Health Insurance Wisconsin
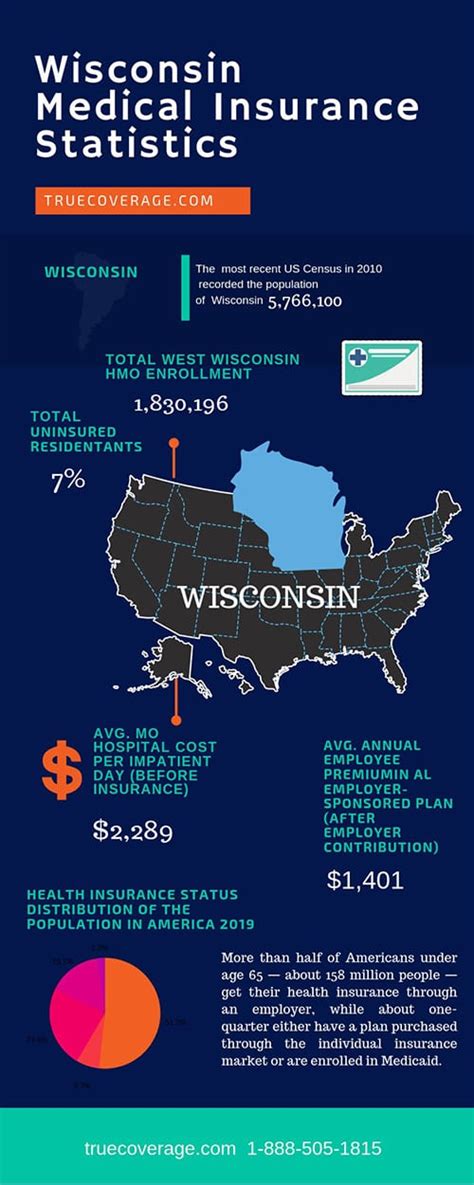
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on Health Insurance in Wisconsin, designed to provide you with an in-depth understanding of the healthcare coverage options available in the Badger State. As a knowledgeable expert, I aim to offer an insightful and engaging exploration of Wisconsin's health insurance landscape, ensuring you have the information you need to make informed decisions about your healthcare.
Understanding Health Insurance in Wisconsin

Wisconsin, with its diverse population and unique healthcare needs, presents a dynamic and evolving market for health insurance. This section will delve into the key aspects of health insurance in the state, exploring the various plans, providers, and initiatives that shape the healthcare landscape.
Wisconsin’s Healthcare Market
The healthcare market in Wisconsin is characterized by a mix of private and public insurance options, catering to the diverse needs of its residents. From major metropolitan areas like Milwaukee and Madison to rural communities, understanding the specific healthcare challenges and opportunities is essential for effective coverage.
Key factors influencing the state's healthcare market include:
- Population Demographics: Wisconsin's population, with its varying ages, income levels, and health needs, presents a complex insurance landscape.
- Economic Conditions: The state's economic health, including employment rates and income levels, plays a significant role in determining the demand and accessibility of health insurance.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: The availability and distribution of healthcare facilities and providers across the state impact the overall healthcare experience and insurance coverage.
Let's explore some real-world examples to illustrate these points. Consider the case of Milwaukee, a major urban center with a diverse population. Here, the demand for comprehensive health insurance plans that cover a wide range of services is high, given the city's mix of income levels and healthcare needs. On the other hand, in rural Wisconsin, where access to healthcare facilities can be limited, insurance plans that offer extensive coverage for telemedicine services may be more appealing and necessary.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Health insurance plans in Wisconsin come in various forms, each with its unique features and benefits. Understanding these plan types is crucial for choosing the right coverage that aligns with your specific healthcare needs and budget.
The main categories of health insurance plans available in Wisconsin include:
- Private Health Insurance Plans: These plans are offered by private insurance companies and are typically purchased by individuals or provided by employers. They offer a wide range of coverage options, from basic health maintenance plans to comprehensive plans that cover a broad spectrum of medical services.
- Government-Sponsored Health Insurance: Wisconsin residents also have access to government-sponsored insurance programs, including Medicaid and Medicare. Medicaid provides health coverage to eligible low-income adults, children, pregnant women, elderly adults, and people with disabilities. Medicare, on the other hand, is primarily for individuals aged 65 and older and certain younger people with disabilities.
