Health Insurance I Can Get Now

In today's fast-paced and often uncertain world, having access to quality healthcare is more important than ever. Health insurance plays a crucial role in ensuring that individuals and families can receive the medical care they need without facing financial burdens. While navigating the complex landscape of health insurance plans can be daunting, there are numerous options available to suit various needs and circumstances. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the diverse range of health insurance options accessible to you, empowering you to make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
Understanding Your Health Insurance Options
The healthcare industry offers a plethora of insurance plans tailored to different demographics and requirements. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the most common types of health insurance plans you can consider:
Individual and Family Plans
Individual health insurance plans are designed for people who do not qualify for employer-sponsored coverage or government-funded programs. These plans offer a wide range of benefits, including coverage for doctor visits, prescription medications, and hospital stays. Family plans, on the other hand, provide comprehensive coverage for the entire household, ensuring that everyone’s healthcare needs are met.
Key features to look for in individual and family plans include:
- Network Size: Choose a plan with an extensive network of healthcare providers to ensure you have access to a diverse range of medical professionals.
- Coverage Options: Evaluate the plan’s coverage for specific services like maternity care, mental health services, and chronic condition management.
- Cost-Sharing: Consider plans with lower deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums to minimize your financial burden in case of unexpected medical expenses.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Many employers offer health insurance plans as part of their employee benefits package. These plans are often more affordable and comprehensive, as employers typically contribute to the cost of coverage. The specific details of employer-sponsored plans can vary greatly, so it’s essential to understand your options.
When evaluating employer-sponsored plans, pay attention to:
- Premium Contributions: Understand how much you and your employer will contribute towards the monthly premium.
- Coverage Benefits: Review the plan’s coverage for essential health benefits, such as preventive care, prescription drugs, and specialty services.
- Dependents’ Coverage: Ensure that the plan includes coverage for your spouse and/or children, if applicable.
Government-Funded Health Insurance Programs
Various government-funded health insurance programs exist to provide coverage for specific populations. These programs often have income-based eligibility criteria and offer essential health benefits at a reduced cost or even no cost.
Notable government-funded programs include:
- Medicare: A federal program for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as younger adults with certain disabilities or end-stage renal disease. Medicare covers a wide range of healthcare services and is divided into different parts (Part A, B, C, and D) for hospital care, medical insurance, private health plans, and prescription drug coverage, respectively.
- Medicaid: A state-administered program that provides healthcare coverage for low-income individuals and families. Medicaid eligibility varies by state, but it generally covers a comprehensive range of medical services.
- Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP): This program provides low-cost health coverage for children in families who earn too much to qualify for Medicaid but cannot afford private health insurance. CHIP may also cover pregnant women in some states.
Short-Term Health Insurance Plans
Short-term health insurance plans are temporary solutions for individuals who need coverage for a limited period. These plans typically have lower premiums but offer more limited benefits and may not cover pre-existing conditions. They are ideal for those transitioning between jobs or experiencing a gap in coverage.
Consider the following when opting for a short-term plan:
- Coverage Duration: Short-term plans usually last between 30 days and one year, with the option to renew for up to three years in some cases.
- Benefits and Limitations: Carefully review the plan’s coverage and exclusions to ensure it aligns with your healthcare needs during the coverage period.
- Pre-Existing Condition Coverage: Some short-term plans may exclude coverage for pre-existing conditions, so it’s crucial to understand the plan’s terms and conditions.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Plans
HMO plans are organized networks of healthcare providers that offer comprehensive medical services to members. These plans typically require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates all their healthcare needs and referrals to specialists within the HMO network.
Key considerations for HMO plans include:
- Network of Providers: Ensure that your preferred healthcare providers are included in the HMO’s network.
- Referral Requirements: Understand the process for obtaining referrals to specialists and the potential costs associated with them.
- Preventive Care: HMO plans often emphasize preventive care, so evaluate the plan’s coverage for annual check-ups, immunizations, and other preventive services.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) Plans
PPO plans offer members the flexibility to choose from a network of preferred providers while still allowing out-of-network coverage at a higher cost. PPOs typically do not require referrals for specialist visits, providing members with more freedom in their healthcare choices.
When considering a PPO plan, keep the following in mind:
- Network Size: Assess the plan’s network of providers and hospitals to ensure it aligns with your healthcare needs and preferences.
- Out-of-Network Coverage: Understand the costs and limitations of seeking care from providers outside the PPO network.
- Specialty Services: Evaluate the plan’s coverage for specialty services, such as mental health treatment, maternity care, and chronic condition management.
High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
HDHPs are insurance plans with higher deductibles, meaning members pay more out-of-pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. These plans are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), allowing members to save pre-tax dollars for future medical expenses.
Consider the following when opting for an HDHP:
- Deductible Amount: Evaluate your ability to cover the high deductible before insurance coverage takes effect.
- HSA Eligibility: HDHPs are ideal for those eligible for HSAs, as they offer tax advantages and the potential for long-term savings.
- Preventive Care Coverage: Ensure that the HDHP covers essential preventive services without requiring you to meet the deductible first.
