehicle type, and mileage. By accurately assessing risk, insurance companies can ensure fair and sustainable pricing for policyholders.
The Benefits of Insurance: Peace of Mind and Financial Security
Insurance offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond the financial protection it provides. Here are some key advantages of having insurance coverage:
Peace of Mind
One of the most significant benefits of insurance is the peace of mind it offers. Knowing that you are financially protected against unexpected events can reduce stress and anxiety. Whether it’s a serious illness, a natural disaster, or an accident, insurance provides a safety net, allowing you to focus on recovery and rebuilding rather than worrying about financial burdens.
Financial Security
Insurance is a powerful tool for safeguarding your financial stability. It ensures that you have the resources to cover expenses and maintain your standard of living during challenging times. For businesses, insurance provides a vital safety net, protecting against potential losses and enabling continuity in the face of unexpected events.
Access to Quality Healthcare
Health insurance is particularly crucial in ensuring access to quality healthcare. With rising healthcare costs, many individuals would struggle to afford necessary medical treatments without insurance coverage. Health insurance provides financial protection, allowing policyholders to seek timely medical care without worrying about the financial implications.
The Future of Insurance: Technological Innovations and Trends
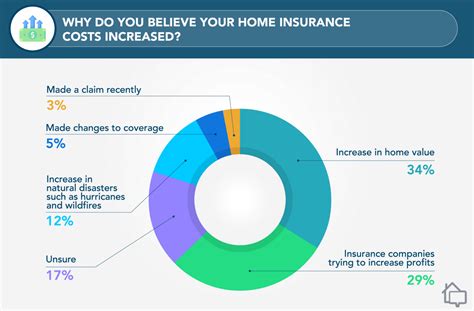
The insurance industry is continually evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer needs. Here’s a glimpse into the future of insurance and some key trends shaping the industry:
Digital Transformation
The digital revolution has transformed the insurance landscape, with online platforms and mobile apps making insurance more accessible and convenient. Insurtech, the fusion of insurance and technology, has led to innovative solutions, such as on-demand insurance, parametric insurance, and the use of artificial intelligence for risk assessment and claims processing.
Personalized Insurance
With the availability of vast amounts of data and advanced analytics, insurance companies are increasingly able to offer personalized insurance products. By leveraging data-driven insights, insurers can tailor policies to individual needs, providing coverage that is more accurate and cost-effective.
Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance
Telematics technology is revolutionizing auto insurance, allowing insurers to track driving behavior and offer usage-based insurance policies. These policies reward safe drivers with lower premiums, promoting safer driving habits and reducing costs for responsible motorists.
Environmental and Social Considerations
Insurance companies are increasingly incorporating environmental and social factors into their risk assessments and product offerings. This includes considering climate change risks, promoting sustainable practices, and offering insurance products that support environmental initiatives and social responsibility.
Conclusion: Embracing Insurance as a Pillar of Financial Stability
Insurance is an essential component of our modern lives, providing a vital safety net against the uncertainties and risks we face. From protecting our health and assets to ensuring the continuity of businesses, insurance plays a critical role in maintaining financial stability and peace of mind. As the insurance industry continues to evolve, embracing technological advancements and adapting to changing needs, it remains a powerful tool for managing risk and securing a brighter future.
What is the average cost of life insurance per month?
+The cost of life insurance can vary widely based on factors such as age, health, and the amount of coverage desired. On average, a 30-year-old non-smoker can expect to pay around 25 to 50 per month for a $500,000 term life insurance policy. However, rates can be significantly higher or lower depending on individual circumstances.
How does health insurance work?
+Health insurance works by providing coverage for medical expenses. Policyholders pay premiums to the insurance company, which in turn covers a portion of their healthcare costs. The specific coverage and benefits vary depending on the policy, but common features include coverage for doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and preventive care.
What is the difference between comprehensive and collision auto insurance coverage?
+Comprehensive auto insurance coverage provides protection against non-collision incidents, such as theft, vandalism, natural disasters, and damage caused by animals. Collision coverage, on the other hand, specifically covers damage to the insured vehicle resulting from a collision with another vehicle or object. Both types of coverage are optional but highly recommended for comprehensive protection.



