How Much Should Health Insurance Cost
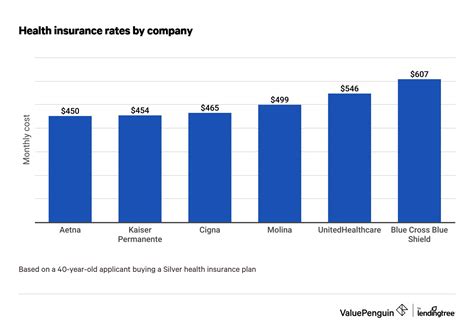
Health insurance is an essential aspect of modern healthcare systems, providing financial protection and access to medical services for individuals and families. The cost of health insurance is a critical concern for many, as it directly impacts personal finances and the ability to obtain quality healthcare. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the factors that influence the cost of health insurance, explore the various plans and coverage options available, and provide insights into how individuals can make informed decisions when selecting a health insurance plan that suits their needs and budget.
Understanding the Cost of Health Insurance

The cost of health insurance is a complex equation influenced by numerous variables. It is important to recognize that the price of a health insurance plan is not solely determined by the insurer; rather, it is a result of a combination of factors that interact within the healthcare ecosystem.
Key Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
- Medical Inflation: Rising healthcare costs due to advanced medical technologies, specialized treatments, and an aging population contribute significantly to insurance premiums. Medical inflation drives up the overall cost of healthcare, and insurers pass on a portion of these costs to policyholders.
- Risk Pool and Adverse Selection: Health insurance operates on the principle of risk pooling, where the premiums paid by healthier individuals subsidize the costs of those with higher healthcare needs. Adverse selection, where individuals with higher health risks are more likely to purchase insurance, can lead to increased premiums for everyone in the pool.
- Regulatory Environment: Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in determining the structure and pricing of health insurance plans. Subsidies, mandates, and benefit requirements can either lower or increase the cost of insurance, depending on the specific regulations in place.
- Administrative Costs: Insurance companies incur significant administrative expenses, including marketing, underwriting, and claims processing. These costs are reflected in the premiums, and efficient management of administrative tasks can help keep premiums more affordable.
- Market Competition: In a competitive insurance market, insurers strive to offer attractive plans at competitive prices to attract customers. However, in less competitive markets, insurers may have more leeway to set premiums based on their assessment of the risk pool.
Health Insurance Plans and Coverage Options
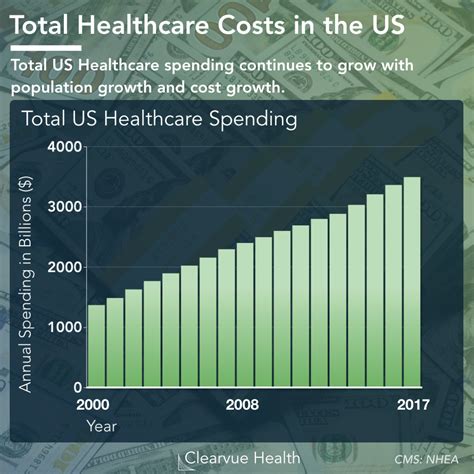
Health insurance plans come in various forms, each offering different levels of coverage and premium structures. Understanding the types of plans available is essential for individuals to make informed choices.
Major Types of Health Insurance Plans
- Fee-for-Service (FFS) Plans: FFS plans provide policyholders with the flexibility to choose their healthcare providers and receive coverage for a wide range of services. These plans often come with higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs but offer more freedom in choosing healthcare professionals.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): HMOs typically have a more structured approach, requiring policyholders to select a primary care physician (PCP) and obtain referrals for specialist care. HMOs often have lower premiums and out-of-pocket expenses but may limit the choice of healthcare providers.
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): PPOs offer a balance between FFS and HMOs, allowing policyholders to choose their healthcare providers without the need for referrals. PPOs usually have a network of preferred providers, and policyholders may incur higher costs when using out-of-network services.
- Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs): EPOs function similarly to PPOs but with a more restricted network of providers. Policyholders generally cannot use out-of-network providers without incurring higher costs.