Navigating the Health Insurance Marketplace
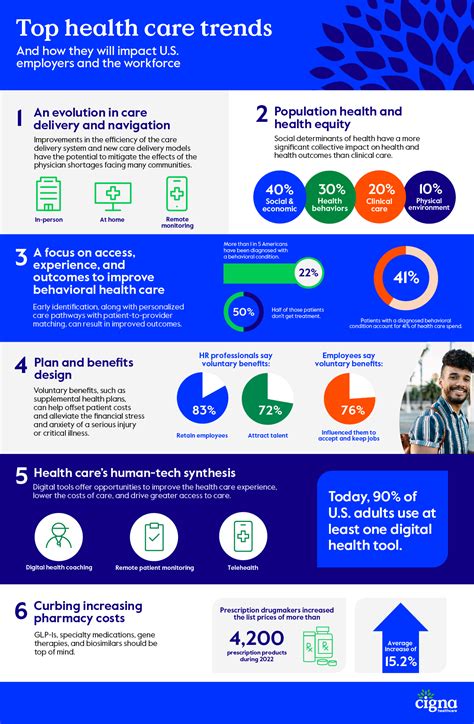
With so many health insurance options available, it’s essential to approach the decision-making process systematically. Here are some steps to guide you through selecting the right health insurance plan:
Assess Your Healthcare Needs
Begin by evaluating your current and potential future healthcare needs. Consider factors such as your age, family size, chronic conditions, and any specialized medical treatments you might require. Understanding your healthcare needs will help you choose a plan that provides adequate coverage.
Research and Compare Plans
Utilize online resources, insurance brokers, or healthcare navigators to research and compare different health insurance plans. Look for plans that offer the coverage you need at a reasonable cost. Consider factors like premium costs, deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums.
Evaluate Network Providers
If you have a preference for certain healthcare providers or hospitals, ensure that they are included in the plan’s network. Check the plan’s directory of providers to verify their participation.
Understand Coverage Exclusions
Read the fine print of each plan to understand what services or conditions are excluded from coverage. This will help you avoid unexpected costs or denials of coverage.
Consider Cost-Sharing Options
Evaluate the plan’s cost-sharing structure, including deductibles, co-pays, and coinsurance. Choose a plan with a cost-sharing arrangement that aligns with your financial situation and healthcare needs.
Seek Professional Guidance
If you’re unsure about your options or need personalized advice, consider consulting an insurance broker or financial advisor who specializes in health insurance. They can provide expert guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
Maximizing Your Health Insurance Benefits
Once you’ve selected your health insurance plan, it’s essential to make the most of your coverage. Here are some tips to ensure you receive the full benefits of your plan:
Understand Your Plan’s Coverage
Familiarize yourself with your plan’s summary of benefits and coverage. Know what services are covered, any exclusions or limitations, and the process for obtaining prior authorization for specific treatments.
Choose In-Network Providers
Whenever possible, choose healthcare providers who are in your insurance plan’s network. This will ensure you receive the best coverage and avoid higher out-of-pocket costs.
Stay Informed about Plan Changes
Keep up-to-date with any changes to your health insurance plan, such as network provider updates, coverage modifications, or premium adjustments. Stay informed to avoid any surprises when seeking medical care.
Utilize Preventive Care Services
Take advantage of the preventive care services covered by your plan. These services, such as annual check-ups, immunizations, and screenings, can help detect potential health issues early on and prevent more significant problems down the line.
Manage Chronic Conditions
If you have a chronic condition, work closely with your healthcare providers to manage your condition effectively. Many health insurance plans offer specialized programs and resources to support individuals with chronic illnesses.
Explore Additional Benefits
Some health insurance plans offer additional benefits, such as wellness programs, discounts on fitness memberships, or access to telemedicine services. Take advantage of these perks to enhance your overall health and well-being.
Future of Health Insurance
The healthcare industry is continually evolving, and so are the options for health insurance. As technology advances and healthcare delivery models change, we can expect to see innovative solutions that improve access to quality healthcare and enhance the overall patient experience.
Some emerging trends in health insurance include:
- Telehealth and Virtual Care: The widespread adoption of telehealth services during the COVID-19 pandemic has paved the way for more accessible and convenient healthcare options. Health insurance plans are increasingly covering virtual doctor visits, mental health counseling, and other remote healthcare services.
- Value-Based Care Models: These models focus on providing high-quality, cost-effective healthcare by rewarding healthcare providers for positive patient outcomes rather than the volume of services delivered. This shift towards value-based care is expected to improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the healthcare system.
- Digital Health Solutions: The integration of digital technologies into healthcare is revolutionizing the way patients access and manage their health. From mobile health apps to wearable devices, these solutions offer convenient and personalized healthcare experiences, empowering individuals to take a more active role in their well-being.
Conclusion

Navigating the complex world of health insurance can be challenging, but with the right information and resources, you can make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage. By understanding your options, assessing your needs, and maximizing your plan’s benefits, you can ensure access to quality healthcare without financial strain. Stay informed about the evolving landscape of health insurance, and don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance when needed. Your health and well-being are worth investing in, and the right health insurance plan can provide the peace of mind and support you deserve.
Can I purchase health insurance if I have a pre-existing condition?
+Yes, thanks to the Affordable Care Act (ACA), insurance companies cannot deny coverage or charge higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions. However, short-term health insurance plans may have exclusions for pre-existing conditions, so it’s important to carefully review the plan’s terms and conditions.
What is the difference between an HMO and a PPO plan?
+HMO plans typically require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and refer to specialists within the HMO network. PPO plans offer more flexibility, allowing members to choose from a network of preferred providers without needing referrals. PPOs often cover out-of-network services at a higher cost.
How can I save money on health insurance premiums?
+To reduce your health insurance premiums, consider plans with higher deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums. You can also explore employer-sponsored plans, as employers often contribute to the cost of coverage. Additionally, government-funded programs like Medicaid and CHIP offer reduced-cost or no-cost coverage for eligible individuals and families.
Are there any tax benefits associated with health insurance plans?
+Yes, certain health insurance plans offer tax advantages. For example, Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) paired with High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) allow individuals to save pre-tax dollars for future medical expenses. Additionally, some employer-sponsored plans may offer tax-free contributions to healthcare flexible spending accounts (FSAs) or health reimbursement arrangements (HRAs).