- Short-Term Health Insurance Plans: These plans are designed to provide temporary coverage for individuals who are between jobs, awaiting enrollment in other plans, or for those who are not eligible for other insurance options. While they offer more limited coverage than traditional plans, they can be a cost-effective solution for short-term healthcare needs.
- Health Sharing Ministries: Wisconsin is home to several health sharing ministries, which are faith-based organizations that facilitate the sharing of medical expenses among members. These plans are an alternative to traditional insurance and are often sought by those with specific religious or philosophical beliefs.
For instance, a young professional in Madison might opt for a private health insurance plan through their employer, which offers comprehensive coverage for various healthcare services, including regular check-ups and potential emergency care. In contrast, an elderly resident in a rural community might rely on Medicare for their healthcare needs, supplemented by a private insurance plan that covers additional services not covered by Medicare.
Health Insurance Providers in Wisconsin
Wisconsin is served by a diverse range of health insurance providers, each with its own network of healthcare facilities and providers. Choosing the right provider is a critical step in ensuring access to quality healthcare and maximizing the benefits of your insurance plan.
Some of the prominent health insurance providers in Wisconsin include:
- UnitedHealthcare: Offering a wide range of health insurance plans, UnitedHealthcare serves individuals, families, and employers across the state. Their plans often include access to a large network of healthcare providers and facilities, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
- Aetna: Aetna provides a variety of health insurance options, including Medicare and Medicaid plans, as well as commercial plans for individuals and families. They are known for their focus on innovative healthcare solutions and a strong provider network.
- Quintessential Health Fund: This provider offers health insurance plans specifically designed for Wisconsin residents, with a focus on providing comprehensive coverage at competitive rates. They partner with a network of trusted healthcare providers across the state.
- Humana: Humana is a well-known provider of health insurance plans, particularly in the Medicare and Medicaid markets. They offer a range of plans that cater to the unique healthcare needs of Wisconsin's senior population and those with disabilities.
Consider the example of a family in Waukesha who chooses UnitedHealthcare for their health insurance needs. With UnitedHealthcare's extensive provider network, they can access a wide range of healthcare services, from their family doctor to specialized medical centers, ensuring they receive the care they need when they need it.
Analyzing Health Insurance Coverage in Wisconsin
Now, let’s delve into a more detailed analysis of health insurance coverage in Wisconsin, exploring key performance metrics and initiatives that are shaping the state’s healthcare landscape.
Healthcare Access and Affordability
One of the primary goals of health insurance is to ensure that residents have access to quality healthcare services at an affordable cost. In Wisconsin, various initiatives and programs are in place to address these critical aspects of healthcare coverage.
Here are some key insights:
- Healthcare Access: Wisconsin has made significant strides in improving access to healthcare, particularly in underserved rural areas. The state's Rural Healthcare Initiative aims to enhance access to healthcare services and improve the overall health of residents in rural communities by supporting the development of healthcare infrastructure and providing funding for healthcare facilities.
- Affordability: Wisconsin recognizes the importance of affordable health insurance, especially for low- and middle-income residents. The state offers various programs and subsidies to make health insurance more accessible, including Wisconsin Shares, a program that provides financial assistance for health insurance premiums to eligible individuals and families.
For instance, the Wisconsin Shares program has helped thousands of Wisconsin residents obtain health insurance coverage by reducing the financial burden of premiums. This initiative has been particularly beneficial for working-class families, ensuring they can access necessary healthcare services without financial strain.
Healthcare Quality and Outcomes
Beyond access and affordability, the quality of healthcare and the outcomes it achieves are critical aspects of any health insurance system. Wisconsin is committed to ensuring its residents receive high-quality healthcare and has implemented several initiatives to monitor and improve healthcare quality.
Key aspects of healthcare quality and outcomes in Wisconsin include:
- Quality Measurement and Improvement: The state actively measures and monitors healthcare quality through various initiatives. For example, the Wisconsin Health Care Quality and Outcomes Report provides an annual assessment of healthcare quality across the state, helping to identify areas for improvement and highlighting successful practices.