- Point-of-Service (POS) Plans: POS plans combine elements of HMOs and PPOs, allowing policyholders to choose between in-network and out-of-network providers. POS plans often have a primary care physician requirement and may have different cost structures for in-network and out-of-network services.
Assessing Coverage and Cost
When evaluating health insurance plans, it is crucial to consider both the coverage provided and the associated costs. Here are some key factors to assess:
- Premiums: The premium is the regular payment made to maintain insurance coverage. Premiums can vary significantly based on the type of plan, coverage limits, and individual risk factors.
- Deductibles: A deductible is the amount an insured individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles can result in lower premiums, but they shift more financial responsibility to the policyholder.
- Coinsurance: Coinsurance is the percentage of covered medical expenses that the policyholder must pay after the deductible is met. For instance, a 20% coinsurance means the insured pays 20% of the cost, while the insurer covers the remaining 80%.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The out-of-pocket maximum is the highest amount an insured individual will pay in a year for covered medical expenses. Once this limit is reached, the insurer covers 100% of eligible expenses.
- Coverage Limits: Health insurance plans have coverage limits, specifying the maximum amount the insurer will pay for specific services or treatments. Understanding these limits is crucial to avoid unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
Factors Influencing Personal Health Insurance Costs
While the broader healthcare ecosystem and plan structures influence health insurance costs, there are also individual factors that can impact the price of insurance.
Personal Risk Factors
Health insurance premiums are influenced by individual health status and lifestyle choices. Here are some factors that can affect personal insurance costs:
- Age: Younger individuals typically have lower health risks and, therefore, lower premiums. As individuals age, their health risks increase, leading to higher insurance costs.
- Gender: Historically, health insurance premiums have been gender-based, with women often paying higher premiums due to their higher utilization of healthcare services. However, this practice is becoming less common due to regulatory changes.
- Smoking Status: Smoking is a significant risk factor for various health conditions. Insurers may charge higher premiums to smokers, as they are more likely to require medical treatment.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions may face higher insurance costs or be subject to waiting periods before their conditions are covered. In some countries, pre-existing conditions are protected by law, ensuring access to insurance regardless of health status.
- Family Size: Health insurance plans often offer family coverage, and the cost increases with the number of family members included in the plan. Family plans provide comprehensive coverage for all members, ensuring access to necessary healthcare services.
Plan Selection and Cost Management
When selecting a health insurance plan, individuals can take several steps to manage costs effectively:
- Assess Healthcare Needs: Evaluate your current and potential future healthcare needs. Consider factors such as chronic conditions, prescription medications, and the likelihood of requiring specialized treatments.
- Compare Plans: Research and compare different health insurance plans, considering factors like coverage, cost, network of providers, and any unique benefits offered. Online tools and insurance brokers can assist in this process.
- Consider High-Deductible Plans: High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) often come with lower premiums but higher deductibles. These plans can be paired with health savings accounts (HSAs) to help cover out-of-pocket expenses and provide tax benefits.
- Utilize Preventive Care: Take advantage of preventive care services, which are typically covered at no additional cost. Preventive care can help identify potential health issues early on, reducing the need for more costly treatments later.
- Shop Around: Health insurance plans and their associated costs can vary significantly between insurers. Shopping around and obtaining quotes from multiple providers can help you find the most affordable plan that meets your needs.
Government Initiatives and Subsidies
In many countries, governments play a crucial role in regulating and supporting health insurance markets. Government initiatives and subsidies can have a significant impact on the affordability and accessibility of health insurance.
Government Regulation and Subsidies
Governments often implement regulations to ensure the stability and accessibility of health insurance markets. These regulations may include:
- Community Rating: Community rating requires insurers to set premiums based on the average health risk of the entire community rather than individual risk factors. This approach aims to reduce the impact of adverse selection and make insurance more affordable for those with higher health risks.
- Guaranteed Issue: Guaranteed issue regulations require insurers to offer coverage to all applicants, regardless of their health status. This prevents insurers from denying coverage to individuals with pre-existing conditions.
- Minimum Coverage Requirements: Governments may mandate that insurance plans include a minimum set of essential health benefits. This ensures that individuals have access to a basic level of healthcare coverage.
- Subsidies and Tax Credits: Governments may provide financial assistance to individuals and families to help cover the cost of health insurance. Subsidies and tax credits can make insurance more affordable, especially for those with lower incomes.
