Gov Insurance
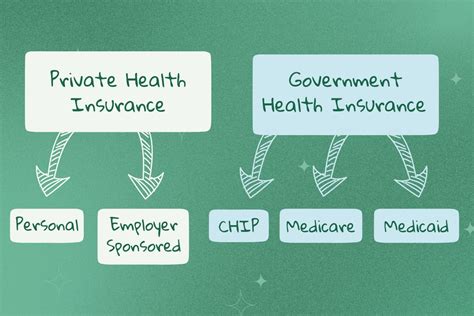
Government insurance, often referred to as public insurance or state-backed insurance, is a vital component of many nations' social safety nets. It serves as a financial safeguard for individuals and businesses, providing coverage and assistance in various aspects of life, from healthcare to property protection. This article delves into the intricate world of government insurance, exploring its types, benefits, and impact on society.
Understanding Government Insurance: A Global Perspective

The concept of government insurance is not a one-size-fits-all approach; it varies greatly across different countries, reflecting their unique cultural, economic, and social landscapes. While some nations offer comprehensive coverage for their citizens, others provide more targeted assistance. Let’s explore the diverse nature of government insurance worldwide.
Healthcare Insurance
Perhaps the most well-known form of government insurance is healthcare coverage. Countries like the United Kingdom, with its National Health Service (NHS), provide free or low-cost healthcare to all citizens. In contrast, nations like the United States have a more complex system, with a mix of public and private insurance options, including Medicare and Medicaid.
The success of these healthcare insurance models often depends on factors such as efficient administration, access to healthcare facilities, and the availability of skilled healthcare professionals. For instance, countries with robust primary healthcare systems, like Cuba, have achieved impressive health outcomes despite limited resources.
Social Security and Retirement Benefits
Government insurance also plays a crucial role in providing financial security during retirement. Many countries have established social security systems that offer pension plans, disability benefits, and unemployment insurance. These programs aim to ensure that individuals can maintain a decent standard of living even when they are no longer working.
However, the sustainability of these programs is a pressing concern, especially with aging populations and changing economic dynamics. Countries like Japan, with one of the world's oldest populations, face significant challenges in funding their social security systems.
Property and Casualty Insurance
Beyond healthcare and retirement, government insurance extends to cover property and casualty risks. This can include natural disaster relief, crop insurance for farmers, and public liability insurance. For instance, the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) in the United States provides essential coverage for property owners in flood-prone areas.
Effective management of these insurance programs is critical, as they can significantly impact a country's economic stability and resilience. Proper risk assessment and underwriting are essential to ensure the long-term viability of such schemes.
Comparison of Global Government Insurance Models
| Country | Healthcare Insurance | Social Security | Property/Casualty Insurance |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | National Health Service (NHS) - Free/Low-Cost | State Pension, Disability Benefits | Flood Re, UK Flood Protection |
| United States | Medicare, Medicaid, Private Insurance | Social Security, Unemployment Insurance | National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) |
| Canada | Provincial Health Insurance Plans | Old Age Security, Canada Pension Plan | Emergency Management Assistance Program (EMAP) |
| Japan | National Health Insurance (NHI) | National Pension System, Elderly Welfare Benefits | Japan Earthquake Reinsurance Co. (JER) |

The Benefits and Impact of Government Insurance

Government insurance schemes have a profound impact on society, offering a range of benefits that extend beyond individual protection.
Financial Security and Stability
One of the primary advantages of government insurance is the financial security it provides. By offering healthcare coverage, retirement benefits, and protection against property losses, these programs reduce the financial burden on individuals and families, especially during times of crisis.
For instance, access to affordable healthcare can prevent medical debts and ensure timely treatment, leading to better health outcomes. Similarly, social security pensions can provide a stable income during retirement, reducing the risk of poverty among the elderly.
Social Equity and Inclusion
Government insurance plays a crucial role in promoting social equity by ensuring that essential services are accessible to all, regardless of income or social status. This includes providing healthcare to the uninsured, disability benefits to those who need them, and financial assistance during natural disasters.
For example, programs like the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) in the United States aim to provide health coverage to children from low-income families, ensuring they receive the care they need to thrive.
Economic Stability and Growth
Well-designed government insurance programs can contribute to economic stability and growth. By providing a safety net for individuals and businesses, these programs reduce the risk of economic shocks and promote consumer confidence. This, in turn, can lead to increased economic activity and growth.
Additionally, government insurance can stimulate economic development by encouraging entrepreneurship and investment. For instance, small business owners may be more willing to take risks and expand their operations if they have access to affordable insurance coverage.
Community Resilience and Disaster Preparedness
Government insurance schemes, particularly those focused on property and casualty risks, play a vital role in building community resilience. By providing coverage for natural disasters, crop failures, and other unforeseen events, these programs help communities recover more quickly and efficiently.
Furthermore, the availability of government insurance can encourage individuals and businesses to take necessary precautions and implement disaster preparedness measures, reducing the overall impact of catastrophic events.
The Future of Government Insurance: Challenges and Innovations
As society evolves and faces new challenges, government insurance programs must adapt and innovate to remain effective. Here are some key considerations for the future of government insurance.
Addressing the Rising Cost of Healthcare
The increasing cost of healthcare is a global concern, and finding sustainable solutions is crucial. Governments and healthcare providers must explore innovative approaches, such as value-based care models and digital health technologies, to reduce costs and improve outcomes.
Additionally, promoting preventive healthcare and healthy lifestyles can help reduce the burden on healthcare systems and lower insurance premiums.
Sustainability of Retirement Benefits
With aging populations and changing economic dynamics, ensuring the long-term sustainability of retirement benefits is a significant challenge. Governments must explore options like increasing retirement ages, encouraging private pension plans, and investing in long-term care facilities to meet the needs of an aging society.
Adapting to Climate Change and Natural Disasters
Climate change is leading to more frequent and severe natural disasters, posing a significant risk to property and communities. Government insurance programs must adapt to these changing conditions by accurately assessing risks, improving disaster response capabilities, and exploring innovative insurance models, such as parametric insurance.
Leveraging Technology for Efficient Administration
Technology can play a transformative role in government insurance, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing the overall customer experience. Digital platforms can streamline claims processes, enable real-time risk assessment, and provide personalized insurance solutions.
Conclusion
Government insurance is a vital component of modern societies, providing financial security, promoting social equity, and supporting economic growth. As we look to the future, continued innovation and adaptation will be key to ensuring these programs remain effective and accessible to all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of government insurance?
+Government insurance serves as a financial safeguard, providing coverage and assistance to individuals and businesses in various aspects of life, including healthcare, retirement, and property protection. Its primary purpose is to ensure financial security, promote social equity, and support economic stability.
How does government insurance differ from private insurance?
+Government insurance is typically funded and administered by the state, offering a social safety net for all citizens. Private insurance, on the other hand, is provided by commercial insurers and is often tailored to individual needs, with premiums varying based on risk factors.
What are some common challenges faced by government insurance programs?
+Common challenges include rising healthcare costs, ensuring the sustainability of retirement benefits, adapting to climate change and natural disasters, and efficiently administering complex programs. These issues require continuous innovation and adaptation to maintain the effectiveness of government insurance.