- Patient Safety: Wisconsin places a strong emphasis on patient safety, with initiatives focused on reducing medical errors and improving patient outcomes. The Wisconsin Patient Safety and Clinical Quality Collaborative brings together healthcare providers and organizations to share best practices and improve patient safety across the state.
- Chronic Disease Management: With a focus on preventative care, Wisconsin has implemented programs to manage and prevent chronic diseases, which are a significant driver of healthcare costs. These initiatives aim to improve the management of conditions like diabetes and heart disease, reducing the need for costly emergency care.
A real-world example of the impact of these initiatives can be seen in Wisconsin's successful management of diabetes. Through comprehensive diabetes management programs, the state has seen a significant reduction in the number of individuals developing diabetes-related complications, leading to improved health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
Healthcare Innovation and Technology
Wisconsin is at the forefront of healthcare innovation, leveraging technology to improve healthcare delivery and patient experiences. The state recognizes the potential of digital health solutions to enhance access, efficiency, and quality of care.
Here are some notable initiatives and trends:
- Telehealth Services: Wisconsin has embraced telehealth services, particularly in rural areas where access to healthcare facilities can be limited. Telehealth allows residents to connect with healthcare providers remotely, offering convenient and timely access to medical advice and treatment.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): The state has made significant progress in implementing EHR systems, which allow for the secure sharing of patient health information across healthcare providers. This technology enhances coordination of care and improves patient safety.
- Digital Health Tools: Wisconsin encourages the use of digital health tools, such as mobile apps and wearable devices, to support patient health and wellness. These tools can help individuals track their health, receive personalized health recommendations, and better manage their conditions.
One innovative example is the Wisconsin Digital Health Initiative, which aims to accelerate the adoption of digital health solutions across the state. Through this initiative, healthcare providers are supported in implementing digital technologies that enhance patient care, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
Future Implications and Trends in Wisconsin’s Health Insurance Market
As we look ahead, several key trends and developments are shaping the future of health insurance in Wisconsin. These factors will influence the healthcare landscape and the insurance options available to residents.
Population Health and Chronic Disease Management
Wisconsin, like many other states, is facing a growing burden of chronic diseases, which are a significant driver of healthcare costs. As the population ages and chronic conditions become more prevalent, the focus on population health and chronic disease management will continue to be a priority.
Key trends and initiatives in this area include:
- Preventative Care: Wisconsin is placing a greater emphasis on preventative care, recognizing that it is more cost-effective and beneficial for long-term health outcomes. This includes initiatives to promote healthy lifestyles, early disease detection, and better management of chronic conditions.
- Chronic Disease Management Programs: The state is investing in comprehensive chronic disease management programs, particularly for conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. These programs aim to improve patient outcomes, reduce complications, and lower healthcare costs.
- Community Health Initiatives: Wisconsin is fostering community-based health initiatives that bring healthcare services closer to residents. These initiatives, often in collaboration with local organizations, aim to improve access to healthcare, promote health education, and address social determinants of health.
For instance, the Wisconsin Chronic Disease Management Program has seen remarkable success in managing diabetes and heart disease. By providing patients with personalized care plans, educational resources, and ongoing support, the program has helped reduce hospitalizations and improve overall health outcomes.
Healthcare Technology and Digital Innovation
The rapid advancement of healthcare technology and digital innovation will continue to shape the health insurance landscape in Wisconsin. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery, making it more efficient, accessible, and patient-centric.
Some key trends and developments in this area include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Healthcare: Wisconsin is exploring the use of AI to improve healthcare outcomes and efficiency. AI-powered tools can assist in diagnosis, treatment planning, and personalized health recommendations, enhancing the quality of care.
- Blockchain for Healthcare Data Security: The state is considering the implementation of blockchain technology to enhance the security and privacy of healthcare data. Blockchain can ensure the integrity of health records, improve data sharing between providers, and reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM): Wisconsin is embracing RPM technologies, which allow healthcare providers to monitor patients' health status remotely. This technology is particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions, ensuring timely interventions, and reducing the need for in-person visits.