Impact on Insurance Costs
Government regulations and subsidies can have both positive and negative effects on insurance costs. While community rating and guaranteed issue can make insurance more accessible and affordable for higher-risk individuals, they may also lead to higher premiums for healthier individuals.
On the other hand, minimum coverage requirements and subsidies can ensure that a larger portion of the population has access to healthcare, reducing the overall financial burden on the healthcare system. Additionally, tax credits and subsidies can provide significant relief for individuals and families struggling to afford insurance.
Future Trends and Implications

The landscape of health insurance is continually evolving, influenced by technological advancements, changing healthcare practices, and shifts in societal needs. Understanding these trends is essential for individuals and policymakers to navigate the future of healthcare coverage effectively.
Key Future Trends
- Digital Health and Telemedicine: The integration of digital technologies into healthcare, known as digital health, is transforming the way medical services are delivered. Telemedicine, a subset of digital health, allows for remote consultations and treatment, reducing the need for in-person visits. This trend has the potential to lower healthcare costs and improve access to care, particularly in rural areas.
- Value-Based Care: Value-based care models focus on delivering high-quality healthcare while controlling costs. These models reward healthcare providers for achieving positive health outcomes rather than simply billing for services rendered. By incentivizing efficient and effective care, value-based models can reduce overall healthcare spending and improve patient outcomes.
- Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs): ACOs are groups of healthcare providers, such as doctors, hospitals, and specialists, who come together to provide coordinated care for Medicare beneficiaries. ACOs aim to improve the quality of care and reduce costs by promoting collaboration and shared accountability among healthcare providers. This trend has the potential to streamline care delivery and reduce unnecessary expenditures.
- Consumer-Directed Health Plans (CDHPs): CDHPs, including Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs), give individuals more control over their healthcare spending. These plans typically have higher deductibles but offer tax advantages and employer contributions to help cover out-of-pocket costs. CDHPs encourage individuals to become more engaged in their healthcare decisions and can lead to more cost-conscious choices.
Implications for Health Insurance Costs
The future trends outlined above have the potential to significantly impact the cost of health insurance. Digital health and telemedicine can reduce the need for expensive in-person visits, lowering healthcare costs overall. Value-based care models and ACOs aim to improve the efficiency of healthcare delivery, potentially reducing unnecessary expenditures and improving patient outcomes.
Consumer-directed health plans shift more financial responsibility to individuals, encouraging cost-conscious choices. While this can lead to lower premiums, it may also result in higher out-of-pocket expenses for individuals who require extensive medical care. It is essential for individuals to carefully evaluate their healthcare needs and select plans that provide adequate coverage while managing costs effectively.
Conclusion
The cost of health insurance is a multifaceted issue influenced by various factors, from medical inflation and risk pools to government regulations and individual health status. Understanding these factors is crucial for individuals to make informed decisions when selecting a health insurance plan that aligns with their needs and budget.
By assessing personal healthcare needs, comparing plans, and considering cost-saving strategies, individuals can navigate the complex landscape of health insurance and secure coverage that provides peace of mind and financial protection. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, staying informed about emerging trends and their potential impact on insurance costs will be essential for individuals and policymakers alike.
How do I choose the right health insurance plan for my needs?
+When selecting a health insurance plan, consider your healthcare needs, such as chronic conditions, prescription medications, and anticipated medical treatments. Compare plans based on coverage, cost, network of providers, and any unique benefits offered. Assess your financial situation and choose a plan that provides adequate coverage while aligning with your budget.
Are there any government programs or subsidies available to help with health insurance costs?
+Yes, many governments offer programs and subsidies to assist individuals and families with health insurance costs. These may include tax credits, subsidies for low-income individuals, and government-sponsored insurance programs. Check with your local or national government agencies to explore the options available to you.
What are some ways to save money on health insurance premiums?
+To save money on health insurance premiums, consider high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) paired with health savings accounts (HSAs). Take advantage of preventive care services, which are often covered at no additional cost. Shop around for quotes from multiple insurers to find the most affordable plan that meets your needs. Additionally, maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of chronic conditions and associated costs.