An exciting example of digital innovation is the Wisconsin Telehealth Network, which connects healthcare providers and patients across the state through a secure, high-speed telecommunications network. This network enables real-time video consultations, remote monitoring of vital signs, and the secure sharing of medical images, improving access to healthcare and reducing travel burdens for patients.
Healthcare Reform and Policy Changes
The future of health insurance in Wisconsin is also influenced by potential healthcare reform and policy changes at both the state and federal levels. These changes can impact the availability, affordability, and quality of health insurance coverage.
Some key areas of focus include:
- Healthcare Financing: Wisconsin is exploring innovative financing models to ensure the sustainability of healthcare coverage. This includes initiatives to reduce administrative costs, improve payment systems, and enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
- Healthcare Delivery Models: The state is considering new models of healthcare delivery, such as value-based care and accountable care organizations (ACOs), which focus on coordinating care and improving health outcomes while reducing costs.
- Healthcare Policy Reforms: Wisconsin may see changes in healthcare policies, particularly in areas like prescription drug pricing, mental health coverage, and long-term care. These reforms aim to address specific healthcare challenges and improve access to necessary services.
For instance, the state's recent focus on value-based care has led to the development of ACOs, which bring together healthcare providers to coordinate patient care and improve health outcomes. This model has the potential to reduce unnecessary healthcare costs and improve the overall patient experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, health insurance in Wisconsin is a dynamic and evolving landscape, shaped by a range of factors including population health needs, economic conditions, and healthcare policies. From private insurance plans to government-sponsored programs, Wisconsin residents have a variety of options to choose from to meet their healthcare needs.
As we've explored, the state is committed to improving access to healthcare, enhancing healthcare quality, and leveraging technology to improve healthcare delivery. By staying informed about the latest developments and initiatives, Wisconsin residents can make informed decisions about their health insurance coverage and access the care they need to live healthy and fulfilling lives.
FAQ
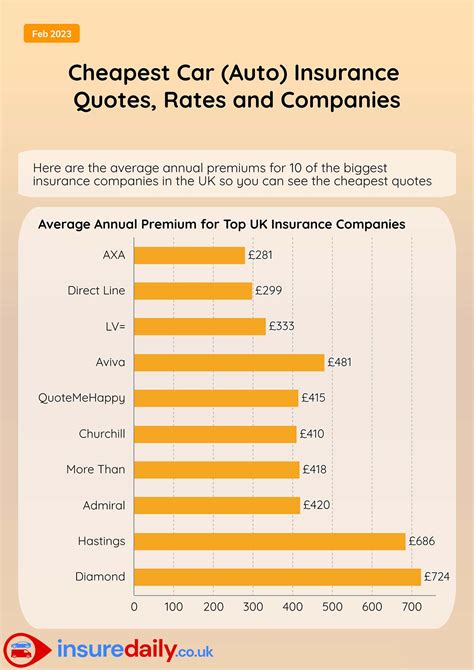
What is the average cost of health insurance in Wisconsin?
+
The average cost of health insurance in Wisconsin varies based on factors such as age, location, and the type of plan. On average, a monthly premium for an individual plan can range from 200 to 500, while family plans can cost between 500 and 1,500. It’s important to note that these are average estimates, and actual costs can vary significantly based on individual circumstances.
Are there any state-specific health insurance programs in Wisconsin?
+
Yes, Wisconsin offers several state-specific health insurance programs. One notable example is the Wisconsin BadgerCare Plus program, which provides health coverage to eligible low-income adults, children, and pregnant women. Additionally, the state also has the Wisconsin Shared Health Insurance Rate program, which provides financial assistance to help reduce health insurance premiums for eligible individuals and families.
What are the benefits of choosing a health insurance provider with a large provider network in Wisconsin?
+
Choosing a health insurance provider with a large provider network in Wisconsin offers several benefits. It ensures that you have access to a wide range of healthcare facilities and providers across the state, making it easier to find in-network doctors and specialists. This can lead to reduced out-of-pocket costs and improved convenience when seeking medical care.
How can I find out if I’m eligible for government-sponsored health insurance programs in Wisconsin?
+
To determine your eligibility for government-sponsored health insurance programs in Wisconsin, you can visit the state’s official healthcare website or contact your local